Abstract
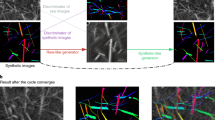
Detection of Clostridioides difficile cells in scanning electron microscopy images is a challenging task due to the challenges of cell rotation and inhomogeneous illumination. Currently, orientation-invariance in deep ConvNets is achieved by data augmentation. However, training with all possible orientations increases computational complexity. Furthermore, conventional illumination-invariance models include pre-processing illumination normalization steps. However, illumination normalization algorithms remove important texture information which is critical for the analysis of SEM images. In this paper, RISEC (Rotational Invariant Segmentation of Elongated Cells in SEM images with Inhomogeneous Illumination) is proposed to address the challenges of cell rotation and inhomogeneous illumination. First, a generative adversarial network segments the candidate cell regions proposals, addressing the inhomogeneous illumination. Then, the region proposals are passed to two capsule layers where a rotation-invariant shape representation is learned for every cell type via dynamic routing. Our experiments indicate that RISEC outperforms the state of the art models (e.g., CapsNet, and U-net) by at least 11% improving the dice score.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Endres, B.T., et al.: Epidemic Clostridioides difficile ribotype 027 lineages: comparisons of Texas versus worldwide strains. In: Open Forum Infectious Diseases, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 1–13. Oxford University Press, New York (2019)
Endres, B.T., et al.: A novel method for imaging the pharmacological effects of antibiotic treatment on clostridium difficile. Anaerobe 40, 10–14 (2016)
Han, H., Shan, S., Chen, X., Gao, W.: A comparative study on illumination preprocessing in face recognition. Pattern Recognit. 46(6), 1691–1699 (2013)
Ko, M., Kim, D., Kim, M., Kim, K.: Illumination-insensitive skin depth estimation from a light-field camera based on cgans toward haptic palpation. Electronics 7(11), 336 (2018)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440, Boston(2015)
Memariani, A., Nikou, C., Endres, B., Bassères, E., Garey, K., Kakadiaris, I.A.: DETCIC: detection of elongated touching cells with inhomogeneous illumination using a stack of conditional random fields. In: Proceedings International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, pp. 574–580 (2018)
Memariani, A., Kakadiaris, I.A.: SoLiD: segmentation of clostridioides difficile cells in the presence of inhomogeneous illumination using a deep adversarial network. In: International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, pp. 285–293, September 2018
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 234–241, Munich (2015)
Sabour, S., Frosst, N., Hinton, G.E.: Dynamic routing between capsules. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3856–3866, Long Beach, December 2017
Sabour, S., Frosst, N., Hinton, G.E.: Matrix capsules with EM routing. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, May 2018
Shen, D., Wu, G., Suk, H.I.: Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 19, 221–248 (2017)
Worrall, D.E., Garbin, S.J., Turmukhambetov, D., Brostow, G.J.: Harmonic networks: deep translation and rotation equivariance. In: Proceedings IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5028–5037, Honolulu (2017)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NIH/NIAID 1UO1 AI-24290-01 and by the Hugh Roy and Lillie Cranz Cullen Endowment Fund. At the time of data collection. Dr. Endres was a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Houston. All statements of facts, opinion or conclusions contained herein are those of the authors and should not be construed as representing official views or policies of the sponsors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Memariani, A., Endres, B.T., Bassères, E., Garey, K.W., Kakadiaris, I.A. (2019). RISEC: Rotational Invariant Segmentation of Elongated Cells in SEM Images with Inhomogeneous Illumination. In: Bebis, G., et al. Advances in Visual Computing. ISVC 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11845. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33723-0_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33723-0_45
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-33722-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-33723-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)