Abstract
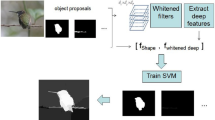
In this paper, we propose a proposal based method for saliency detection. Our method separates the salient proposals out by assigning them a novel attention mechanism, semantic attention (SeA). The attention are established based on the observation that regions with high attention should have similarly semantic concepts with salient objects. The SeA takes the high-level semantic features from Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (Faster R-CNN) to assist the proposal selection in images with complex background. We select the salient proposals according to their semantic attention probabilities. Quantitative and qualitative experiments on four datasets demonstrate that the proposed algorithm performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mahadevan, V., Vasconcelos, N.: Saliency-based discriminant tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, FL, pp. 1007–1013. IEEE (2009)
Dhavale, N., Itti, L.: Saliency-based multifoveated MPEG compression. In: Seventh International Symposium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Paris, vol. 1, pp. 229–232. IEEE (2003)
Luo, P., Tian, Y., Wang, X., Tang, X.: Switchable deep network for pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, OH, pp. 899–906. IEEE (2014)
Malik, J., Shi, J.: Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(8), 888–905 (2000)
Chang, K.-Y., Liu, T.-L., Chen, H.-T., Lai, S.-H.: Fusing generic objectness and visual saliency for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, pp. 914–921. IEEE (2011)
Li, S., Lu, H., Lin, Z., Shen, X., Price, B.: Adaptive metric learning for saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(11), 3321–3331 (2015)
Jiang, P., Ling, H., Yu, J., Peng, J.: Salient region detection by UFO: uniqueness, focusness and objectness. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, NSW, pp. 1976–1983. IEEE (2013)
Krähenbühl, P., Koltun, V.: Geodesic object proposals. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 725–739. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_47
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., Susstrunk, S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, FL, pp. 1597–1604. IEEE (2009)
Cheng, M.-M., Zhang, G.-X., Mitra, N., Huang, X., Hu, S.-M.: Global contrast based salient region detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CO, pp. 409–416. IEEE (2011)
Liu, Z., Zou, W., Le Meur, O.: Saliency tree: a novel saliency detection framework. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(5), 1937–1952 (2014)
Yan, Q., Xu, L., Shi, J., Jia, J.: Hierarchical saliency detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, OR, pp. 1155–1162. IEEE (2013)
Wei, Y., Wen, F., Zhu, W., Sun, J.: Geodesic saliency using background priors. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012. LNCS, vol. 7574, pp. 29–42. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33712-3_3
Yang, C., Zhang, L., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.-H.: Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, OR, pp. 3166–3173. IEEE (2013)
Zhu, W., Liang, S., Wei, Y., Sun, J.: Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, OH, pp. 2814–2821. IEEE (2014)
Jiang, Z., Davis, L.S.: Submodular salient region detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, OR, pp. 2043–2050. IEEE (2013)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, NV, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, pp. 91–99 (2015)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Computer Science arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Rother, C., Kolmogorov, V., Blake, A.: GrabCut: interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. ACM Trans. Graph. 23(3), 309–314 (2004)
Liu, T., et al.: Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(2), 353–367 (2011)
Movahedi, V., Elder, J.H.: Design and perceptual validation of performance measures for salient object segmentation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CA, pp. 49–56. IEEE (2010)
Li, Y., Hou, X., Koch, C., Rehg, J.M., Yuille, A.L.: The secrets of salient object segmentation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, OH, pp. 280–287. IEEE (2014)
Zhao, R., Ouyang, W., Li, H., Wang, X.: Saliency detection by multi-context deep learning. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, MA, pp. 1265–1274. IEEE (2015)
Tong, N., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.-H.: Salient object detection via bootstrap learning. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, MA, pp. 1884–1892. IEEE (2015)
Qin, Y., Lu, H., Xu, Y., Wang, H.: Saliency detection via cellular automata. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, MA, pp. 110–119. IEEE (2015)
Jiang, H., Wang, J., Yuan, Z., Wu, Y., Zheng, N., Li, S.: Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, OR, pp. 2083–2090. IEEE (2013)
Li, X., Lu, H., Zhang, L., Ruan, X., Yang, M.-H.: Saliency detection via dense and sparse reconstruction. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, NSW, pp. 2976–2983. IEEE (2013)
Kim, J., Han, D., Tai, Y.-W., Kim, J.: Salient region detection via high-dimensional color transform. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, OH. IEEE (2014)
Wang, L., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.-H.: Deep networks for saliency detection via local estimation and global search. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, MA. IEEE (2015)
Li, C., Yuan, Y., Cai, W., Xia, Y.: Robust saliency detection via regularized random walks ranking. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, MA, pp. 2710–2717. IEEE (2015)
Wang, T., Zhang, L., Lu, H., Sun, C., Qi, J.: Kernelized subspace ranking for saliency detection. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9912, pp. 450–466. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, L., Song, T., Katayama, T., Shimamoto, T. (2019). Proposal-Aware Visual Saliency Detection with Semantic Attention. In: Cui, Z., Pan, J., Zhang, S., Xiao, L., Yang, J. (eds) Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. Visual Data Engineering. IScIDE 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11935. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36188-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36189-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)