Abstract
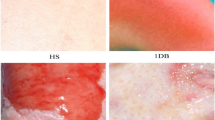
More than 10 million people requiring medical attention and 265,000 deaths are recorded every year in the world as a result of burn injuries in both low/middle- and high-income countries. Patients with acute burn injuries are at risk of developing hospital-acquired complications due to long hospitalizations such as bedsore (pressure ulcer) as a result of immobility. The developed complications are wounds that share similar physical appearances with burns wounds, as such misdiagnosis may likely to occur and leads to long hospitalization and increases cost of medical intervention. This study focused on discriminating burns and pressure ulcer using machine learning approach. We used transfer learning technique where pre-trained deep Convolutional Neural Networks (ConvNet) which includes VGG-face model and two variants of Residual Network (ResNet101 and ResNet152) were employed for extracting discriminatory features from the images and subsequently these features were fed into a Support Vector Machine for classification. Our result shows a recognition accuracy of up to 99.9%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson, C.: Management of Burns. Surg. (Oxford) 36(8), 435–440 (2018)
Log, T.: Modeling skin injury from hot rice porridge spills. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15(4), 808 (2018)
Gianfaldoni, R., Gianfaldoni, S., Lotti, J., Tchernev, G., Wollina, U., Lotti, T.: The importance of first aid to burned patients: 30 years of experience at the burns centre in Pisa. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 5(4), 420 (2017)
Gilbert, A.D., Rajha, E., El Khuri, C., Chebl, R.B., Mailhac, A., Makki, M., El Sayed, M.: Epidemiology of burn patients presenting to a tertiary hospital emergency department in Lebanon. Burns 44(1), 218–225 (2018)
Deeter, L., Seaton, M., Carrougher, G.J., McMullen, K., Mandell, S.P., Amtmann, D., Gibran, N.S.: Hospital-acquired complications alter quality of life in adult burn survivors: report from a burn model system. Burns (2018)
Hopkins, A., Dealey, C., Bale, S., Defloor, T., Worboys, F.: Patient stories of living with a pressure ulcer. J. Adv. Nurs. 56(4), 345–353 (2006)
Posnett, J., Franks, P.J.: The costs of skin breakdown and ulceration in the UK. In: Skin Breakdown–the Silent Epidemic. The Smith and Nephew Foundation, Hull (2007)
Bennett, G., Dealey, C., Posnett, J.: The cost of pressure ulcers in the UK. Age Ageing 33(3), 230–235 (2004)
Still, J.M., Wilson, J., Rinker, C., Law, E., Craft-Coffman, B.: A retrospective study to determine the incidence of pressure ulcers in burn patients using an alternating pressure mattress. Burns 29(5), 505–507 (2003)
Elmogy, M., García-Zapirain, B., Burns, C., Elmaghraby, A., Ei-Baz, A.: Tissues classification for pressure ulcer images based on 3D convolutional neural network. In: 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3139–3143 (2018)
Garcia-Zapirain, B., Shalaby, A., El-Baz, A., Elmaghraby, A.: Automated framework for accurate segmentation of pressure ulcer images. Comput. Biol. Med. 90, 137–145 (2017)
Griswold, L.H., Griffin, R.L., Swain, T., Kerby, J.D.: Validity of the Braden Scale in grading pressure ulcers in trauma and burn patients. J. Surg. Res. 219, 151–157 (2017)
Perednia, D.A.: What dermatologists should know about digital imaging. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 25(1), 89–108 (1991)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Lan, H., Duan, T., Zhong, H., Zhou, M., Gao, F.: Photoacoustic classification of tumor model morphology based on support vector machine: a simulation and phantom study. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 25(1), 1–9 (2019)
Yu, W., Yang, K., Bai, Y., Xiao, T., Yao, H., Rui, Y.: Visualizing and comparing AlexNet and VGG using deconvolutional layers. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Abubakar, A., Ugail, H., Bukar, A.M. (2020). Can Machine Learning Be Used to Discriminate Between Burns and Pressure Ulcer?. In: Bi, Y., Bhatia, R., Kapoor, S. (eds) Intelligent Systems and Applications. IntelliSys 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1038. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29513-4_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29513-4_64
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-29512-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-29513-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)