Abstract
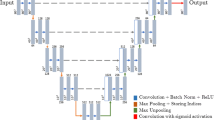
Lung cancer is among the deadliest diseases in the world. The detection and characterization of pulmonary nodules are crucial for an accurate diagnosis, which is of vital importance to increase the patients’ survival rates. The segmentation process contributes to the mentioned characterization, but faces several challenges, due to the diversity in nodular shape, size, and texture, as well as the presence of adjacent structures. This paper proposes two methods for pulmonary nodule segmentation in Computed Tomography (CT) scans. First, a conventional approach which applies the Sliding Band Filter (SBF) to estimate the center of the nodule, and consequently the filter’s support points, matching the initial border coordinates. This preliminary segmentation is then refined to include mainly the nodular area, and no other regions (e.g. vessels and pleural wall). The second approach is based on Deep Learning, using the U-Net to achieve the same goal. This work compares both performances, and consequently identifies which one is the most promising tool to promote early lung cancer screening and improve nodule characterization. Both methodologies used 2653 nodules from the LIDC database: the SBF based one achieved a Dice score of 0.663, while the U-Net achieved 0.830, yielding more similar results to the ground truth reference annotated by specialists, and thus being a more reliable approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: SegNet: a deepconvolutional encoder-decoder architecture for imagesegmentation, November 2015. arXiv:1511.00561 [cs]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.00561
Dashtbozorg, B., Mendonça, A.M., Campilho, A.: Optic disc segmentation using the sliding band filter. Comput. Biol. Med. 56, 1–12 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2014.10.009. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0010482514002832
Jiang, F., et al.: Medical image semantic segmentation based on deep learning. Neural Comput. Appl. 29(5), 1257–1265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3158-6. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00521-017-3158-6
Litjens, G., et al.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1361841517301135
Pereira, C.S., Mendonça, A.M., Campilho, A.: Evaluation of contrast enhancement filters for lung nodule detection. In: Kamel, M., Campilho, A. (eds.) ICIAR 2007. LNCS, vol. 4633, pp. 878–888. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74260-9_78
Quelhas, P., Marcuzzo, M., Mendonca, A.M., Campilho, A.: Cell nuclei and cytoplasm joint segmentation using the sliding band filter. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 29(8), 1463–1473 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2010.2048253. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5477157/
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Roth, H.R., et al.: Deep learning and its application to medical image segmentation, March 2018. arXiv:1803.08691 [cs]. https://doi.org/10.11409/mit.36.63. http://arxiv.org/abs/1803.08691
Shakibapour, E., Cunha, A., Aresta, G., Mendonça, A.M., Campilho, A.: An unsupervised metaheuristic search approach for segmentation and volume measurement of pulmonary nodules in lung CT scans. Exp. Syst. Appl. 119, 415–428 (2019)
Torre, L.A., Siegel, R.L., Jemal, A.: Lung cancer statistics. In: Ahmad, A., Gadgeel, S. (eds.) Lung Cancer and Personalized Medicine. AEMB, vol. 893, pp. 1–19. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24223-1_1
Wang, S., et al.: Central focused convolutional neural networks: developing a data-driven model for lung nodule segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 40, 172–183 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.06.014. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1361841517301019
Acknowledgements
This work is financed by National Funds through the Portuguese funding agency, FCT – Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia within project: UID/EEA/50014/2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rocha, J., Cunha, A., Maria Mendonça, A. (2019). Comparison of Conventional and Deep Learning Based Methods for Pulmonary Nodule Segmentation in CT Images. In: Moura Oliveira, P., Novais, P., Reis, L. (eds) Progress in Artificial Intelligence. EPIA 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11804. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30241-2_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30241-2_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-30240-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-30241-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)