Abstract
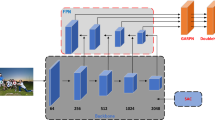
Pedestrian detection is a popular yet challenging research topic in the computer vision community. Although it has achieved great progress in recent years, it still remains an open question how to handle scale variation, which commonly exists in real world applications. To address this problem, this paper presents a novel pedestrian detector to better classify and regress proposals of different scales given by a region proposal network (RPN). Specifically, we have made the following major modifications to the Adapted FasterRCNN baseline. First, we divide all proposals into small and large pools according to their scales, and deal with each pool in a separate classification network. Also, we employ two auxiliary supervisions to balance the effect of two parts of proposals on the back propagation. It is worth noting that the proposed new detector does not bring extra computational overhead and only introduces very few additional parameters. We have conducted experiments on the CityPersons, Caltech and ETH datasets and achieved significant improvements to the baseline method, especially on the small scale subset. In particular, on the CityPersons and ETH datasets, our method surpasses previous state-of-the-art methods with lower computational costs at test time.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ouyang, W., Wang, X.: Joint deep learning for pedestrian detection. In: ICCV, pp. 2056–2063 (2013)
Ess, A., Leibe, B., Van Gool, L.: Depth and appearance for mobile scene analysis. In: ICCV, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Li, W., Zhao, R., Xiao, T., Wang, X.: DeepReID: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: CVPR, pp. 152–159 (2014)
Wang, X., Wang, M., Li, W.: Scene-specific pedestrian detection for static video surveillance. PAMI 36(2), 361–374 (2014)
Dollar, P., Wojek, C., Schiele, B., Perona, P.: Pedestrian detection: an evaluation of the state of the art. PAMI 34(4), 743–761 (2011)
Zhang, S., Benenson, R., Omran, M., Hosang, J., Schiele, B.: Towards reaching human performance in pedestrian detection. PAMI 40(4), 973–986 (2017)
Chen, D., Zhang, S., Ouyang, W., Yang, J., Tai, Y.: Person search via a mask-guided two-stream CNN model. In: ECCV, pp. 734–750 (2018)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: NIPS, pp. 91–99 (2015)
Cordts, M., et al.: The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: CVPR, pp. 3213–3223 (2016)
Girshick, R.: Fast R-CNN. In: ICCV, pp. 1440–1448 (2015)
Liu, W., et al.: SSD: single shot multibox detector. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9905, pp. 21–37. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
Brazil, G., Yin, X., Liu, X.: Illuminating pedestrians via simultaneous detection & segmentation. In: ICCV, pp. 4950–4959 (2017)
Zhang, S., Yang, J., Schiele, B.: Occluded pedestrian detection through guided attention in CNNs. In: CVPR, pp. 6995–7003 (2018)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger. In: CVPR, pp. 7263–7271 (2017)
Zhou, C., Yuan, J.: Multi-label learning of part detectors for heavily occluded pedestrian detection. In: ICCV, pp. 3486–3495 (2017)
Song, T., Sun, L., Xie, D., Sun, H., Pu, S.: Small-scale pedestrian detection based on somatic topology localization and temporal feature aggregation. In: arXiv preprint. arXiv:1807.01438 (2018)
Hosang, J., Omran, M., Benenson, R., Schiele, B.: Taking a deeper look at pedestrians. In: CVPR, pp. 4073–4082 (2015)
Zhang, S., Benenson, R., Omran, M., Hosang, J., Schiele, B.: How far are we from solving pedestrian detection? In: CVPR, pp. 1259–1267 (2016)
Zhang, S., Benenson, R., Schiele, B.: Citypersons: a diverse dataset for pedestrian detection. In: CVPR, pp. 3213–3221 (2017)
Singh, B., Davis, L.S.: An analysis of scale invariance in object detection snip. In: CVPR, pp. 3578–3587 (2018)
Cai, Z., Fan, Q., Feris, R.S., Vasconcelos, N.: A unified multi-scale deep convolutional neural network for fast object detection. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9908, pp. 354–370. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_22
Kong, T., Sun, F., Yao, A., Liu, H., Lu, M., Chen, Y.: Ron: reverse connection with objectness prior networks for object detection. In: CVPR, pp. 5936–5944 (2017)
Lin, T.-Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: CVPR, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Wang, X., Xiao, T., Jiang, Y., Shao, S., Sun, J., Shen, C.: Repulsion loss: detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: CVPR, pp. 7774–7783 (2018)
Zhang, S., Wen, L., Bian, X., Lei, Z., Li, S.Z.: Occlusion-aware R-CNN: detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: ECCV, pp. 637–653 (2018)
Yang, F., Choi, W., Lin, Y.: Exploit all the layers: fast and accurate CNN object detector with scale dependent pooling and cascaded rejection classifiers. In: CVPR, pp. 2129–2137 (2016)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: CVPR, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Daniel Costea, A., Nedevschi, S.: Semantic channels for fast pedestrian detection. In: CVPR, pp. 2360–2368 (2016)
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 580–587 (2014)
Li, J., Liang, X., Shen, S., Xu, T., Feng, J., Yan, S.: Scale-aware fast R-CNN for pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 20(4), 985–996 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61702262), Funds for International Cooperation and Exchange of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61861136011), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. BK20181299), CCF-Tencent Open Fund (RAGR20180113), “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities” (No. 30918011322) and Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (2018QNRC001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cheng, Q., Zhang, S. (2019). Efficiently Handling Scale Variation for Pedestrian Detection. In: Cui, Z., Pan, J., Zhang, S., Xiao, L., Yang, J. (eds) Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. Visual Data Engineering. IScIDE 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11935. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36188-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36189-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)