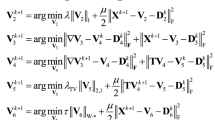Abstract
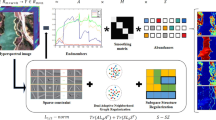
In this paper, a nonlocal low rank prior associated with spatial smoothness and spectral collaborative sparsity are integrated together for unmixing the hyperspectral data. Based on a fact that the hyperspectral images have self-similarity in nonlocal sense and smoothness in the local sense. To explore the spatial self-similarity, the nonlocal cubic patches are grouped together to form a low-rank matrix. Then, in the framework of linear mixture model, the nuclear norm is constrained to the abundance matrix of these similar patches to enforce low-rank property. In addition, the spectral and local spatial information is also taken into account by introducing collaborative sparsity and TV regularization terms, respectively. Finally, the proposed method is tested on two simulated data sets and a real data set and the results show that the proposed algorithm produces better performance than other state-of-the-art algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiao, C., Chen, C., McGarvey, R.G., et al.: Multiple instance hybrid estimator for hyperspectral target characterization and sub-pixel target detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 146, 235–250 (2018)
Shi, C., Wang, L.: Linear spatial spectral mixture model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 54(6), 3599–3611 (2016)
Marinoni, A., Plaza, A., Gamba, P.: Harmonic mixture modeling for efficient nonlinear hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 9(9), 4247–4256 (2016)
Li, C., Liu, Y., Cheng, J., et al.: Hyperspectral unmixing with bandwise generalized bilinear model. Remote Sens. 10(10), 1600 (2018)
Tang, W., Shi, Z., Wu, Y., et al.: Sparse unmixing of hyperspectral data using spectral a priori information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 53(2), 770–783 (2016)
Iordache, M.D., Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Plaza, A.: Collaborative sparse regression for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52(1), 341–354 (2013)
Iordache, M.D., Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Plaza, A.: Total variation spatial regularization for sparse hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 50(11), 4484–4502 (2012)
Rizkinia, M., Okuda, M.: Joint local abundance sparse unmixing for hyperspectral images. Remote Sens. 9(12), 1224 (2017)
Qu, Q., Nasrabadi, N.M., Tran, T.D.: Abundance estimation for bilinear mixture models via joint sparse and low-rank representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 7(52), 4404–4423 (2014)
Zhang, X., Li, C., Zhang, J., et al.: Hyperspectral unmixing via low-rank representation with space consistency constraint and spectral library pruning. Remote Sens. 10(2), 339 (2018)
Lou, Y., Yin, P., He, Q., et al.: Computing sparse representation in a highly coherent dictionary based on difference of L1 and L2. J. Sci. Comput. 64(1), 178–196 (2015)
Chang, Y., Yan, L., Zhong, S.: Hyper-Laplacian regularized unidirectional low-rank tensor recovery for multispectral image denoising. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, pp. 5901–5909 (2017)
Eckstein, J., Bertsekas, D.P.: On the Douglas-Rachford splitting method and the proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators. Math. Program. 55(1–3), 293–318 (1992)
USGS digital spectral library 06. https://speclab.cr.usgs.gov/spectral.lib06. Accessed 08 June 2016
Altmann, Y., Pereyra, M., Bioucas-Dias, J.: Collaborative sparse regression using spatially correlated supports-application to hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(12), 5800–5811 (2015)
Guerra, R., Santos, L., López, S., et al.: A new fast algorithm for linearly unmixing hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 53(12), 6752–6765 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, F., Zheng, Y., Sun, L. (2019). Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Image with Nonlocal Low-Rank Prior. In: Cui, Z., Pan, J., Zhang, S., Xiao, L., Yang, J. (eds) Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. Visual Data Engineering. IScIDE 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11935. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_42
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36188-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36189-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)