Abstract
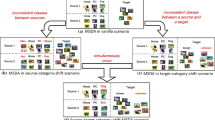
We address the problem of multi-source unsupervised domain adaptation (MS-UDA) for the purpose of visual recognition. As opposed to single source UDA, MS-UDA deals with multiple labeled source domains and a single unlabeled target domain. Notice that the conventional MS-UDA training is based on formalizing independent mappings between the target and the individual source domains without explicitly assessing the need for aligning the source domains among themselves. We argue that such a paradigm invariably overlooks the inherent category-level correlation among the source domains which, on the contrary, is deemed to bring meaningful complementarity in the learned shared feature space. In this regard, we propose a novel approach which simultaneously (i) aligns the source domains at the class-level in a shared feature space, and (ii) maps the target domain data in the same space through an adversarially trained ensemble of source domain classifiers. Experimental results obtained on the Office-31, ImageCLEF-DA, and Office-CalTech dataset validate that our approach achieves a superior accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods .
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baktashmotlagh, M., Harandi, M.T., Lovell, B.C., Salzmann, M.: Unsupervised domain adaptation by domain invariant projection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 769–776 (2013)
Ben-David, S., Blitzer, J., Crammer, K., Kulesza, A., Pereira, F., Vaughan, J.W.: A theory of learning from different domains. Mach. Learn. 79(1–2), 151–175 (2010)
Chen, M., Xu, Z., Weinberger, K., Sha, F.: Marginalized denoising autoencoders for domain adaptation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1206.4683 (2012)
Crammer, K., Kearns, M., Wortman, J.: Learning from multiple sources. In: Schölkopf, B., Platt, J.C., Hoffman, T. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19, pp. 321–328. MIT Press (2007). http://papers.nips.cc/paper/2972-learning-from-multiple-sources.pdf
Fernando, B., Habrard, A., Sebban, M., Tuytelaars, T.: Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2960–2967 (2013)
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, E., Ajakan, H., Germain, P., Larochelle, H., Laviolette, F., Marchand, M., Lempitsky, V.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 2030–2096 (2016)
Ghifary, M., Kleijn, W.B., Zhang, M.: Domain adaptive neural networks for object recognition. In: Pham, D.-N., Park, S.-B. (eds.) PRICAI 2014. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 8862, pp. 898–904. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13560-1_76
Gong, B., Shi, Y., Sha, F., Grauman, K.: Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2066–2073. IEEE (2012)
Guo, J., Shah, D.J., Barzilay, R.: Multi-source domain adaptation with mixture of experts. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.02256 (2018)
Jhuo, I.H., Liu, D., Lee, D., Chang, S.F.: Robust visual domain adaptation with low-rank reconstruction. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2168–2175. IEEE (2012)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Long, M., Cao, Y., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.02791 (2015)
Long, M., Zhu, H., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Unsupervised domain adaptation with residual transfer networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 136–144 (2016)
Mansour, Y., Mohri, M., Rostamizadeh, A.: Domain adaptation with multiple sources. In: Koller, D., Schuurmans, D., Bengio, Y., Bottou, L. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 21, pp. 1041–1048. Curran Associates, Inc. (2009). http://papers.nips.cc/paper/3550-domain-adaptation-with-multiple-sources.pdf
Pan, S.J., Tsang, I.W., Kwok, J.T., Yang, Q.: Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 22(2), 199–210 (2011)
Patel, V.M., Gopalan, R., Li, R., Chellappa, R.: Visual domain adaptation: a survey of recent advances. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 32(3), 53–69 (2015)
Peng, X., Bai, Q., Xia, X., Huang, Z., Saenko, K., Wang, B.: Moment matching for multi-source domain adaptation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.01754 (2018)
Redko, I., Courty, N., Flamary, R., Tuia, D.: Optimal transport for multi-source domain adaptation under target shift. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.04899 (2018)
Saito, K., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T., Saenko, K.: Adversarial dropout regularization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.01575 (2017)
Sun, B., Feng, J., Saenko, K.: Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In: AAAI, vol. 6, p. 8 (2016)
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7167–7176 (2017)
Wang, J., Feng, W., Chen, Y., Yu, H., Huang, M., Yu, P.S.: Visual domain adaptation with manifold embedded distribution alignment. In: 2018 ACM Multimedia Conference on Multimedia Conference, pp. 402–410. ACM (2018)
Xu, R., Chen, Z., Zuo, W., Yan, J., Lin, L.: Deep cocktail network: multi-source unsupervised domain adaptation with category shift. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3964–3973 (2018)
Yang, J., Yan, R., Hauptmann, A.G.: Cross-domain video concept detection using adaptive SVMS. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 188–197. ACM (2007)
Zhang, L., He, Z., Liu, Y.: Deep object recognition across domains based on adaptive extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 239, 194–203 (2017)
Zhao, H., Zhang, S., Wu, G., Moura, J.M., Costeira, J.P., Gordon, G.J.: Adversarial multiple source domain adaptation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 8559–8570 (2018)
Zhu, J.Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. arXiv preprint (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rakshit, S., Banerjee, B., Roig, G., Chaudhuri, S. (2019). Unsupervised Multi-source Domain Adaptation Driven by Deep Adversarial Ensemble Learning. In: Fink, G., Frintrop, S., Jiang, X. (eds) Pattern Recognition. DAGM GCPR 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11824. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33676-9_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33676-9_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-33675-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-33676-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)