Abstract
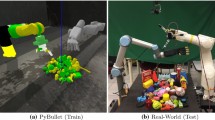
Can a robot grasp an unknown object without seeing it? In this paper, we present a tactile-sensing based approach to this challenging problem of grasping novel objects without prior knowledge of their location or physical properties. Our key idea is to combine touch based object localization with tactile based re-grasping. To train our learning models, we created a large-scale grasping dataset, including more than 30K RGB frames and over 2.8 million tactile samples from 7800 grasp interactions of 52 objects. Moreover, we propose an unsupervised auto-encoding scheme to learn a representation of tactile signals. This learned representation shows a significant improvement of 4–9% over prior works on a variety of tactile perception tasks. Our system consists of two steps. First, our touch localization model sequentially “touch-scans” the workspace and uses a particle filter to aggregate beliefs from multiple hits of the target. It outputs an estimate of the object’s location, from which an initial grasp is established. Next, our re-grasping model learns to progressively improve grasps with tactile feedback based on the learned features. This network learns to estimate grasp stability and predict adjustment for the next grasp. Re-grasping thus is performed iteratively until our model identifies a stable grasp. Finally, we demonstrate extensive experimental results on grasping a large set of novel objects using tactile sensing alone. Furthermore, when applied on top of a vision-based policy, our re-grasping model significantly boosts the overall accuracy by \(10.6\%\). We believe this is the first attempt at learning to grasp with only tactile sensing and without any prior object knowledge. For supplementary video and dataset see: cs.cmu.edu/GraspingWithoutSeeing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Correll, N., Bekris, K., Berenson, D., Brock, O., Causo, A., Hauser, K., Okada, K., Rodriguez, A., Romano, J., Wurman, P.: Analysis and observations from the first amazon picking challenge. IEEE T-ASE 15(1), 172–188 (2017)
Bicchi, A., Kumar, V.: Robotic grasping and contact: a review. In: ICRA (2000)
Tegin, J., Wikander, J.: Tactile sensing in intelligent robotic manipulation-a review. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 32, 64–70 (2005)
Bohg, J., Morales, A., Asfour, T., Kragic, D.: Data-driven grasp synthesis-a survey. IEEE Trans. Robot. 30, 289–309 (2014)
Miller, A.T., Knoop, S., Christensen, H.I., Allen, P.K.: Automatic grasp planning using shape primitives. In: ICRA (2003)
Collet, A., Berenson, D., Srinivasa, S.S., Ferguson, D.: Object recognition and full pose registration from a single image for robotic manipulation. In: ICRA (2009)
Saxena, A., Driemeyer, J., Kearns, J., Osondu, C., Ng, A.Y.: Learning to grasp novel objects using vision. In: ISER (2006)
Watter, M., Springenberg, J., Boedecker, J., Riedmiller, M.: Embed to control: a locally linear latent dynamics model for control from raw images. In: NIPS (2015)
Levine, S., Finn, C., Darrell, T., Abbeel, P.: End-to-end training of deep visuomotor policies. JMLR 17, 1334–1373 (2016)
Pinto, L., Gupta, A.: Supersizing self-supervision: learning to grasp from 50k tries and 700 robot hours. In: ICRA (2016)
Levine, S., Pastor, P., Quillen, D.: Learning hand-eye coordination for grasping with deep learning and large-scale data collection. In: ISER (2016)
Mahler, J., Liang, J., Niyaz, S., Laskey, M., Doan, R., Liu, X., Ojea, J.A., Goldberg, K.: Dex-net 2.0: deep learning to plan robust grasps with synthetic point clouds and analytic grasp metrics. RSS (2017)
Johansson, R.S., Flanagan, J.R.: Coding and use of tactile signals from the fingertips in object manipulation tasks. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 345 (2009)
Chu, V., McMahon, I., Riano, L., McDonald, C.G., He, Q., Perez-Tejada, J.M., Arrigo, M., Fitter, N., Nappo, J.C., Darrell, T., et al.: Using robotic exploratory procedures to learn the meaning of haptic adjectives. In: ICRA (2013)
Spiers, A., Liarokapis, M., Calli, B., Dollar, A.: Single-grasp object classification and feature extraction with simple robot hands and tactile sensors. IEEE Trans. Haptics 9, 207–220 (2016)
Yuan, W., Zhu, C., Owens, A., Srinivasan, M., Adelson, E.: Shape-independent hardness estimation using deep learning and a gelsight tactile sensor. In: ICRA (2017)
Yi, Z., Calandra, R., Veiga, F., van Hoof, H., Hermans, T., Zhang, Y., Peters, J.: Active tactile object exploration with gaussian processes. In: IROS (2016)
Meier, M., Schopfer, M., Haschke, R., Ritter, H.: A probabilistic approach to tactile shape reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27, 630–635 (2011)
Petrovskaya, A., Khatib, O.: Global localization of objects via touch. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27, 569–585 (2011)
Saund, B., Chen, S., Simmons, R.: Touch based localization of parts for high precision manufacturing. In: ICRA (2017)
Javdani, S., Klingensmith, M., Bagnell, J.A., Pollard, N.S., Srinivasa, S.S.: Efficient touch based localization through submodularity. In: ICRA (2013)
Pezzementi, Z., Reyda, C., Hager, G.D.: Object mapping, recognition, and localization from tactile geometry. In: ICRA (2011)
Kaboli, M., Feng, D., Yao, K., Lanillos, P., Cheng, G.: A tactile-based framework for active object learning and discrimination using multimodal robotic skin. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2, 2143–2150 (2017)
Fearing, R.: Simplified grasping and manipulation with dextrous robot hands. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 2, 188–195 (1986)
Hsiao, K., Chitta, S., Ciocarlie, M., Jones, E.G.: Contact-reactive grasping of objects with partial shape information. In: IROS (2010)
Romano, J.M., Hsiao, K., Niemeyer, G., Chitta, S., Kuchenbecker, K.J.: Human-inspired robotic grasp with tactile sensing. Trans. Robot. 27, 1067–1079 (2011)
Bekiroglu, Y., Laaksonen, J., Jorgensen, J.A., Kyrki, V., Kragic, D.: Assessing grasp stability based on learning and haptic data. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27, 616–629 (2011)
Chebotar, Y., Hausman, K., Su, Z., Sukhatme, G.S., Schaal, S.: Self-supervised regrasping using spatio-temporal tactile features and reinforcement learning. In: IROS (2016)
Dang, H., Allen, P.K.: Grasp adjustment on novel objects using tactile experience from similar local geometry. In: IROS (2013)
Dragiev, S., Toussaint, M., Gienger, M.: Uncertainty aware grasping and tactile exploration. In: ICRA (2013)
Calandra, R., Owens, A., Upadhyaya, M., Yuan, W., Lin, J., Adelson, E.H., Levine, S.: The feeling of success: does touch sensing help predict grasp outcomes? In: Conference on Robot Learning (2017)
Dang, H., Weisz, J., Allen, P.K.: Blind grasping: Stable robotic grasping using tactile feedback and hand kinematics. In: ICRA (2011)
Koval, M.C., Pollard, N.S., Srinivasa, S.S.: Pre-and post-contact policy decomposition for planar contact manipulation under uncertainty. IJRR 35, 244–264 (2016)
Felip, J., Bernabe, J., Morales, A.: Contact-based blind grasping of unknown objects. In: IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots (2012)
Dang, H., Allen, P.K.: Stable grasping under pose uncertainty using tactile feedback. Auton. Robot. 36, 309–330 (2013)
Erickson, Z., Chernova, S., Kemp, C.C.: Semi-supervised haptic material recognition for robots using generative adversarial networks, arXiv (2017)
Chebotar, Y., Hausman, K., Su, Z., Molchanov, A., Kroemer, O., Sukhatme, G., Schaal, S.: BIGS: BioTac grasp stability dataset. In: ICRA Workshop (2016)
Chebotar, Y., Hausman, K., Kroemer, O., Sukhatme, G., Schaal, S.: Generalizing regrasping with supervised policy learning. In: ISER (2016)
Schneider, A., Sturm, J., Stachniss, C., Reisert, M., Burkhardt, H., Burgard, W.: Object identification with tactile sensors using bag-of-features. In: IROS (2009)
Madry, M., Bo, L., Kragic, D., Fox, D.: ST-HMP: unsupervised spatio-temporal feature learning for tactile data. In: ICRA (2014)
Murali, A., Pinto, L., Gandhi, D., Gupta, A.: CASSL: curriculum accelerated self-supervised learning. In: ICRA (2018)
Roberge, J.-P., Rispal, S., Wong, T., Duchaine, V.: Unsupervised feature learning for classifying dynamic tactile events using sparse coding. In: ICRA (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Google Focused Award and ONR MURI N000141612007. Abhinav Gupta was supported in part by Sloan Research Fellowship and Adithya Murali was partly supported by a Uber Fellowship. The authors would also like to thank Brian Okorn, Reuben Aronson, Ankit Bhatia, Lerrel Pinto, Tess Hellebrekers and Suren Jayasuriya for discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (mp4 49537 KB)
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Murali, A., Li, Y., Gandhi, D., Gupta, A. (2020). Learning to Grasp Without Seeing. In: Xiao, J., Kröger, T., Khatib, O. (eds) Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Experimental Robotics. ISER 2018. Springer Proceedings in Advanced Robotics, vol 11. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33950-0_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33950-0_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-33949-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-33950-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)