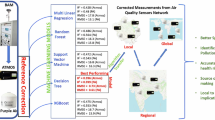
Abstract
The use of low-cost Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) for air quality monitoring has recently attracted a great deal of interest. Indeed, the cost-effectiveness of emerging sensors and their small size allow for dense deployments and hence improve the spatial granularity. However, these sensors offer a low accuracy and their measurement errors may be significant due to the underlying sensing technologies. The main aim of this work is to reconsider and compare some regression approaches to assimilation ones while taking into account the intrinsic characteristics of dense deployment of low-cost WSN for air quality monitoring (high density, numerical model errors and sensing errors). For that, we propose a general framework that allows the comparison of different strategies based on numerical simulations and adequate estimation of the simulation error covariances as well as the sensing errors covariances. While considering the case of Lyon city and a widely used numerical model, we characterize the simulation errors, conduct extensive simulations and compare several regression and assimilation approaches. The results show that from a given sensing error threshold, regression methods present an optimal sensor density from which the mapping quality decreases. Results also show that the Random Forest method is often the best regression approach but still less efficient than the BLUE assimilation approach when using adequate correction parameters.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization: Burden of disease from the joint effects of household and ambient air pollution for 2016 (2018). https://www.who.int/airpollution/data/AP_joint_effect_BoD_results_May2018.pdf
Kumar, P., Morawska, L., Martani, C., Biskos, G., Neophytou, M., Di Sabatino, S., Bell, M., Norford, L., Britter, R.: The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ. Int. 75, 199–205 (2015)
Schneider, P., Castell, N., Dauge, F.R., Vogt, M., Lahoz, W.A., Bartonova, A.: A network of low-cost air quality sensors and its use for mapping urban air quality. In: Mobile Information Systems Leveraging Volunteered Geographic Information for Earth Observation, pp. 93–110. Springer (2018)
Arroyo, P., Herrero, J.L., Suárez, J.I., Lozano, J.: Wireless sensor network combined with cloud computing for air quality monitoring. Sensors 19(3), 691 (2019)
Hasenfratz, D., Saukh, O., Walser, C., Hueglin, C., Fierz, M., Arn, T., Beutel, J., Thiele, L.: Deriving high-resolution urban air pollution maps using mobile sensor nodes. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 16, 268–285 (2015)
Anjomshoaa, A., Duarte, F., Rennings, D., Matarazzo, T.J., de Souza, P., Ratti, C.: City scanner: building and scheduling a mobile sensing platform for smart city services. IEEE Internet Things J. 5(6), 4567–4579 (2018)
Gerboles, M., Borowiak, A., Spinelle, L.: Measuring Air Pollution with Low-Cost Sensors. European Commission, Brochure (2017)
Boubrima, A., Bechkit, W., Rivano, H.: Optimal WSN deployment models for air pollution monitoring. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 16(5), 2723–2735 (2017)
Boubrima, A., Bechkit, W., Hervé, R.: On the deployment of wireless sensor networks for air quality mapping: optimization models and algorithms. IEEE Trans. Networking 27, 1629–1642 (2019)
Soulhac, L., Salizzoni, P., Cierco, F.-X., Perkins, R.: The model sirane for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion; Part I, presentation of the model. Atmos. Environ. 45(39), 7379–7395 (2011)
Soulhac, L., Salizzoni, P., Mejean, P., Didier, D., Rios, I.: The model sirane for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion; Part II, validation of the model on a real case study. Atmos. Environ. 49, 320–337 (2012)
Soulhac, L., Nguyen, C.V., Volta, P., Salizzoni, P.: The model sirane for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion, Part III: validation against NO2 yearly concentration measurements in a large urban agglomeration. Atmos. Environ. 167, 377–388 (2017)
Kerckhoffs, J., Wang, M., Meliefste, K., Malmqvist, E., Fischer, P., Janssen, N.A., Beelen, R., Hoek, G.: A national fine spatial scale land-use regression model for ozone. Environ. Res. 140, 440–448 (2015)
Marjovi, A., Arfire, A., Martinoli, A.: Extending urban air quality maps beyond the coverage of a mobile sensor network: data sources, methods, and performance evaluation. In: EWSN (2017)
Adam-Poupart, A., Brand, A., Fournier, M., Jerrett, M., Smargiassi, A.: Spatiotemporal modeling of ozone levels in Quebec (Canada): a comparison of kriging, land-use regression (LUR), and combined bayesian maximum entropy-lur approaches. Environ. Health Perspect. 122(9), 970–976 (2014)
Bocquet, M., Elbern, H., Eskes, H., Hirtl, M., Žabkar, R., Carmichael, G., Flemming, J., Inness, A., Pagowski, M., Pérez Camaño, J., et al.: Data assimilation in atmospheric chemistry models: current status and future prospects for coupled chemistry meteorology models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 15(10), 5325–5358 (2015)
Tilloy, A., Mallet, V., Poulet, D., Pesin, C., Brocheton, F.: Blue-based no 2 data assimilation at urban scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118(4), 2031–2040 (2013)
Kumar, U., De Ridder, K., Lefebvre, W., Janssen, S.: Data assimilation of surface air pollutants (O3 and NO2) in the regional-scale air quality model aurora. Atmos. Environ. 60, 99–108 (2012)
Wang, X., Mallet, V., Berroir, J.-P., Herlin, I.: Assimilation of OMI NO2 retrievals into a regional chemistry-transport model for improving air quality forecasts over europe. Atmos. Environ. 45(2), 485–492 (2011)
Xie, X., Semanjski, I., Gautama, S., Tsiligianni, E., Deligiannis, N., Rajan, R., Pasveer, F., Philips, W.: A review of urban air pollution monitoring and exposure assessment methods. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inform. 6(12), 389 (2017)
Jerrett, M., Arain, M., Kanaroglou, P., Beckerman, B., Crouse, D., Gilbert, N., Brook, J., Finkelstein, N., Finkelstein, M.: Modeling the intra-urban variability of ambient traffic pollution in Toronto, Canada. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 70(3–4), 200–212 (2007)
Chen, T., He, T., Benesty, M., Khotilovich, V., Tang, Y.: Xgboost: extreme gradient boosting. R package version 0.4-2, pp. 1–4 (2015)
Biau, G.: Analysis of a random forests model. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13, 1063–1095 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the “LABEX IMU” (ANR-10-LABX-0088) of Université de Lyon, within the program “Investissements d’Avenir” (ANR-11-IDEX-0007) operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fekih, M.A., Mokhtari, I., Bechkit, W., Belbaki, Y., Rivano, H. (2020). On the Regression and Assimilation for Air Quality Mapping Using Dense Low-Cost WSN. In: Barolli, L., Amato, F., Moscato, F., Enokido, T., Takizawa, M. (eds) Advanced Information Networking and Applications. AINA 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1151. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44041-1_51
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44041-1_51
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-44040-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-44041-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)