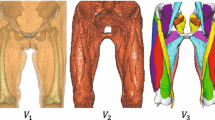
Abstract
Due to a steady increase of total hip arthroplasty, biomechanical multibody simulations are moving more and more into focus. These simulations allow to calculate forces, moments and muscle activities in the human body and, thus, can help to improve surgery planning and outcomes. However, generic human body models based on anthropometric data are mostly used for these simulations. Since these models are not customized to patients, there is a need to adapt the models to the individual patient. Therefore, 3D models of bones are created by segmentation of CT and MRI scans and assigned different landmarks. This allows to define both, the shape and size of bones, in this case the femur, which leads to patient-specific adjustments of muscle attachment points. Also muscles can be segmented to determine important parameters such as muscle volume, allowing the definition of important simulation parameters, like the maximum isometric force or the tendon slack length of individual patients leading to customized models.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eingartner, C.: Current trends in total hip arthroplasty. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 9(1), 8–14 (2007)
Pabinger, C., Lothaller, H., Geissler, A.: Utilization rates of knee-arthroplasty in OECD countries. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 23(10), 1664–1673 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 May 29
Singh, J.A.: Epidemiology of knee and hip arthroplasty: a systematic review. Open Orthop. J. 5, 80 (2011)
Learmonth, I.D., Young, C., Rorabeck, C.: The operation of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet 370(9597), 1508–1519 (2007)
Sesselmann, S., Miehling, J., Wartzack, S., Forst, R.: Enhancement of surgical planning through patient-specific biomechanical modeling and simulation. In: SICOT Orthopaedic World Congress – Rome (2016)
Scherb, D., Fleischmann, C.: Conceptual approach to estimate the musculoskeletal follow-ups of endoprosthetic hip replacements. In: CAMS-Knee OpenSim Workshop – Zürich (2020)
Sesselmann, S., Reinmuth, M., Tiefenböck, S., Strödick, N., Forst, R.: Retrospektiver Vergleich der Ergebnisse präoperativer Planung in der Hüftendoprothetik mittels 2D-bzw. 3D-Software – DKOU – Berlin (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fleischmann, C. et al. (2021). Segmentation of Musculotendinous Structures of the Hip from 3D Imaging for Patient-Specific Individualization of Biomechanical Simulations. In: Ahram, T., Taiar, R., Langlois, K., Choplin, A. (eds) Human Interaction, Emerging Technologies and Future Applications III. IHIET 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1253. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-55307-4_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-55307-4_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-55306-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-55307-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)