Abstract
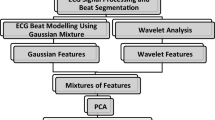
In this work, we are focusing on the problem of heartbeat classification in electrocardiogram (ECG) signals. First we develop a patient-specific feature extraction scheme by using adaptive orthogonal transformations based on wavelets, B-splines, Hermite and rational functions. The so-called variable projection provides the general framework to find the optimal nonlinear parameters of these transformations. After extracting the features, we train a support vector machine (SVM) for each model whose outputs are combined via ensemble learning techniques. In the experiments, we achieved an accuracy of \(94.2\%\) on the PhysioNet MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database that shows the potential of the proposed signal models in arrhythmia detection.
EFOP-3.6.3-VEKOP-16-2017-00001: Talent Management in Autonomous Vehicle Control Technologies – The Project is supported by the Hungarian Government and co-financed by the European Social Fund.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Testing and Reporting Performance Results of Cardiac Rhythm and ST-Segment Measurement Algorithms. American National Standard, ANSI/AAMI/ISO EC57. 1998-(R) (2008)
Goldberger, A.L., et al.: PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101, 215–220 (2000)
Moody, G.B., Mark, R.G.: The impact of the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 20, 45–50 (2001)
Gabbouj, M., Karczewicz, M.: ECG data compression by spline approximation. Signal Process. 59, 43–59 (1997)
Kovács, P., Fekete, A.M.: Nonlinear least-squares spline fitting with variable knots. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019(354), 490–501 (2019)
Dózsa, T., Kovács, P.: ECG signal compression using adaptive hermite functions. In: Loshkovska, S., Koceski, S. (eds.) ICT Innovations 2015. AISC, vol. 399, pp. 245–254. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25733-4_25
Fridli, S., Lócsi, L., Schipp, F.: Rational function systems in ECG processing. In: Moreno-Díaz, R., Pichler, F., Quesada-Arencibia, A. (eds.) EUROCAST 2011. LNCS, vol. 6927, pp. 88–95. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27549-4_12
Fridli, S., Kovács, P., Lócsi, L., Schipp, F.: Rational modeling of multi-lead QRS complexes in ECG signals. Ann. Univ. Sci. Budapest Sect. Comp. 37, 145–155 (2012)
Bognár, G., Fridli, S.: Heartbeat classification of ECG signals using rational function systems. In: Moreno-Díaz, R., Pichler, F., Quesada-Arencibia, A. (eds.) EUROCAST 2017. LNCS, vol. 10672, pp. 187–195. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74727-9_22
Golub, G.H., Pereyra, V.: The differentiation of pseudo-inverses and nonlinear least squares problems whose variables separate. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 10, 413–432 (1973)
Ye, C., Kumar, B.V.K.V., Coimbra, M.T.: Heartbeat classification using morphological and dynamic features of ECG signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59, 2930–2941 (2012)
de Chazal, P., O’Dwyer, M., Reilly, B.R.: Automatic classification of heartbeats using ECG morphology and heartbeat interval features. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51, 1196–1206 (2004)
Szegő, G.: Orthogonal Polynomials, 3rd edn. AMS Colloquium Publications, New York (1967)
Hsu, C.-W., Chang, C.-C., Lin, C.-J.: A Practical Guide to Support Vector Machine Classification. National Taiwan University, pp. 1–16 (2016)
Llamendo, M., Khawaja, A., Martínez, J.P.: Cross-database evaluation of a multilead heartbeat classifier. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 16, 658–664 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dózsa, T., Bognár, G., Kovács, P. (2020). Ensemble Learning for Heartbeat Classification Using Adaptive Orthogonal Transformations. In: Moreno-Díaz, R., Pichler, F., Quesada-Arencibia, A. (eds) Computer Aided Systems Theory – EUROCAST 2019. EUROCAST 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12014. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45096-0_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45096-0_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-45095-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-45096-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)