Abstract
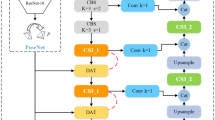
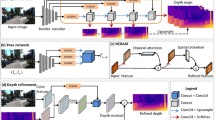
We propose an unsupervised novel method, Attention-Pixel and Attention-Channel Network (APAC-Net), for unsupervised monocular learning of estimating scene depth and ego-motion. Our model only utilizes monocular image sequences and does not need additional sensor information, such as IMU and GPS, for supervising. The attention mechanism is employed in APAC-Net to improve the networks’ efficiency. Specifically, three attention modules are proposed to adjust feature weights when training. Moreover, to minimum the effect of noise, which is produced in the reconstruction processing, the Image-reconstruction loss based on PSNR \(L_{PSNR}\) is used to evaluation the reconstruction quality. In addition, due to the fail depth estimation of the objects closed to camera, the Temporal-consistency loss \(L_{Temp}\) between adjacent frames and the Scale-based loss \(L_{Scale}\) among different scales are proposed. Experimental results showed APAC-Net can perform well in both the depth and ego-motion tasks, and it even behaved better in several items on KITTI and Cityscapes.
G. Lu—The work is supported by the NSFC fund (61332011), Shenzhen Fundamental Research fund (JCYJ20170811155442454, JCYJ20180306172023949), and Medical Biometrics Perception and Analysis Engineering Laboratory, Shenzhen, China.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, S., Min, D., Ham, B., Kim, Y., Oh, C., Sohn, K.: Depth analogy: data-driven approach for single image depth estimation using gradient samples. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(12), 5953–5966 (2015)
Clark, R., Wang, S., Wen, H., Markham, A., Trigoni, N.: VINet: visual-inertial odometry as a sequence-to-sequence learning problem. National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 3995–4001 (2017)
Cordts, M., et al.: The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3213–3223 (2016)
Eigen, D., Puhrsch, C., Fergus, R.: Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network. Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2366–2374 (2014)
Engel, J., Koltun, V., Cremers, D.: Direct sparse odometry. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(3), 611–625 (2018)
Garg, R., Kumar, B.G.V., Carneiro, G., Reid, I.: Unsupervised CNN for single view depth estimation: geometry to the rescue. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9912, pp. 740–756. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_45
Geiger, A., Lenz, P., Stiller, C., Urtasun, R.: Vision meets robotics: the KITTI dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 32(11), 1231–1237 (2013)
Godard, C., Aodha, O.M., Brostow, G.J.: Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6602–6611 (2017)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization (2015)
Klein, G., Murray, D.W.: Parallel tracking and mapping for small AR workspaces, pp. 1–10 (2007)
Li, R., Wang, S., Long, Z., Gu, D.: UnDeepVO: monocular visual odometry through unsupervised deep learning. In: International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 7286–7291 (2018)
Liu, B., Gould, S., Koller, D.: Single image depth estimation from predicted semantic labels, pp. 1253–1260 (2010)
Mahjourian, R., Wicke, M., Angelova, A.: Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from monocular video using 3D geometric constraints. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5667–5675 (2018)
Murartal, R., Montiel, J.M.M., Tardos, J.D.: ORB-SLAM: a versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(5), 1147–1163 (2015)
Newcombe, R.A., Lovegrove, S., Davison, A.J.: DTAM: dense tracking and mapping in real-time, pp. 2320–2327 (2011)
Pillai, S., Leonard, J.J.: Towards visual ego-motion learning in robots, pp. 5533–5540 (2017)
Pinard, C., Chevalley, L., Manzanera, A., Filliat, D.: Learning structure-from-motion from motion. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 363–376 (2018). arXiv
Repala, V.K., Dubey, S.R.: Dual CNN models for unsupervised monocular depth estimation. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018). arXiv
Saxena, A., Sun, M., Ng, A.Y.: Make3D: learning 3D scene structure from a single still image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31(5), 824–840 (2009)
Vijayanarasimhan, S., Ricco, S., Schmid, C., Sukthankar, R., Fragkiadaki, K.: SfM-Net: learning of structure and motion from video. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017). arXiv
Wang, S., Clark, R., Wen, H., Trigoni, N.: DeepVO: towards end-to-end visual odometry with deep recurrent convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2043–2050 (2017)
Yin, Z., Shi, J.: GeoNet: unsupervised learning of dense depth, optical flow and camera pose. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1983–1992 (2018)
Zhou, T., Brown, M., Snavely, N., Lowe, D.G.: Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from video. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6612–6619 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lin, R., Lu, Y., Lu, G. (2019). APAC-Net: Unsupervised Learning of Depth and Ego-Motion from Monocular Video. In: Cui, Z., Pan, J., Zhang, S., Xiao, L., Yang, J. (eds) Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. Visual Data Engineering. IScIDE 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11935. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36188-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36189-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)