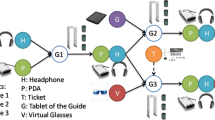
Abstract
This paper focuses first on the formal modeling of complex application scenarios using autonomic proximity-based federation among smart objects with wireless network connectivity, and then on a new framework for complex secure federation scenarios. Our modeling consists of three different levels. In the first-level modeling, each smart object is modeled as a set of ports, each of which represents an I/O interface for a function of this smart object to interoperate with some function of another smart object. The federation between a pair of smart objects having a pair of ports of the same type with opposite polarities is modeled as the port matching between these two ports. The second-level modeling describes the dynamic change of the federation structure among smart objects as a graph rewriting system, where each node and each directed link respectively represent a smart object and a connection between two smart objects. The third-level modeling uses a binary autocatalytic-reaction network to describe each complex federation scenario in which more than one federation are involved, and an output federation of a reaction may work either as an input federation of another reaction and/or a catalyst to activate another composition or decomposition reaction. Based on these models previously proposed by the current author, this paper proposes a new simplified application framework for implementing any complex application scenario describable as a binary autocatalytic-reaction network as a graph rewriting system of smart objects, and then proposes a new framework-level solution to the secure federation of smart objects, which is independent from the encryption-based technologies for secure communication between two smart objects.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Milner, R.: Theories for the global ubiquitous computer. In: Walukiewicz, I. (ed.) FoSSaCS 2004. LNCS, vol. 2987, pp. 5–11. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24727-2_2
Henricksen, K., Indulska, J., Rakotonirainy, A.: Modeling context information in pervasive computing systems. In: Mattern, F., Naghshineh, M. (eds.) Pervasive 2002. LNCS, vol. 2414, pp. 167–180. Springer, Heidelberg (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45866-2_14
Tanaka, Y.: Proximity-based federation of smart objects: liberating ubiquitous computing from stereotyped application scenarios. In: Setchi, R., Jordanov, I., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C. (eds.) KES 2010. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6276, pp. 14–30. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15387-7_6
Julia, J., Tanaka, Y.: Proximity-based federation of smart objects: its graph-rewriting framework and correctness. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 46(1), 147–178 (2016)
Tanaka, Y.: Proximity-based federation of smart objects and their application framework. In: Kyung, C.-M., Yasuura, H., Liu, Y., Lin, Y.-L. (eds.) Smart Sensors and Systems, pp. 411–439. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-33201-7_15
Edwards, W.K., Joy, B., Murphy, B.: Core JINI. Prentice Hall Professional Technical Reference, Upper Saddle River (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tanaka, Y. (2020). Proximity-Based Federation of Smart Objects: Its Application Framework for Complex Secure Federation Scenarios. In: Flouris, G., Laurent, D., Plexousakis, D., Spyratos, N., Tanaka, Y. (eds) Information Search, Integration, and Personalization. ISIP 2019. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1197. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44900-1_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44900-1_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-44899-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-44900-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)