Abstract
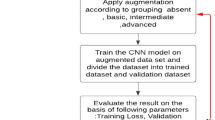
Deep neural networks models have achieved state-of-the-art results in a great number of different tasks in different domains (e.g., natural language processing and computer vision). However, the notions of robustness, causality, and fairness are not measured in traditional evaluated settings. In this work, we proposed an active data augmentation method to improve the model robustness to new data. We use the Vanilla Backpropagation to visualize what the trained model consider important in the input information. Based on that information, we augment the training dataset with new data to refine the model training. The objective is to make the model robust and effective for important input information. We evaluated our approach in a Spinal Cord Gray Matter Segmentation task and verified improvement in robustness while keeping the model competitive in the traditional metrics. Besides, we achieve the state-of-the-art results on that task using a U-Net based model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antol, S., et al.: VQA: visual question answering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2425–2433 (2015)
Bishop, C.M.: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer, New York (2006)
Dice, L.R.: Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26(3), 297–302 (1945)
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2672–2680 (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. CoRR abs/1512.03385 (2015). http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436 (2015)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., et al.: Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series. In: The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks, vol. 3361, no. 10 (1995)
Mikołajczyk, A., Grochowski, M.: Data augmentation for improving deep learning in image classification problem. In: 2018 International Interdisciplinary PhD Workshop (IIPhDW), pp. 117–122. IEEE (2018)
Pereira, S., Meier, R., Alves, V., Reyes, M., Silva, C.A.: Automatic brain tumor grading from MRI data using convolutional neural networks and quality assessment. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) MLCN/DLF/IMIMIC -2018. LNCS, vol. 11038, pp. 106–114. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02628-8_12
Pereira, S., Pinto, A., Alves, V., Silva, C.A.: Brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks in MRI images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1240–1251 (2016)
Perez, L., Wang, J.: The effectiveness of data augmentation in image classification using deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.04621 (2017)
Perone, C.S., Calabrese, E., Cohen-Adad, J.: Spinal cord gray matter segmentation using deep dilated convolutions. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 5966 (2018)
Porisky, A., et al.: Grey matter segmentation in spinal cord MRIs via 3D convolutional encoder networks with shortcut connections. In: Cardoso, M.J., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2017. LNCS, vol. 10553, pp. 330–337. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67558-9_38
Prados, F.: Spinal cord grey matter segmentation challenge. Neuroimage 152, 312–329 (2017)
Rieke, J., Eitel, F., Weygandt, M., Haynes, J., Ritter, K.: Visualizing convolutional networks for MRI-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. CoRR abs/1808.02874 (2018). http://arxiv.org/abs/1808.02874
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Simonyan, K., Vedaldi, A., Zisserman, A.: Deep inside convolutional networks: visualising image classification models and saliency maps. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6034 (2013)
Springenberg, J.T., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T., Riedmiller, M.: Striving for simplicity: the all convolutional net. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6806 (2014)
Xie, X., Li, Y., Shen, L.: Active learning for breast cancer identification. CoRR abs/1804.06670 (2018). http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.06670
Zeiler, M.D., Fergus, R.: Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8689, pp. 818–833. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53
Zeiler, M.D., Krishnan, D., Taylor, G.W., Fergus, R.: Deconvolutional networks (2010)
Zhang, Q., Cao, R., Shi, F., Wu, Y.N., Zhu, S.C.: Interpreting CNN knowledge via an explanatory graph. In: Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2018)
Zhang, Y., Li, K., Li, K., Wang, L., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. CoRR abs/1807.02758 (2018). http://arxiv.org/abs/1807.02758
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia within the Project Scope: UID/CEC/00319/2019. The authors also thanks CAPES and CNPq for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Santos, F.A.O., Zanchettin, C., Matos, L.N., Novais, P. (2019). Active Image Data Augmentation. In: Pérez García, H., Sánchez González, L., Castejón Limas, M., Quintián Pardo, H., Corchado Rodríguez, E. (eds) Hybrid Artificial Intelligent Systems. HAIS 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11734. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29859-3_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29859-3_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-29858-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-29859-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)