Abstract
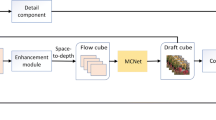
Recent studies on video super-resolution (SR) has shown that convolutional neural network (CNN) combined with motion compensation (MC) is able to merge information from multiple low-resolution (LR) frames to generate high quality images. However, Most SR and MC modules based on deep CNN simply increase the depth of the network, which cannot make full use of hierarchical and multi-scale features, thereby achieving relatively low performance. To address the above problem, a novel multi-scale residual dense Network (MSRDN) is proposed in this paper. A multi-scale residual density block (MSRDB) is first designed to extract abundant local features through dense convolution layer, which helps to adaptively detect image features of different scales with convolution kernels of different scales. Then, we redesign SR module and MC module with MSRDB, which adaptively learns more effective features from local features and uses global feature fusion to jointly and adaptively learn global hierarchical features. Comparative results on Vid4 dataset demonstrate that MSRDB can make more full use of feature information, which helps to effectively improve the reconstruction performance of video SR.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Fattal, R.: Image upsampling via imposed edge statistics. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 26(3), 95 (2007)
Freedman, G., Fattal, R.: Image and video upscaling from local self-examples. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 30(2), 12 (2011)
Nguyen, N., Milanfar, P., Golub, G.: A computationally efficient superresolution image reconstruction algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(4), 573–583 (2001)
Liao, R., Tao, X., Li, R., et al.: Video super-resolution via deep draft-ensemble learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 531–539 (2015)
Caballero, J., Ledig, C., Aitken, A., et al.: Real-time video super-resolution with spatio-temporal networks and motion compensation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4778–4787 (2017)
Ma, Z., Liao, R., Tao, X., et al.: Handling motion blur in multi-frame super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5224–5232 (2015)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., He, K., Tang, X.: Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8692, pp. 184–199. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_13
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., Tang, X.: Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9906, pp. 391–407. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_25
Shi, W., Caballero, J., Huszár, F., et al.: Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1874–1883 (2016)
Kim, J., Kwon Lee, J., Mu Lee, K.: Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1646–1654 (2016)
Tai, Y., Yang, J., Liu, X.: Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3147–3155 (2017)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–9 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Tong, T., Li, G., Liu, X., et al.: Image super-resolution using dense skip connections. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4799–4807 (2017)
Tao, X., Gao, H., Liao, R., et al.: Detail-revealing deep video super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4472–4480 (2017)
Kappeler, A., Yoo, S., Dai, Q., et al.: Video super-resolution with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2(2), 109–122 (2016)
Liu, D., Wang, Z., Fan, Y., et al.: Robust video super-resolution with learned temporal dynamics. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2507–2515 (2017)
Sajjadi, M.S.M., Vemulapalli, R., Brown, M.: Frame-recurrent video super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6626–6634 (2018)
Brox, T., Bruhn, A., Papenberg, N., Weickert, J.: High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In: Pajdla, T., Matas, J. (eds.) ECCV 2004. LNCS, vol. 3024, pp. 25–36. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24673-2_3
Farnebäck, G.: Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. In: Bigun, J., Gustavsson, T. (eds.) SCIA 2003. LNCS, vol. 2749, pp. 363–370. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45103-X_50
Dosovitskiy, A., Fischer, P., Ilg, E., et al.: FlowNet: learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2758–2766 (2015)
Ahmadi, A., Patras, I.: Unsupervised convolutional neural networks for motion estimation. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1629–1633. IEEE (2016)
De Boor, C.: Bicubic spline interpolation. J. Math. Phys. 41(1–4), 212–218 (1962)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., et al.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cui, H., Sun, Q. (2019). Multi-scale Residual Dense Block for Video Super-Resolution. In: Cui, Z., Pan, J., Zhang, S., Xiao, L., Yang, J. (eds) Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. Visual Data Engineering. IScIDE 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11935. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_35
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36188-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36189-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)