Abstract
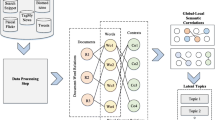
From online reviews and product descriptions to tweets and chats, many modern applications revolve around understanding both semantic structure and topics of short texts. Due to significant reliance on word co-occurrence, traditional topic modeling algorithms such as LDA perform poorly on sparse short texts. In this paper, we propose an unsupervised short text tagging algorithm that generates latent topics, or clusters of semantically similar words, from a corpus of short texts, and labels these short texts by stable predominant topics. The algorithm defines a weighted undirected network, namely the one mode projection of the bipartite network between words and users. Nodes represent all unique words from the corpus of short texts, edges mutual presence of pairs of words in a short text, and weights the number of short texts in which pairs of words appear. We generate the latent topics using nested stochastic block models (NSBM), dividing the network of words into communities of similar words. The algorithm is versatile—it automatically detects the appropriate number of topics. Many applications stem from the proposed algorithm, such as using the short text topic representations as the basis of a short text similarity metric. We validate the results using inter-semantic similarity and normalized mutual information, which show the method is competitive with industry short text topic modeling algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amancio, D.R., Nunes, M.G.V., Oliveira Jr., O., Pardo, T.A.S., Antiqueira, L., Costa, L.F.: Using metrics from complex networks to evaluate machine translation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 390(1), 131–142 (2011)
Arun, R., Suresh, V., Madhavan, C.V., Murthy, M.N.: On finding the natural number of topics with latent dirichlet allocation: some observations. In: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 391–402. Springer (2010)
Biemann, C., Roos, S., Weihe, K.: Quantifying semantics using complex network analysis. In: Proceedings of COLING 2012, pp. 263–278 (2012)
Blei, D.M., Ng, A.Y., Jordan, M.I.: Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3(Jan), 993–1022 (2003)
Bollegala, D., Matsuo, Y., Ishizuka, M.: A web search engine-based approach to measure semantic similarity between words. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 23(7), 977–990 (2010)
Byrd, R.J., Ravin, Y.: Identifying and extracting relations in text. na (1999)
Chen, M., Jin, X., Shen, D.: Short text classification improved by learning multi-granularity topics. In: Twenty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2011)
Drieger, P.: Semantic network analysis as a method for visual text analytics. Proc.-Soc. Behav. Sci. 79, 4–17 (2013)
Eagle, N., Pentland, A.S., Lazer, D.: Inferring friendship network structure by using mobile phone data. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 106(36), 15274–15278 (2009)
Fortunato, S.: Community detection in graphs. Phys. Rep. 486(3–5), 75–174 (2010)
Gerlach, M., Peixoto, T.P., Altmann, E.G.: A network approach to topic models. Sci. Adv. 4(7) (2018). https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/4/7/eaaq1360
Gomaa, W.H., Fahmy, A.A.: A survey of text similarity approaches. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 68(13), 13–18 (2013)
Hartman, R., Seyednezhad, S.M., Pinheiro, D., Faustino, J., Menezes, R.: Entropy in network community as an indicator of language structure in emoji usage: a Twitter study across various thematic datasets. In: International Conference on Complex Networks and Their Applications, pp. 328–337. Springer (2018)
Hong, L., Davison, B.D.: Empirical study of topic modeling in Twitter. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Social Media Analytics, pp. 80–88. ACM (2010)
Lee, D.D., Seung, H.S.: Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 401(6755), 788 (1999)
Peixoto, T.P.: Efficient Monte Carlo and greedy heuristic for the inference of stochastic block models. Phys. Rev. E 89(1), 012804 (2014)
Peixoto, T.P.: Hierarchical block structures and high-resolution model selection in large networks. Phys. Rev. X 4(1), 011047 (2014)
Quan, X., Kit, C., Ge, Y., Pan, S.J.: Short and sparse text topic modeling via self-aggregation. In: Twenty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2015)
Seifzadeh, S., Farahat, A.K., Kamel, M.S., Karray, F.: Short-text clustering using statistical semantics. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 805–810. ACM (2015)
Seyednezhad, S.M.M., Fede, H., Herrera, I., Menezes, R.: Emoji-word network analysis: sentiments and semantics. In: The Thirty-First International Flairs Conference (2018)
Silva, F.N., Amancio, D.R., Bardosova, M., Costa, L.F., Oliveira Jr., O.N.: Using network science and text analytics to produce surveys in a scientific topic. J. Inform. 10(2), 487–502 (2016)
Yelp: The complete yelp category list (2018). https://blog.yelp.com/2018/01/yelp_category_list
Yelp: Yelp open dataset (2018). https://www.yelp.com/dataset
Zhang, P.: Evaluating accuracy of community detection using the relative normalized mutual information. J. Stat. Mech: Theory Exp. 2015(11), P11006 (2015)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the NSF for funding the AMALTHEA REU and Florida Institute of Technology for hosting the program. The authors would also like to acknowledge support from the NSF grant No. 1560345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bowllan, J., Cozart, K., Seyednezhad, S.M.M., Smith, A., Menezes, R. (2020). Short Text Tagging Using Nested Stochastic Block Model: A Yelp Case Study. In: Cherifi, H., Gaito, S., Mendes, J., Moro, E., Rocha, L. (eds) Complex Networks and Their Applications VIII. COMPLEX NETWORKS 2019. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 881. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36687-2_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36687-2_68
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36686-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36687-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)