Abstract
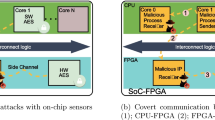
Thanks to their performance and flexibility, FPGAs are increasingly adopted for hardware acceleration on various platforms such as system on chip and cloud datacenters. Their use for commercial and industrial purposes raises concern about potential hardware security threats. By getting access to the FPGA fabric, an attacker could implement malicious logic to perform remote hardware attacks. Recently, several papers demonstrated that FPGA can be used to eavesdrop or disturb the activity of resources located within and outside the chip. In a complex SoC that contains a processor and a FPGA within the same die, we experimentally demonstrate that FPGA-based voltage sensors can eavesdrop computations running on the CPU and that advanced side-channel attacks can be conducted remotely to retrieve the secret key of a symmetric crypto-algorithm.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang, A., Sethumadhavan, S., Stolfo, S.: CLKSCREW: exposing the perils of security-oblivious energy management. In: 26th USENIX Security Symposium (2017)
Kim, Y., et al.: Flipping bits in memory without accessing them. ACM SIGARCH 42(3), 361–372 (2014)
Kocher, P., et al.: Spectre attacks: exploiting speculative execution, January 2018
Lipp, M., et al.: Meltdown. CoRR, abs/1801.0, January 2018
Van Bulck, J., et al.: FORESHADOW: extracting the keys to the intel SGX kingdom with transient out-of-order execution. In: USENIX Security Symposium (2018)
Pellerin, D.: FPGA accelerated computing using AWS F1 instances (2017)
Alibaba Cloud ECS: Deep Dive into Alibaba Cloud F3 FPGA as a Service Instances (2018)
Schellenberg, F., Gnad, D.R.E., Moradi, A., Tahoori, M.B.: An inside job: remote power analysis attacks on FPGAs. In: Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition. IEEE (2018)
Krautter, J., Gnad, D.R.E., Tahoori, M.B.: FPGAhammer : remote voltage fault attacks on shared FPGAs, suitable for DFA on AES. IACR Trans. Cryptograph. Hardware Embed. Syst. 14, 44–68 (2018)
Chen, F., et al.: Enabling FPGAs in the cloud. In: ACM Computing Frontiers (2014)
Gnad, D.R.E., Oboril, F., Tahoori, M.B.: Voltage drop-based fault attacks on FPGAs using valid bitstreams. In: 2017 27th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, FPL 2017 (2017)
Zhao, M., Suh, G.E.: FPGA-based remote power side-channel attacks. In: IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (2018)
Kocher, P.C.: Timing attacks on implementations of Diffie-Hellman, RSA, DSS, and other systems. In: CRYPTO 1996 (1996)
Kocher, P., Jaffe, J., Jun, B.: Differential power analysis. In: Wiener, M. (ed.) CRYPTO 1999. LNCS, vol. 1666, pp. 388–397. Springer, Heidelberg (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-48405-1_25
Brier, E., Clavier, C., Olivier, F.: Correlation power analysis with a leakage model. In: Joye, M., Quisquater, J.-J. (eds.) CHES 2004. LNCS, vol. 3156, pp. 16–29. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28632-5_2
Dutertre, J.-M., Robisson, B., Tria, A., Zussa, L.: Investigation of timing constraints violation as a fault injection means. In: Design of Circuits and Integrated Systems (2012)
Zick, K.M., Hayes, J.P.: Low-cost sensing with ring oscillator arrays for healthier reconfigurable systems. ACM Trans. Reconfigurable Technol. Syst. 5(1), 1–26 (2012)
Gnad, D.R.E., Oboril, F., Kiamehr, S., Tahoori, M.B.: An experimental evaluation and analysis of transient voltage fluctuations in FPGAs. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 26(10), 1817–1830 (2018)
Schellenberg, F., Gnad, D.R.E., Moradi, A., Tahoori, M.B.: Remote inter-chip power analysis side-channel attacks at board-level. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (2018)
Ueno, M., Hashimoto, M., Onoye, T.: Real-time on-chip supply voltage sensor and its application to trace-based timing error localization. In: International On-Line Testing Symposium (IOLTS). IEEE, July 2015
Zick, K.M., Srivastav, M., Zhang, W., French, M.: Sensing nanosecond-scale voltage attacks and natural transients in FPGAs. In: ACM/SIGDA (2013)
Kokke: Tiny AES in C (2018)
OpenSSL: OpenSSL AES (2002)
Mestiri, H., Benhadjyoussef, N., Machhout, M., Tourki, R.: A comparative study of power consumption models for CPA attack. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Inf. Secur. 5(3), 25 (2013)
Daemen, J., Rijmen, V.: The Rijndael Block Cipher (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gravellier, J., Dutertre, JM., Teglia, Y., Moundi, P.L., Olivier, F. (2020). Remote Side-Channel Attacks on Heterogeneous SoC. In: Belaïd, S., Güneysu, T. (eds) Smart Card Research and Advanced Applications. CARDIS 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11833. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42068-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42068-0_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-42067-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-42068-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)