Abstract
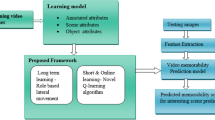
In this paper, we explore the problem of interesting scene prediction for mobile robots. This area is currently underexplored but is crucial for many practical applications such as autonomous exploration and decision making. Inspired by industrial demands, we first propose a novel translation-invariant visual memory for recalling and identifying interesting scenes, then design a three-stage architecture of long-term, short-term, and online learning. This enables our system to learn human-like experience, environmental knowledge, and online adaption, respectively. Our approach achieves much higher accuracy than the state-of-the-art algorithms on challenging robotic interestingness datasets.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Team Explorer won the first place at the DARPA SubT Tunnel Circuit.
- 2.
Real-time means processing images as fast as human brain, i.e., 100 ms/frame [31].
References
Abati, D., Porrello, A., Calderara, S., Cucchiara, R.: Latent space autoregression for novelty detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 481–490 (2019)
Amengual, X., Bosch, A., de la Rosa, J.L.: Review of methods to predict social image interestingness and memorability. In: Azzopardi, G., Petkov, N. (eds.) CAIP 2015. LNCS, vol. 9256, pp. 64–76. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23192-1_6
Brady, T.F., Konkle, T., Alvarez, G.A., Oliva, A.: Visual long-term memory has a massive storage capacity for object details. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105(38), 14325–14329 (2008)
Chaabouni, S., Benois-Pineau, J., Zemmari, A., Ben Amar, C.: Deep saliency: prediction of interestingness in video with CNN. In: Benois-Pineau, J., Le Callet, P. (eds.) Visual Content Indexing and Retrieval with Psycho-Visual Models. MSA, pp. 43–74. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57687-9_3
Constantin, M.G., Redi, M., Zen, G., Ionescu, B.: Computational understanding of visual interestingness beyond semantics: literature survey and analysis of covariates. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 52(2), 25 (2019)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2005), vol. 1, pp. 886–893. IEEE (2005)
Demarty, C.-H., et al.: Predicting interestingness of visual content. In: Benois-Pineau, J., Le Callet, P. (eds.) Visual Content Indexing and Retrieval with Psycho-Visual Models. MSA, pp. 233–265. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57687-9_10
Demarty, C.H., Sjöberg, M., Ionescu, B., Do, T.T., Gygli, M., Duong, N.: Mediaeval 2017 predicting media interestingness task (2017)
Dhar, S., Ordonez, V., Berg, T.L.: High level describable attributes for predicting aesthetics and interestingness. In: CVPR 2011, pp. 1657–1664. IEEE (2011)
Fu, Y., Hospedales, T.M., Xiang, T., Gong, S., Yao, Y.: Interestingness prediction by robust learning to rank. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8690, pp. 488–503. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10605-2_32
Fu, Y., et al.: Robust subjective visual property prediction from crowdsourced pairwise labels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(3), 563–577 (2015)
Gong, D., et al.: Memorizing normality to detect anomaly: memory-augmented deep autoencoder for unsupervised anomaly detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1705–1714 (2019)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep Learning. MIT Press, New York (2016)
Grabner, H., Nater, F., Druey, M., Van Gool, L.: Visual interestingness in image sequences. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1017–1026. ACM (2013)
Graves, A., Wayne, G., Danihelka, I.: Neural turing machines. arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.5401 (2014)
Gygli, M., Soleymani, M.: Analyzing and predicting gif interestingness. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 122–126. ACM (2016)
Hasan, M., Choi, J., Neumann, J., Roy-Chowdhury, A.K., Davis, L.S.: Learning temporal regularity in video sequences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 733–742 (2016)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Ito, Y., Kitani, K.M., Bagnell, J.A., Hebert, M.: Detecting interesting events using unsupervised density ratio estimation. In: Fusiello, A., Murino, V., Cucchiara, R. (eds.) ECCV 2012. LNCS, vol. 7585, pp. 151–161. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33885-4_16
Jiang, Y.G., Wang, Y., Feng, R., Xue, X., Zheng, Y., Yang, H.: Understanding and predicting interestingness of videos. In: Twenty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2013)
Kim, Y., Kim, M., Kim, G.: Memorization precedes generation: learning unsupervised GANs with memory networks. In: The International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) (2018)
Kramer, M.A.: Nonlinear principal component analysis using autoassociative neural networks. AIChE J. 37(2), 233–243 (1991)
Lin, T.-Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 740–755. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Liu, W., Luo, W., Lian, D., Gao, S.: Future frame prediction for anomaly detection-a new baseline. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6536–6545 (2018)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Luo, W., Liu, W., Gao, S.: A revisit of sparse coding based anomaly detection in stacked RNN framework. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 341–349 (2017)
Oßwald, S., Bennewitz, M., Burgard, W., Stachniss, C.: Speeding-up robot exploration by exploiting background information. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 1(2), 716–723 (2016)
Paszke, A., et al.: Automatic differentiation in PyTorch (2017)
Phillips, W.: On the distinction between sensory storage and short-term visual memory. Percept. Psychophys. 16(2), 283–290 (1974)
Potter, M.C., Levy, E.I.: Recognition memory for a rapid sequence of pictures. J. Exp. Psychol. 81(1), 10 (1969)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J., et al.: Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Cognit. Model. 5(3), 1 (1988)
Santoro, A., Bartunov, S., Botvinick, M., Wierstra, D., Lillicrap, T.: Meta-learning with memory-augmented neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1842–1850 (2016)
Shen, Y., Demarty, C.H., Duong, N.Q.: Deep learning for multimodal-based video interestingness prediction. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1003–1008. IEEE (2017)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: International Conference on Learning Research (2015)
Wang, C.: Kernel learning for visual perception. Ph.D. thesis, Nanyang Technological University (2019)
Wang, C., Yang, J., Xie, L., Yuan, J.: Kervolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 31–40 (2019)
Wang, C., Zhang, L., Xie, L., Yuan, J.: Kernel cross-correlator. In: Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2018)
Wang, S., Chen, S., Zhao, J., Jin, Q.: Video interestingness prediction based on ranking model. In: Proceedings of the Joint Workshop of the 4th Workshop on Affective Social Multimedia Computing and first Multi-Modal Affective Computing of Large-Scale Multimedia Data, pp. 55–61. ACM (2018)
Wang, W., Ahuja, A., Zhang, Y., Bonatti, R., Scherer, S.: Improved generalization of heading direction estimation for aerial filming using semi-supervised regression. In: 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5901–5907. IEEE (2019)
Zhang, P., Wang, D., Lu, H., Wang, H., Yin, B.: Learning uncertain convolutional features for accurate saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 212–221 (2017)
Zhao, B., Fei-Fei, L., Xing, E.P.: Online detection of unusual events in videos via dynamic sparse coding. In: CVPR 2011, pp. 3313–3320. IEEE (2011)
Zhao, Y., Deng, B., Shen, C., Liu, Y., Lu, H., Hua, X.S.: Spatio-temporal autoencoder for video anomaly detection. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1933–1941 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by ONR grant #N0014-19-1-2266. The human subject survey was approved under #2019_00000522.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, C., Wang, W., Qiu, Y., Hu, Y., Scherer, S. (2020). Visual Memorability for Robotic Interestingness via Unsupervised Online Learning. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, JM. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2020. ECCV 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12347. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58535-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58536-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)