Abstract
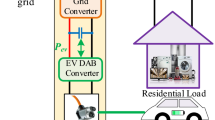
The number of electric vehicles is expected to increase exponentially in the next decade. This represents a huge potential for grid support, such as energy storage in their batteries, with advantages for grid operators and for customers. For this purpose, flexible power interfaces are required. This paper presents a simulation of a bidirectional single-phase power interface between an electric vehicle battery and the grid. The proposed system is fully simulated and counts with features such as vehicle-to-grid, vehicle-to-home and grid-to-vehicle. All power flow and the controllers for these modes of operation are described in detail. The simulation was developed in a Software-in-the-Loop scheme to facilitate a future physical implementation with a Hardware-in-the-Loop platform. The proposed system was extensively tested via simulation, the results proving the system is stable, able to change operation modes smoothly and definition of the exchanged active and reactive powers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Energy Agency: Global EV Outlook 2018: towards cross-modal electrification. https://webstore.iea.org/global-ev-outlook-2018
Kempton, W., Letendre, S.E.: Electric vehicles as a new power source for electric utilities. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Environ. 2(3), 157–175 (1997) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1361920997000011
Kempton, W., Tomić, J.: Vehicle-to-grid power fundamentals: calculating capacity and net revenue. J. Power Sources 144(1), 268–279 (2005)
Kempton, W., Tomić, J.: Vehicle-to-grid power implementation: From stabilizing the grid to supporting large-scale renewable energy. J. Power Sources 144(1), 280–294 (2005)
Sovacool, B.K., Axsen, J., Kempton, W.: The future promise of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration: a sociotechnical review and research agenda. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 42(1), 377–406 (2017)
Tan, K.M., Ramachandaramurthy, V.K., Yong, J.Y.: Integration of electric vehicles in smart grid: a review on vehicle to grid technologies and optimization techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 53, 720–732 (2016)
Mwasilu, F., Justo, J.J., Kim, E.K., Do, T.D., Jung, J.W.: Electric vehicles and smart grid interaction: a review on vehicle to grid and renewable energy sources integration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 34, 501–516 (2014)
Ferdowsi, M.: Plug-in hybrid vehicles - a vision for the future. In: 2007 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, pp. 457–462, September 2007
Nissan: Vehicle to Home Electricity Supply System. https://www.nissan-global.com/EN/TECHNOLOGY/OVERVIEW/vehicle_to_home.html
Pinto, J.G., et al.: Bidirectional battery charger with grid-to-vehicle, vehicle-to-grid and vehicle-to-home technologies. In: IECON 2013–39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pp. 5934–5939, November 2013
Vittorias, I., Metzger, M., Kunz, D., Gerlich, M., Bachmaier, G.: A bidirectional battery charger for electric vehicles with V2G and V2H capability and active and reactive power control. In: 2014 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), pp. 1–6, June 2014
Sharma, A., Sharma, S.: Review of power electronics in vehicle-to-grid systems. J. Energy Storage 21, 337–361 (2019)
Leite, V., Ferreira, A., Batista, J.: Bidirectional vehicle-to-grid interface under a microgrid project. In: 2014 IEEE 15th Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics (COMPEL), pp. 1–7, June 2014
Zgheib, R., Al-Haddad, K., Kamwa, I.: V2G, G2V and active filter operation of a bidirectional battery charger for electric vehicles. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), pp. 1260–1265, March 2016
Samerchur, S., Premrudeepreechacharn, S., Kumsuwun, Y., Higuchi, K.: Power control of single-phase voltage source inverter for grid-connected photovoltaic systems. In: 2011 IEEE/PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, pp. 1–6, March 2011
Ciobotaru, M., Teodorescu, R., Blaabjerg, F.: A new single-phase PLL structure based on second order generalized integrator. In: 2006 37th IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, pp. 1–6, June 2006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Breve, M.M., Leite, V. (2020). Control of a Bidirectional Single-Phase Grid Interface for Electric Vehicles. In: Nesmachnow, S., Hernández Callejo, L. (eds) Smart Cities. ICSC-CITIES 2019. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1152. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38889-8_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38889-8_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-38888-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-38889-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)