Abstract
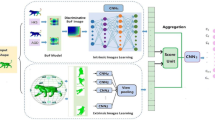
This paper proposes a novel method for 3D shape representation learning, namely Hyperbolic Embedded Attentive Representation (HEAR). Different from existing multi-view based methods, HEAR develops a unified framework to address both multi-view redundancy and single-view incompleteness. Specifically, HEAR firstly employs a hybrid attention (HA) module, which consists of a view-agnostic attention (VAA) block and a view-specific attention (VSA) block. These two blocks jointly explore distinct but complementary spatial saliency of local features for each single-view image. Subsequently, a multi-granular view pooling (MVP) module is introduced to aggregate the multi-view features with different granularities in a coarse-to-fine manner. The resulting feature set implicitly has hierarchical relations, which are therefore projected into a Hyperbolic space by adopting the Hyperbolic embedding. A hierarchical representation is learned by Hyperbolic multi-class logistic regression based on the Hyperbolic geometry. Experimental results clearly show that HEAR outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on three 3D shape recognition tasks including generic 3D shape retrieval, 3D shape classification and sketch-based 3D shape retrieval.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, S., Bai, X., Zhou, Z., Zhang, Z., Jan Latecki, L.: GIFT: a real-time and scalable 3D shape search engine. In: CVPR (2016)
Bai, S., Zhou, Z., Wang, J., Bai, X., Jan Latecki, L., Tian, Q.: Ensemble diffusion for retrieval. In: ICCV (2017)
Brock, A., Lim, T., Ritchie, J.M., Weston, N.: Generative and discriminative voxel modeling with convolutional neural networks. In: NeurIPS (2016)
Chami, I., Ying, Z., Ré, C., Leskovec, J.: Hyperbolic graph convolutional neural networks. In: NeurIPS (2019)
Chatfield, K., Simonyan, K., Vedaldi, A., Zisserman, A.: Return of the devil in the details: delving deep into convolutional nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1405.3531 (2014)
Chen, D.Y., Tian, X.P., Shen, Y.T., Ouhyoung, M.: On visual similarity based 3D model retrieval. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 22, pp. 223–232. Wiley Online Library (2003)
Chen, J., Fang, Y.: Deep cross-modality adaptation via semantics preserving adversarial learning for sketch-based 3D shape retrieval. In: ECCV (2018)
Chen, J., et al.: Deep sketch-shape hashing with segmented 3D stochastic viewing. In: CVPR (2019)
Dai, G., Xie, J., Fang, Y.: Deep correlated holistic metric learning for sketch-based 3D shape retrieval. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27, 3374–3386 (2018)
Dai, G., Xie, J., Fang, Y.: Siamese CNN-BiLSTM architecture for 3D shape representation learning. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2018, pp. 670–676 (2018)
Dai, G., Xie, J., Zhu, F., Fang, Y.: Deep correlated metric learning for sketch-based 3D shape retrieval. In: AAAI (2017)
Feng, Y., You, H., Zhang, Z., Ji, R., Gao, Y.: Hypergraph neural networks. In: AAAI (2019)
Feng, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhao, X., Ji, R., Gao, Y.: GVCNN: group-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition. In: CVPR (2018)
Feng, Y., Feng, Y., You, H., Zhao, X., Gao, Y.: MeshNet: mesh neural network for 3D shape representation. In: AAAI 2019 (2018)
Furuya, T., Ohbuchi, R.: Ranking on cross-domain manifold for sketch-based 3D model retrieval. In: International Conference on Cyberworlds (2013)
Furuya, T., Ohbuchi, R.: Deep aggregation of local 3D geometric features for 3D model retrieval. In: BMVC (2016)
Bécigneul, G., Ganea, O.E.: Riemannian adaptive optimization methods (2019)
Gabeur, V., Franco, J.S., Martin, X., Schmid, C., Rogez, G.: Moulding humans: non-parametric 3D human shape estimation from single images. In: The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
Gulcehre, C., et al.: Hyperbolic neural networks. In: NeurIPS (2018)
Gulcehre, C., et al.: Hyperbolic attention networks. In: ICLR (2019)
Han, Z., et al.: 3D2SeqViews: aggregating sequential views for 3D global feature learning by CNN with hierarchical attention aggregation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(8), 3986–3999 (2019)
Han, Z., et al.: SeqViews2SeqLabels: learning 3D global features via aggregating sequential views by RNN with attention. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(2), 658–672 (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
He, X., Huang, T., Bai, S., Bai, X.: View n-gram network for 3D object retrieval. In: ICCV (2019)
He, X., Zhou, Y., Zhou, Z., Bai, S., Bai, X.: Triplet-center loss for multi-view 3D object retrieval. In: CVPR (2018)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: CVPR (2018)
Johns, E., Leutenegger, S., Davision, A.J.: Pairwise decomposition of image sequences for active multiview recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Kanezaki, A., Matsushita, Y., Nishida, Y.: RotationNet: joint object categorization and pose estimation using multiviews from unsupervised viewpoints. In: CVPR (2018)
Kazhdan, M., Funkhouser, T., Rusinkiewicz, S.: Rotation invariant spherical harmonic representation of 3D shape descriptors. In: Symposium on Geometry Processing, vol. 6, pp. 156–164 (2003)
Khrulkov, V., Mirvakhabova, L., Ustinova, E., Oseledets, I., Lempitsky, V.: Hyperbolic image embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.02239 (2019)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: ICLR (2015)
Klokov, R., Lempitsky, V.: Escape from cells: deep Kd-networks for the recognition of 3D point cloud models. In: CVPR (2017)
Kolotouros, N., Pavlakos, G., Black, M.J., Daniilidis, K.: Learning to reconstruct 3D human pose and shape via model-fitting in the loop. In: The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
Kumawat, S., Raman, S.: LP-3DCNN: unveiling local phase in 3D convolutional neural networks. In: CVPR (2019)
Leng, B., Zhang, C., Zhou, X., Xu, C., Xu, K.: Learning discriminative 3D shape representations by view discerning networks. IEEE Trans. Visual. Comput. Graph. 25, 2896–2909 (2018)
Li, B., et al.: SHREC13 track: large scale sketch-based 3D shape retrieval (2013)
Li, B., et al.: A comparison of methods for sketch-based 3D shape retrieval. CVIU 119, 57–80 (2014)
Li, B., et al.: SHREC14 track: extended large scale sketch-based 3D shape retrieval. In: Eurographics Workshop on 3D Object Retrieval (2014)
Li, J., Chen, B., Hee, L.G.: SO-Net: self-organizing network for point cloud analysis. In: CVPR (2018)
Liu, Y., Fan, B., Meng, G., Lu, J., Xiang, S., Pan, C.: DensePoint: learning densely contextual representation for efficient point cloud processing. In: The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
Mao, J., Wang, X., Li, H.: Interpolated convolutional networks for 3D point cloud understanding. In: The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
Maturana, D., Scherer, S.: Multi-view harmonized bilinear network for 3D object recognition. In: IROS (2015)
Phong, B.T.: Illumination for computer generated pictures. Commun. ACM 18(6), 311–317 (1975)
Qi, A., Song, Y., Xiang, T.: Semantic embedding for sketch-based 3D shape retrieval. In: BMVC (2018)
Qi, C.R., Su, H., Mo, K., Guibas, L.J.: PointNet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In: CVPR (2017)
Qi, C.R., Su, H., Niebner, M., Dai, A., Yan, M.: Volumetric and multi-view CNNs for object classification on 3D data. In: CVPR (2016)
Qi, C.R., Yi, L., Su, H., Guibas, L.J.: PointNet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In: NeurIPS (2017)
Russakovsky, O., et al.: ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 115(3), 211–252 (2015)
Sala, F., De Sa, C., Gu, A., R\(\acute{e}\), C.: Representation tradeoffs for hyperbolic embeddings. In: ICML (2019)
Sarkar, R.: Low distortion delaunay embedding of trees in hyperbolic plane. In: van Kreveld, M., Speckmann, B. (eds.) GD 2011. LNCS, vol. 7034, pp. 355–366. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25878-7_34
Shi, B., Bai, S., Zhou, Z., Bai, X.: DeepPano: deep panoramic representation for 3D shape recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(12), 2339–2343 (2015)
Shilane, P., Min, P., Kazhdan, M., Funkhouser, T.: The Princeton shape benchmark. In: Shape Modeling Applications (2004)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Sousa, P., Fonseca, M.J.: Sketch-based retrieval of drawings using spatial proximity. J. Vis. Lang. Comput. 21(2), 69–80 (2010)
Su, H., Maji, S., Kalogerakis, E., Learned-Miller, E.: Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition. In: ICCV (2015)
Su, J.C., Gadelha, M., Wang, R., Maji, S.: A deeper look at 3D shape classifiers. In: ECCV (2018)
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V., Alemi, A.A.: Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: AAAI (2017)
Szegedy, C., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: CVPR (2015)
Tabia, H., Laga, H.: Learning shape retrieval from different modalities. Neurocomputing 253, 24–33 (2017)
Tasse, F.P., Dodgson, N.: Shape2Vec: semantic-based descriptors for 3D shapes, sketches and images. ACM Trans. Graph. 35(6), 208 (2016)
Tatsuma, A., Koyanagi, H., Aono, M.: A large-scale shape benchmark for 3D object retrieval: Toyohashi shape benchmark. In: Asia-Pacific Signal & Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (2012)
Thomas, H., Qi, C.R., Deschaud, J.E., Marcotegui, B., Goulette, F., Guibas, L.J.: KPConv: flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds. In: The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
Wang, C., Li, H., Zhao, D.: Preconditioning Toeplitz-plus-diagonal linear systems using the Sherman-Morrison-Woodbury formula. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 309, 312–319 (2017)
Wang, C., Li, H., Zhao, D.: Improved block preconditioners for linear systems arising from half-quadratic image restoration. Appl. Math. Comput. 363, 124614 (2019)
Wang, C., Pelillo, M., Siddiqi, K.: Dominant set clustering and pooling for multi-view 3D object recognition. In: BMVC (2017)
Wang, F., Kang, L., Li, Y.: Sketch-based 3D shape retrieval using convolutional neural networks. In: CVPR (2015)
Wu, Z., et al.: RotationNet: joint object categorization and pose estimation using multiviews from unsupervised viewpoints. In: CVPR (2015)
Wu, Z., et al.: 3D ShapeNets: a deep representation for volumetric shapes. In: CVPR (2015)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: CVPR (2018)
Xie, J., Dai, G., Zhu, F., Fang, Y.: Learning barycentric representations of 3D shapes for sketch-based 3D shape retrieval. In: CVPR (2017)
Xu, C., Li, Z., Qiu, Q., Leng, B., Jiang, J.: Enhancing 2D representation via adjacent views for 3D shape retrieval. In: ICCV (2019)
Xu, L., Sun, H., Liu, Y.: Learning with batch-wise optimal transport loss for 3D shape recognition. In: CVPR (2019)
Yang, Z., Wang, L.: Learning relationships for multi-view 3D object recognition. In: ICCV (2019)
Yasseen, Z., Verroust-Blondet, A., Nasri, A.: View selection for sketch-based 3D model retrieval using visual part shape description. Vis. Comput. 33(5), 565–583 (2017)
Yu, T., Meng, J., Yuan, J.: Multi-view harmonized bilinear network for 3D object recognition. In: CVPR (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, J., Qin, J., Shen, Y., Liu, L., Zhu, F., Shao, L. (2020). Learning Attentive and Hierarchical Representations for 3D Shape Recognition. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, JM. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2020. ECCV 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12360. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58555-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58555-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58554-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58555-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)