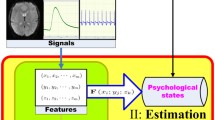
Abstract
Machines that are able to recognize and predict human affective states or emotions have become increasingly desirable over the last three decades [10]. This can be attributed to their relevance to human endeavors accompanied by the ubiquity of computing devices and an increasing trend for technology to be ever more present and engrained in people’s daily lives. There have been advancements in AI applications that are able to detect a person’s affective states through the use of machine learning models. These advancements are mostly based on architectures that take as inputs facial expression image data instances or highly specific sensor data, such as ECG or skin conductivity readings. The problem with these approaches is that models are not being designed with capabilities to receive, and modularly add multiple sensory inputs, therefore failing to operate and deal with the differences that exist on how individuals experience emotions. The present publication proposes a methodology consisting of a continuous multi sensory data acquisition process, and the construction of a feed forward classification neural network with three, 200 neuron, hidden layers. Experimentation was carried out on six different subjects, collecting over 100 h of data points containing environmental and personal variables such as activity (accelerations), light exposure, temperature and humidity. A different model was trained for each one of the subjects for 60–1500 epochs, yielding individual prediction accuracies, on test sets, of 82(%)–95(%).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amores, J., et al.: BioEssence: a wearable olfactory display that monitors cardio-respiratory information to support mental wellbeing. In: 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE (2018)
Barrett, L.F.: How Emotions are Made: The Secret Life of the Brain. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, New York (2017)
Barrett, L.F.: The theory of constructed emotion: an active inference account of interoception and categorization. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 12(1), 1–23 (2017)
Dietterich, T.G.: Ensemble methods in machine learning. In: Kittler, J., Roli, F. (eds.) MCS 2000. LNCS, vol. 1857, pp. 1–15. Springer, Heidelberg (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45014-9_1
Glorot, X., Bordes, A., Bengio, Y.: Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (2011)
Hernandez, J., Hoque, M.E., Picard, R.W.: Mood meter: large-scale and long-term smile monitoring system (2012)
Keras Documentation. https://keras.io/. Accessed 05 May 2019
Maas, A.L., Hannun, A.Y., Ng, A.Y.: Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Proceedings ICML, vol. 30, no. 1 (2013)
Mollahosseini, A., Hasani, B., Mahoor, M.H.: Affectnet: a database for facial expression, valence, and arousal computing in the wild. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 10, 18–31 (2017)
Picard, R.W.: Affective Computing. MIT Press, Cambridge (2000)
Rumelhart, D.E., et al.: Backpropagation: the basic theory. In: Backpropagation: Theory, Architectures and Applications, pp. 1–34 (1995)
Russell, J.A.: A circumplex model of affect. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 39(6), 1161 (1980)
Tensor Flow Documentation. http://tensorflow.org/api_docs/. Accessed 05 May 2019
Teo, J., et al.: Classification of affective states via EEG and deep learning. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 9(5), 132–142 (2018)
TerMITes Homepage. http://termites.synthetic.space/. Accessed 05 May 2019
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of Writing Lab, TecLabs, Tecnologico de Monterrey as well as the MIT Media Lab’s City Science Group, specifically Carson Smuts, Jason Nawyn and Kent Larson, for the technical development and facilitation of the environmental sensors used for this publication’s data acquisition process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rico, A., Garrido, L. (2019). Feed Forward Classification Neural Network for Prediction of Human Affective States Using Continuous Multi Sensory Data Acquisition. In: Martínez-Villaseñor, L., Batyrshin, I., Marín-Hernández, A. (eds) Advances in Soft Computing. MICAI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11835. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33749-0_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33749-0_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-33748-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-33749-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)