Abstract
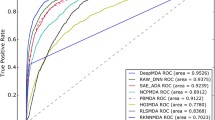
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs of approximately 22 nucleotides. Cumulative evidence from biological experiments has confirmed that miRNAs play a key role in many complex human diseases. Therefore, the accurate identification of potential associations between miRNAs and diseases is beneficial to understanding the mechanisms of diseases, developing drugs and treating complex diseases. We propose a new method to predict miRNA-disease associations based on a negative sample selection strategy and multi-layer perceptron (called NMLPMDA). For obtaining more similarity information, NMLPMDA integrates the miRNA functional similarity and the Gaussian interaction profile (GIP) kernel similarity of miRNAs as the final miRNA similarity, and integrates the disease semantic similarity and the GIP kernel similarity of diseases as the final disease similarity. In particular, we propose a negative sample selection strategy based on common gene information to select more reliable negative samples from unknown miRNA-disease associations. The 5-fold cross validation is used to evaluate the performance of NMLPMDA and other competing methods. On four datasets (HMDD2.0-Yan, HMDD2.0-Lan, HMDD2.0-You, HMDD3.0), the AUC values of NMLPMDA are 0.9278, 0.9206, 0.9301 and 0.9350, respectively. In addition, we also illustrate the prediction ability of NMLPMDA in Lymphoma. As a result, 28 of the top 30 miRNAs associated with the disease have been validated experimentally in dbDEMC and previous studies, respectively. These experimental results indicate that NMLPMDA is a reliable model for predicting associations between miRNAs and diseases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao, P., Wong, C.C.L., Tung, E.K.K., Lee, J.M.F., Wong, C.M., Ng, I.O.L.: Deregulation of microrna expression occurs early and accumulates in early stages of hbv-associated multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 54(6), 1177–1184 (2011)
You, Z.H., et al.: PBMDA: a novel and effective path-based computational model for mirna-disease association prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13(3), e1005455 (2017)
Lan, W., Wang, J., Li, M., Liu, J., Wu, F.X., Pan, Y.: Predicting microRNA-disease associations based on improved microRNA and disease similarities. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 15(6), 1774–1782 (2018)
Yan, C., Wang, J., Ni, P., Lan, W., Wu, F.X., Pan, Y.: DNRLMF-MDA: predicting microrna-disease associations based on similarities of micrornas and diseases. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 16(1), 233–243 (2017)
Giardine, B., et al.: Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res. 15(10), 1451–1455 (2005)
Zhao, Y., Chen, X., Yin, J.: Adaptive boosting-based computational model for predicting potential mirna-disease associations. Bioinformatics 35(22), 4730–4738 (2019)
Chen, X., Huang, L., Xie, D., Zhao, Q.: EGBMMDA: extreme gradient boosting machine for mirna-disease association prediction. Cell Death Dis. 9(1), 3 (2018)
Li, Y., et al.: HMDD v2.0: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(D1), D1070–D1074 (2013)
Huang, Z., et al.: HMDD v3.0: a database for experimentally supported human microrna-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1), D1013–D1017 (2018)
Pinero, J., et al.: DisGeNET: a discovery platform for the dynamical exploration of human diseases and their genes. Database 2015, bav028 (2015)
Hsu, S.D., et al.: Mirtarbase: a database curates experimentally validated microrna-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 39((suppl–1)), D163–D169 (2010)
Wang, D., Wang, J., Lu, M., Song, F., Cui, Q.: Inferring the human microrna functional similarity and functional network based on microrna-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 26(13), 1644–1650 (2010)
van Laarhoven, T., Nabuurs, S.B., Marchiori, E.: Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug-target interaction. Bioinformatics 27(21), 3036–3043 (2011)
Yu, H., Chen, X., Lu, L.: Large-scale prediction of microrna-disease associations by combinatorial prioritization algorithm. Sci. Rep. 7, 43792 (2017)
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Jemal, A.: Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66(1), 7–30 (2016)
Leucci, E., et al.: Inhibition of mir-9 de-represses hur and dicer1 and impairs hodgkin lymphoma tumour outgrowth in vivo. Oncogene 31(49), 5081 (2012)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61772552, No. 61832019 and No. 61962050), 111 Project (No. B18059), Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Program (No. 2018WK4001), the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province of China under Grant NO. [2020]1Y264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, N., Duan, G., Yan, C., Wu, FX., Wang, J. (2020). MiRNA-Disease Associations Prediction Based on Negative Sample Selection and Multi-layer Perceptron. In: Cai, Z., Mandoiu, I., Narasimhan, G., Skums, P., Guo, X. (eds) Bioinformatics Research and Applications. ISBRA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12304. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57821-3_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57821-3_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-57820-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-57821-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)