Abstract
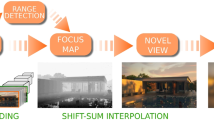
With increasing popularity holographic method, 3D scene and augmented reality, needless to say, that 3D holography would be playing the most important role of real-time recording display. This paper demonstrates a setup that shows and records the scene in a real-time 3D appearance. We speed up the holographic processing by using a hardware accelerator to take advantage of its parallel specificities (architecture). The results clarify the system’s ability for viewing the holographic objects by applying four cameras running at the same time with a difference in partial of millisecond attributed to reason the clock of cameras and the VGA update.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, X., Chen, C.P., Li, Y., Zhou, P., Jiang, X., Rong, N., Liu, S., He, G., Lu, J., Su, Y.: High-efficiency video-rate holographic display using quantum dot doped liquid crystal. J. Disp. Technol. 12(4), 362–367 (2016)
Zhang, Z., Chen, C.P., Li, Y., Yu, B., Zhou, L., Wu, Y.: Angular multiplexing of holographic display using tunable multi-stage gratings. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. (Phila. Pa.) 657(1), 102–106 (2017)
Lippmann, G.: Epreuves reversibles photographies integrals. C. R. Acad. Sci. 146, 446–451 (1908)
Yang, R., Huang, X., Li, S., Jaynes, C.: Toward the light field display: autostereoscopic rendering via a cluster of projectors. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 14(1), 84–96 (2008)
Johnson, P.V., Parnell, J.A., Kim, J., Saunter, C.D., Love, G.D., Banks, M.S.: Dynamic lens and monovision 3D displays to improve viewer comfort. Opt. Express 24(11), 11808–11827 (2016)
Lee, S., Park, J., Heo, J., Kang, B., Kang, D., Hwang, H., Lee, J., Choi, Y., Choi, K., Nam, D.: Autostereoscopic 3D display using directional subpixel rendering. Opt. Express 26(16), 20233 (2018)
Hilaire, P.S., Benton, S.A., Lucente, M., Jepsen, M.L., Kollin, J., Yoshikawa, H., Underkoffler, J.: Electronic display system for computational holography. Proc. SPIE 1212, 174–182 (1990)
Masuda, N., Ito, T., Tanaka, T., Shiraki, A., Sugie, T.: Computer generated holography using a graphics processing unit. Opt. Express 14(2), 603–608 (2006)
Hahn, J., Kim, H., Lim, Y., Park, G., Lee, B.: Wide viewing angle dynamic holographic stereogram with a curved array of spatial light modulators. Opt. Express 16(16), 12372–12386 (2008)
Xue, G., Liu, J., Li, X., Jia, J., Zhang, Z., Hu, B., Wang, Y.: Multiplexing encoding method for full-color dynamic 3D holographic display. Opt. Express 22(15), 18473–18482 (2014)
Kang, H., Ahn, C., Lee, S., Lee, S.: Computer-generated 3D holograms of depth-annotated images. Proc. SPIE 5742, 234–241 (2005)
Kakue, T., Wagatsuma, Y., Yamada, S., Nishitsuji, T., Endo, Y., Nagahama, Y., Hirayama, R., Shimobaba, T., Ito, T.: Review of real-time reconstruction techniques for aerial-projection holographic displays. Opt. Eng. 57(06), 1 (2018)
Mishina, T., Okui, M., Okano, F.: Calculation of holograms from elemental images captured by integral photography. Appl. Opt. 45(17), 4026–4036 (2006)
Chang, E.Y., Choi, J., Lee, S., Kwon, S., Yoo, J., Park, M., Kim, J.: 360-degree color hologram generation for real 3D objects. Appl. Opt. 57(1), A91–A100 (2018)
Zhao, Y., Kwon, K.C., Erdenebat, M.U., Islam, M.S., Jeon, S.H., Kim, N.: Quality enhancement and GPU acceleration for a full-color holographic system using a relocated point cloud gridding method. Appl. Opt. 57(15), 4253–4262 (2018)
Zhao, Y., Piao, Y., Park, S., Lee, K., Kim, N.: Fast calculation method for full-color computer-generated hologram of real objects captured by depth camera. Electron. Imaging 2018(4), 250–251 (2018)
Zhao, Y., Shi, C., Kwon, K., Piao, Y., Piao, M., Kim, N.: Fast calculation method of computer-generated hologram using a depth camera with point cloud gridding. Opt. Commun. 411, 166–169 (2018)
Ichihashi, Y., Oi, R., Senoh, T., Yamamoto, K., Kurita, T.: Real-time capture and reconstruction system. Opt. Express 20(19), 21645–21655 (2012)
Yamaguchi, M.: Light-field and holographic three-dimensional displays [Invited]. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 33(12), 2348–2364 (2016)
Wakunami, K., Yamashita, H., Yamaguchi, M.: Occlusion culling for computer generated hologram based on ray-wavefront conversion. Opt. Express 21(19), 21811–21822 (2013)
Wakunami, K., Yamaguchi, M.: Calculation for computer generated hologram using ray-sampling plane. Opt. Express 19(10), 9086–9101 (2011)
Igarashi, S., Nakamura, T., Matsushima, K., Yamaguchi, M.: Efficient tiled calculation of over-10-gigapixel holograms using ray-wavefront conversion. Opt. Express 26(8), 10773–10786 (2018)
Heikklä, M., Pietikäinen, M.: A texture-based method for modeling the background and detecting moving objects. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(4), 657–662 (2006)
Al-Shamma, O., Fadhel, M., Hameed, R., Alzubaidi, L., Zhang, J.: Boosting convolutional neural networks performance based on FPGA accelerator. In: International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, pp. 509–517. Springer, Cham (2018)
Fadhel, M., Al-Shamma, O., Oleiwi, S., Taher, B., Alzubaidi, L.: Real-time PCG diagnosis using FPGA. In: International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, pp. 518–529. Springer, Cham (2018)
Al-Shamma, O., Fadhel, M.A., Hasan, H.S.: Employing FPGA accelerator in real-time speaker identification systems. In: Recent Trends in Signal and Image Processing, pp. 125–134. Springer, Singapore (2019)
OV7670, CMOS VGA. CAMERACHIPTM Sensor Datasheet, OmniVision. http://www.cutedigi.com/pub/sensor/Imaging.OV7670-Datasheet.pdf
Board, DE1-SoC. Terasic (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fadhel, M.A., Al-Shamma, O., Alzubaidi, L. (2021). Hardware Accelerator for Real-Time Holographic Projector. In: Abraham, A., Siarry, P., Ma, K., Kaklauskas, A. (eds) Intelligent Systems Design and Applications. ISDA 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1181. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49342-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49342-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-49341-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-49342-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)