Abstract
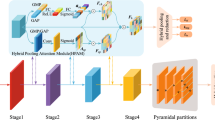
Person re-identification (re-ID) is a challenging task since the same person captured by different cameras can appear very differently, due to the uncontrolled factors such as occlusion, illumination, viewpoint and pose variation etc. Attention-based person re-ID methods have been extensively studied to focus on discriminative regions of the last convolutional layer, which, however, ignore the low-level fine-grained information. In this paper, we propose a novel SliceNet with efficient feature augmentation modules for open-world person re-identification. Specifically, with the philosophy of divide and conquer, we divide the baseline network into three sub-networks from low, middle and high levels, which are called slice networks, followed by a Self-Alignment Attention Module respectively to learn multi-level discriminative parts. In contrast with existing works that uniformly partition the images into multiple patches, our attention module aims to learn self-alignment masks for discovering and exploiting the align-attention regions. Further, SliceNet is combined with the attention free baseline network to characterize global features. Extensive experiments on the benchmark datasets including Market-1501, CUHK03, and DukeMTMC-reID show that our proposed SliceNet achieves favorable performance compared with the state-of-the art methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, X., Hospedales, T.M., Tao, X.: Multi-level factorisation net for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2018)
Chen, W., Chen, X., Zhang, J., Huang, K.: Beyond triplet loss: a deep quadruplet network for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2017)
Chen, Y., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Person re-identification by deep learning multi-scale representations. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (2017)
Cheng, D., Gong, Y., Zhou, S., Wang, J., Zheng, N.: Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function. In: Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (2016)
Chi, S., Li, J., Zhang, S., Xing, J., Wen, G., Qi, T.: Pose-driven deep convolutional model for person re-identification. In: ICCV (2017)
Dai, J., Yi, L., He, K., Jian, S.: R-FCN: object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks. In: CVPR (2016)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Li, F.F.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (2009)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: ICLR (2015)
Fei, W., et al.: Residual attention network for image classification. In: CVPR (2017)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Mcallester, D.A., Ramanan, D.: A discriminatively trained, multiscale, deformable part model. In: CVPR IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (2008)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Hermans, A., Beyer, L., Leibe, B.: In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2017)
Ba, J., Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K.: Multiple object recognition with visual attention. In: CVPR (2014)
Jing, X., Rui, Z., Feng, Z., Wang, H., Ouyang, W.: Attention-aware compositional network for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2018)
Kalayeh, M.M., Basaran, E., Gokmen, M., Kamasak, M.E., Shah, M.: Human semantic parsing for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2018)
Li, W., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Person re-identification by deep joint learning of multi-loss classification. In: CVPR (2017)
Lin, Y., Liang, Z., Zheng, Z., Yu, W., Yi, Y.: Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning. In: CVPR (2017)
Liu, H., Feng, J., Qi, M., Jiang, J., Yan, S.: End-to-end comparative attention networks for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Publ. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 26(7), 3492–3506 (2017)
Liu, W., et al.: SSD: single shot multibox detector. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9905, pp. 21–37. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
Prosser, B., Zheng, W.S., Gong, S., Tao, X.: Person re-identification by support vector ranking. In: British Machine Vision Conference (2010)
Si, J., et al.: Dual attention matching network for context-aware feature sequence based person re-identification. In: CVPR (2018)
Sun, Y., Liang, Z., Yi, Y., Qi, T., Wang, S.: Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: European Conference on Computer Vision (2018)
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Deng, W., Wang, S.: SVDNet for pedestrian retrieval. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Wei, L., Rui, Z., Tong, X., Wang, X.G.: DeepReID: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (2014)
Wei, L., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2018)
Yan, W., Wang, L., You, Y., Xu, Z., Weinberger, K.Q.: Resource aware person re-identification across multiple resolutions. In: CVPR (2018)
Yao, H., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Qi, T.: Deep representation learning with part loss for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. PP(99), 1 (2017)
Zhang, S., Wen, L., Xiao, B., Zhen, L., Li, S.Z.: Single-shot refinement neural network for object detection. In: CVPR (2017)
Zhao, H., et al.: Spindle net: Person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (2017)
Zhao, L., Li, X., Wang, J., et al.: Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In: ICCV (2017)
Zheng, F., Sun, X., Jiang, X., Guo, X., Yu, Z., Huang, F.: A coarse-to-fine pyramidal model for person re-identification via multi-loss dynamic training. In: CVPR (2019)
Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., Tian, Q.: Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2015)
Zheng, Z., Liang, Z., Yi, Y.: Pedestrian alignment network for large-scale person re-identification. In: CVPR (2017)
Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Cao, D., Li, S.: Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (2017)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Kang, G., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Random erasing data augmentation. In: CVPR (2017)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Zheng, Z., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Camera style adaptation for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, Z., Zhang, L. (2019). SliceNet: Mask Guided Efficient Feature Augmentation for Attention-Aware Person Re-Identification. In: Cui, Z., Pan, J., Zhang, S., Xiao, L., Yang, J. (eds) Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. Visual Data Engineering. IScIDE 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11935. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36189-1_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36188-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36189-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)