Abstract
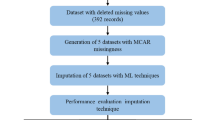
Missing data imputation is an important task when dealing with crucial data that cannot be discarded such as medical data. This study evaluates and compares the impacts of two statistical and two machine learning imputation techniques when classifying breast cancer patients, using several evaluation metrics. Mean, Expectation-Maximization (EM), Support Vector Regression (SVR) and K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) were applied to impute 18% of missing data missed completely at random in the two Wisconsin datasets. Thereafter, we empirically evaluated these four imputation techniques when using five classifiers: decision tree (C4.5), Case Based Reasoning (CBR), Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP). In total, 1380 experiments were conducted and the findings confirmed that classification using imputation based machine learning outperformed classification using statistical imputation. Moreover, our experiment showed that SVR was the best imputation method for breast cancer classification.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oskouei, R.J., Kor, N.M., Maleki, S.A.: Data mining and medical world: Breast cancers’ diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and challenges. Am. J. Cancer Res. 7, 610–627 (2017)
Garg, B.: Optimizing number of inputs to classify breast cancer using artificial neural network. J. Comput. Sci. Syst. Biol. 02, 247–254 (2009). https://doi.org/10.4172/jcsb.1000037
Sibbering, M., Courtney, C.A.: Management of breast cancer: basic principles. Surg. (United Kingdom) 34, 25–31 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpsur.2015.10.005
Morimoto, L.M., et al.: Obesity, body size, and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer: the women’s health initiative (United States). Cancer Causes Control 13, 741–751 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020239211145
Schafer, J.L., Graham, J.W.: Missing data: our view of the state of the art. Psychol. Methods 7, 147–177 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.7.2.147
Bhat, V.H., Rao, P.G., Krishna, S., Shenoy, P.D., Venugopal, K.R., Patnaik, L.M.: An efficient framework for prediction in healthcare data using soft computing techniques. In: Abraham, A., Mauri, J.L., Buford, J.F., Suzuki, J., Thampi, S.M. (eds.) ACC 2011. CCIS, vol. 192, pp. 522–532. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22720-2_55
Idri, A., Benhar, H., Fernández-Alemán, J.L., Kadi, I.: A systematic map of medical data preprocessing in knowledge discovery. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 162, 69–85 (2018)
Albayrak, M., Turhan, K., Informatics, M., Introduction, I.: A missing data imputation approach using clustering and maximum likelihood estimation. In: IEEE (ed.) 2017 Medical Technologies National Congress (TIPTEKNO), Trabzon, Turkey, pp. 1–4 (2017)
Kadi, I., Idri, A., Fernandez-Aleman, J.L.: Knowledge discovery in cardiology: a systematic literature review. Int. J. Med. Inform. 97, 12–32 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.09.005
Lang, K.M., Little, T.D.: Principled missing data treatments. Prev. Sci. 19(3), 284–294 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0644-5
Idri, A., Abnane, I., Abran, A.: Missing data techniques in analogy-based software development effort estimation. J. Syst. Softw. 117, 595–611 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.04.058
Jerez, J.M., et al.: Missing data imputation using statistical and machine learning methods in a real breast cancer problem. Artif. Intell. Med. 50, 105–115 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2010.05.002
Gayathri, B.M., Sumathi, C.P.: Mamdani fuzzy inference system for breast cancer risk detection. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research, ICCIC 2015, Madurai, Tamilnadu, India, pp. 1–6 (2016)
Myers, T.A.: Goodbye, listwise deletion: presenting hot deck imputation as an easy and effective tool for handling missing data. Commun. Methods Meas. 5, 297–310 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/19312458.2011.624490
Barzi, F., Woodward, M.: Imputations of missing values in practice: results from imputations of serum cholesterol in 28 cohort studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 160, 34–45 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwh175
Liu, Y., Gopalakrishnan, V.: An overview and evaluation of recent machine learning imputation methods using cardiac imaging data. Data (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/data2010008
Penone, C., et al.: Imputation of missing data in life-history trait datasets: which approach performs the best? Methods Ecol. Evol. 5, 961–970 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12232
Vateekul, P., Sarinnapakorn, K.: Tree-based approach to missing data imputation. In: ICDM Workshops 2009 - IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 70–75 (2009)
Idri, A., Abnane, I., Abran, A.: Support vector regression-based imputation in analogy-based software development effort estimation. J. Softw. Evol. Process. 30, 1–23 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smr.2114
Wu, X., Akbarzadeh Khorshidi, H., Aickelin, U., Edib, Z., Peate, M.: Imputation techniques on missing values in breast cancer treatment and fertility data. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 7(1), 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-019-0082-4
Acuña, E., Rodriguez, C.: The treatment of missing values and its effect on classifier accuracy. In: Banks, D., McMorris, F.R., Arabie, P., Gaul, W. (eds.) Classification, Clustering, and Data Mining Applications. STUDIES CLASS, pp. 639–647. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-17103-1_60
Chlioui, I., Idri, A., Abnane, I.: Data preprocessing in knowledge discovery in breast cancer: systematic mapping study. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis., 1–15
Musil, C.M., Warner, C.B., Yobas, P.K., Jones, S.L.: A comparison of imputation techniques for handling Missing data. West. J. Nurs. Res. 24, 815–829 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1177/019394502762477004
Santos, M.S., Soares, J.P., Henriques Abreu, P., Araújo, H., Santos, J.: Influence of data distribution in missing data imputation. In: ten Teije, A., Popow, C., Holmes, J.H., Sacchi, L. (eds.) AIME 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10259, pp. 285–294. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59758-4_33
Peng, L., Lei, L.: A review of missing data treatment methods. Int. J. Intell. Inf. Manag. Syst. Technol. 1, 412–419 (2005)
Moon, T.K.: The expectation-maximization algorithm (1996)
Chlioui, I., Idri, A., Abnane, I., de Gea, J.M.C., Fernández-Alemán, J.L.: Breast cancer classification with missing data imputation. In: Rocha, Á., Adeli, H., Reis, L.P., Costanzo, S. (eds.) WorldCIST 2019. AISC, vol. 932, pp. 13–23. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16187-3_2
Vapnik, V.: The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory (2013)
Debasish, B., Srimanta, P., Dipak Chandra, P.: Support vector regression. Neural Inf. Process. Lett. Rev. 11, 699–708 (2007)
Drucker, H., Surges, C.J.C., Kaufman, L., Smola, A., Vapnik, V.: Support vector regression machines. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (1997)
Smola, A.J., Schölkopf, B.: A tutorial on support vector regression (2004)
Müller, K.-R., Smola, A.J., Rätsch, G., Schölkopf, B., Kohlmorgen, J., Vapnik, V.: Predicting time series with support vector machines. In: Gerstner, W., Germond, A., Hasler, M., Nicoud, J.-D. (eds.) ICANN 1997. LNCS, vol. 1327, pp. 999–1004. Springer, Heidelberg (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0020283
Quinlan, J.R.: C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1992)
Witten, I.H., Frank, E., Hall, M.A.: Data Mining. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2011)
Alpaydın, E.: Introduction to machine learning, London (2014)
Cristianini, N., Shawe-Taylor, J.: An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel Based Learning Methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Burges, C.J.C.: A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2, 121–167 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009715923555
Marsilin, J.R.: An efficient CBIR approach for diagnosing the stages of breast cancer using KNN classifier. Bonfring Int. J. Adv. Image Process. 2, 01–05 (2012). https://doi.org/10.9756/bijaip.1127
Odajima, K., Pawlovsky, A.P.: A detailed description of the use of the kNN method for breast cancer diagnosis. In: 2014 7th International Conference on BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, BMEI 2014, Dalian, China, pp. 688–692 (2014)
Kowarik, A., Templ, M.: Imputation with the R Package VIM. J. Stat. Softw. 74, 1–16 (2016). https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v074.i07
Hu, S., Liang, Y., Ma, L., He, Y.: MSMOTE: improving classification performance when training data is imbalanced. In: 2nd International Workshop on Computer Science and Engineering, WCSE 2009, Qingdao, China, pp. 13–17 (2009)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Pavlov, Y.L.: Random forest. In: Probabilistic Methods in Discrete Mathematics, pp. 11–18 (2000)
Ghosh, S., Mondal, S., Ghosh, B.: A comparative study of breast cancer detection based on SVM and MLP BPN classifier. In: 1st International Conference on Automation, Control, Energy and Systems, ACES 2014, Hooghly, West Bengal, India, pp. 1–4 (2014)
Brockmann, D., Hufnagel, L., Geisel, T.: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook. Springer, Boston (2006)
Jhajharia, S., Varshney, H.K., Verma, S., Kumar, R.: A neural network based breast cancer prognosis model with PCA processed features. In: 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics, ICACCI 2016, Jaipur, India, pp. 1896–1901 (2016)
Song, Q., Shepperd, M., Chen, X., Liu, J.: Can k-NN imputation improve the performance of C4.5 with small software project data sets? A comparative evaluation. J. Syst. Softw. 81, 2361–2370 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2008.05.008
Dua, D., Graff, C.: UCI Machine Learning Repository. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
Chlioui, I., Idri, A., Abnane, I., de Gea, J.M.C., Fernández-Alemán, J.L.: Breast cancer classification with missing data imputation (2019)
Idri, A., Hosni, M., Abnane, I., Carrillo de Gea, J.M., Fernández Alemán, J.L.: Impact of parameter tuning on machine learning based breast cancer classification. In: World Conference on Information Systems and Technologies, Galicia, Spain, pp. 115–125 (2019)
García, V., Mollineda, R.A., Sánchez, J.S.: Index of balanced accuracy: a performance measure for skewed class distributions. In: Araujo, H., Mendonça, A.M., Pinho, A.J., Torres, M.I. (eds.) IbPRIA 2009. LNCS, vol. 5524, pp. 441–448. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02172-5_57
Jonsdottir, T., Hvannberg, E.T., Sigurdsson, H., Sigurdsson, S.: The feasibility of constructing a Predictive Outcome Model for breast cancer using the tools of data mining. Expert Syst. Appl. 34, 108–118 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2006.08.029
Cohen, J.: A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 20, 37–46 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1177/001316446002000104
Cortes, C., Mohri, M.: AUC optimization vs. error rate minimization. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 313–320 (2004)
Jelihovschi, E., Faria, J.C., Allaman, I.B.: ScottKnott: a package for performing the Scott-Knott clustering algorithm in R. TEMA (São Carlos) 15, 003 (2014). https://doi.org/10.5540/tema.2014.015.01.0003
Hosni, M., Idri, A., Abran, A., Nassif, A.B.: On the value of parameter tuning in heterogeneous ensembles effort estimation. Soft. Comput. 22(18), 5977–6010 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2945-4
Vuurpijl, L., Schomaker, L.: An overview and comparison of voting methods for pattern recognition. In: IEEE (ed.) Proceedings Eighth International Workshop on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition, pp. 195–200 (2002)
García-Laencina, P.J., Sancho-Gómez, J.L., Figueiras-Vidal, A.R.: Pattern classification with missing data: a review. Neural Comput. Appl. 19, 263–282 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-009-0295-6
Salzberg, S.L.: On comparing classifiers: pitfalls to avoid and a recommended approach. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1, 317–328 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009752403260
Hosni, M., Abnane, I., Idri, A., de Gea, J.M.C., Alemán, J.L.F.: Reviewing ensemble classification methods in breast cancer. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 177, 89–112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.05.019
Abnane, I., Hosni, M., Idri, A., Abran, A.: Analogy software effort estimation using ensemble KNN imputation. In: IEEE (ed.) 2019 45th Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA), Kallithea, Greece, pp. 228–235 (2019)
Twala, B.: An empirical comparison of techniques for handling incomplete data using decision trees. Appl. Artif. Intell. 23, 373–405 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/08839510902872223
Abnane, I., Idri, A.: Improved analogy-based effort estimation with incomplete mixed data. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, FedCSIS 2018, Poznań, Poland, pp. 1015–1024 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chlioui, I., Abnane, I., Idri, A. (2020). Comparing Statistical and Machine Learning Imputation Techniques in Breast Cancer Classification. In: Gervasi, O., et al. Computational Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2020. ICCSA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12252. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58811-3_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58811-3_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58810-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58811-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)