Abstract
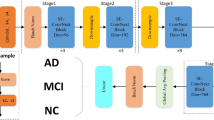
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder which leads to memory and behaviour impairment. Early discovery and diagnosis can delay the progress of this disease. In this paper, we propose a new deep learning method called selective kernel network with attention for early diagnosis of AD using magnetic resonance imaging. Generally, deep learning methods for high-accuracy recognition are based on structure of deep neural networks by stacking a myriad of convolutional layers in the model. In this paper, the structure of SKANet is constructed similarly to that of ResNeXt by repeating residual blocks with the same topology and group convolution for saving computational costs. Different from ResNeXt, the primary convolution is replaced by using selective kernel convolution to adaptively adjust the receptive field based on imported information. Then, attention mechanism is added to the bottom of the block to emphasize on important features and suppress unnecessary ones for more accurate representation of the network. The block is termed as selective kernel with attention block that consists of a sequence of operations followed by the order: a convolution with kernel size \(1\times 1\), a selective kernel convolution, a convolution with kernel size \(1\times 1\), and spatial attention mechanism. The effectiveness of this proposed model is verified based on the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative dataset. Our experimental results show superiority of the proposed model for the early diagnosis of AD. The classification accuracy of AD and mild cognitive impairment reaches up to \(98.82\%\).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbabshirani, M.R., Plis, S., Sui, J., Calhoun, V.D.: Single subject prediction of brain disorders in neuroimaging: promises and pitfalls. NeuroImage 145, 137–165 (2017)
Arribas, J., Calhoun, V., Adali, T.: A automatic Bayesian classification of healthy controls, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia using intrinsic connectivity maps from fMRI data. IEEE Trans. Bio-med. Eng. 57(12), 2850–2860 (2010)
Brookmeyer, R., Johnson, E., Ziegler-Graham, K.: Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Assoc. 3(3), 186–191 (2007)
Billones, D., Demetria, D., Hostallero, D.: DemNet: a convolutional neural network for the detection of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. In: TENCON. IEEE, Singapore (2016)
Cheng, B., Zhang, D., Chen, S., Shen, D.: Predicting clinical scores using semi-supervised multimodal relevance vector regression. In: Suzuki, K., Wang, F., Shen, D., Yan, P. (eds.) MLMI 2011. LNCS, vol. 7009, pp. 241–248. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24319-6_30
Chollet, F.: Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: CVPR. IEEE, Piscataway (2016)
Chyzhykand, D., Grana, M., Savio, A., Maiora, J.: Hybrid dendritic computing with kernel-LICA applied to Alzheimer’s disease detection in MRI. Neurocomputing 75(1), 72–77 (2012)
Cuingnet, R., Gerardin, E., Tessieras, J.: Automatic classification of patients with Alzheimer’s disease from structural MRI: a comparison of ten methods using the ADNI database. Neuroimage 56(2), 766–781 (2011)
Frisoni, G.B., Fox, N.C., Jack, C.R., Scheltens, P., Thompson, P.M.: The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 6(2), 67–77 (2010)
Gupta, A., Ayhan, M., Maida, A.: Natural image bases to represent neuroimaging data. In: ICML 2013, USA, pp. 987–994 (2013)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778. IEEE, Piscataway (2016)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: CVPR, pp. 7132–7141. IEEE, Piscataway (2018)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Laurens, M.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: CVPR, pp. 4700–4708. IEEE, Piscataway (2017)
Itti, L., Koch, C., Niebur, E.: A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE TPAMI 20(11), 1254–1259 (1998)
Itti, L., Koch, C.: Computational modelling of visual attention. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2(3), 194–203 (2001)
Ji, H., Liu, Z., Yan, W., Klette, R.: Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using deep learning. In: ICCCV, Korea (2019)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS (2012)
Larochelle, H., Hinton, G.: Learning to combine foveal glimpses with a third-order Boltzmann machine. In: NIPS (2010)
Lecun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., et al.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Li, X., Wang, W., Hu, X., Yang, J.: Selective kernel networks. In: CVPR, pp. 510–519. IEEE, Piscataway (2019)
Lian, C., Liu, M., Zhang, J., Shen, D.: Hierarchical fully convolution network for joint atrophy localization and Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using structural MRI. IEEE Trans. PAMI 12, 1–14 (2018)
Litjens, G., Kooi, T., Bejnordi, B., Setio, A., Ciompi, F., Ghafoorian, M.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017)
Liu, F., Wee, C., Chen, H., Shen, D.: Inter-modality relationship constrained multi-modality multi-task feature selection for Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment identification. NeuroImage 84, 466–475 (2014)
Liu, M., Zhang, D., Chen, S., Xue, H.: Joint binary classifier learning for ECOC-based multi-class classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(11), 2335–2341 (2016)
Liu, M., Zhang, D., Shen, D.: View-centralized multi-atlas classification for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 36(5), 1847–1865 (2015)
Liu, Z., Xu, T., Ma, C., Yang, H.: T-test based Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis with multi-feature in MRIs. Multimedia Tools Appl. 77(22), 29687–29703 (2018)
Lu, J., Yan, W., Nguyen, M.: Human behaviour recognition using deep learning. In: AVSS (2018)
Mnih, V., Heess, N., Graves, A.: Recurrent models of visual attention. In: NIPS (2014)
Ortiz, A., Munilla, J., Gorriz, M.: Ensembles of deep learning architectures for the early diagnosis of the Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Neural Syst. 26(7), 1650025 (2016)
Ortiz, A., Munilla, J., Martínez-Murcia, F.J., Górriz, J.M., Ramírez, J.: Learning longitudinal MRI patterns by SICE and deep learning: assessing the Alzheimer’s disease progression. In: Valdés Hernández, M., González-Castro, V. (eds.) MIUA 2017. CCIS, vol. 723, pp. 413–424. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-60964-5_36
Rathore, S., Habes, M., Iftikhar, M.A., Shacklett, A., Davatzikos, C.: A review on neuroimaging-based classification studies and associated feature extraction methods for Alzheimer’s disease and its prodromal stages. NeuroImage 155, 530–548 (2017)
Sarraf, S., Tofighi, G.: Deep learning-based pipeline to recognize Alzheimer’s disease using fMRI data. In: Future Technologies Conference, pp. 816–820. IEEE, San Francisco (2016)
Shen, D., Davatzikos, C.: HAMMER: hierarchical attribute matching mechanism for elastic registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 21(11), 1421–1439 (2002)
Spillmann, L., Dresp-Langley, B., Tseng, C.: Beyond the classical receptive field: the effect of contextual stimuli. J. Vis. 15(9), 7 (2015)
Suk, H., Lee, S., Shen, D.: Deep sparse multi-task learning for feature selection in Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Brain Struct. Funct. 221(15), 2569–2587 (2016)
Suk, H., Lee, S., Shen, D.: Deep ensemble learning of sparse regression models for brain disease diagnosis. Med. Image Anal. 37, 101–113 (2017)
Szegedy, C., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: CVPR, pp. 1–9. IEEE, Piscataway (2015)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: CVPR, pp. 2818–2826. IEEE, Piscataway (2016)
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V.: Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: AAAI, San Francisco (2017)
Wang, F., et al.: Residual attention network for image classification. In: CVPR, pp. 3156–3164. IEEE, Piscataway (2017)
Xie, S., Girshick, R., Dollar, P., Tu, Z., He, K.: Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: CVPR, pp. 1492–1500. IEEE, Piscataway (2017)
You, Q., Jin, H., Wang, Z., Fang, C., Luo, J.: Image captioning with semantic attention. In: CVPR, pp. 4651–4659. IEEE, USA (2016)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the study abroad program for graduate student of the Guilin University of Electronic Technology China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants (61866009). The data used in this paper was downloaded from Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (adni.loni.usc.edu). We are grateful to everyone who provided their support for this research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ji, H., Liu, Z., Yan, W.Q., Klette, R. (2020). Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Selective Kernel Network with Spatial Attention. In: Palaiahnakote, S., Sanniti di Baja, G., Wang, L., Yan, W. (eds) Pattern Recognition. ACPR 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12047. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41299-9_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41299-9_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-41298-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-41299-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)