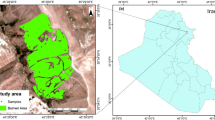
Abstract
Monitoring the large number of active fires and their consequences in such an extensive area such as the Brazilian territory is an important task. Machine Learning techniques are a promising approach to contribute to this area, but the challenge is the building of rich example datasets, whose previous examples are unavailable in many areas. Our aim in this article is to move towards the development of an approach to detect burned areas in regions for which there is no previously validated samples. We deal with that by presenting some experiments to classify burned areas through Machine Learning techniques that combine remote sensing data from nearby areas and it can distinguish between burned and non burned polygons with good results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Andrade, R.N., Bittencourt, O., Morelli, F., Santos, R.: Classificação semiautomática de áreas queimadas com o uso de redes neurais. In: XVIII Brazilian Symposium on Geoinformatics - GeoInfo 2017, pp. 92–97 (2017)
Bittencourt, O.O., Morelli, F., dos Santos Júnior, C.A., Santos, R.: Evaluating classification models in a burned areas’ detection approach. In: Misra, S., et al. (eds.) ICCSA 2019. LNCS, vol. 11622, pp. 577–591. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24305-0_43
Bowman, D., et al.: Fire in the earth system. Science 324, 481–484 (2009)
Chuvieco, E., Martín, M.: Cartografí de grandes incendios forestales en la península ibérica a partir de imágenes noaa-avhrr. Serie Geográfica 7, 109–128 (1998)
Chuvieco, E., et al.: Historical background and current developments for mapping burned area from satellite earth observation. In: Remote Sensing of Environment (2019)
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE): Programa de monitoramento de queimadas. http://www.inpe.br/queimadas/portal. Accessed 28 Jan 2018
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE): Programa de monitoramento de queimadas, área queimada, resolu cão 30m. https://prodwww-queimadas.dgi.inpe.br/aq30m/. Accessed 28 Jan 2018
JPI Climate and European Union: Serv-for fire integrated services and approaches for assessing effects of climate change and extreme events for fire and post fire risk prevention. https://servforfire-era4cs.eu/
Katagis, T., Gitas, I., Toukiloglou, P., Veraverbeke, S., Goossens, R.: Trend analysis of medium- and coarse-resolution time series image data for burned area mapping in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Int. J. Wildland Fire 23, 668–677 (2014)
Key, C., Benson, N.: Landscape assessment: Ground measure of severity, the composite burn index; and remote sensing of severity, the normalized burn ratio. In: FIREMON: Fire Effects Monitoring and Inventory System, pp. 1–51 (2006)
Li, J., Roy, D.: A global analysis of sentinel-2a, sentinel-2b and Landsat-8 data revisit intervals and implications for terrestrial monitoring. Remote Sens. 9, 902 (2017)
Liu, J., Heiskanen, J., Maeda, E.E., Pellikka, P.K.: Burned area detection based on Landsat time series in savannas of southern Burkina Faso. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obser. Geoinf. 64, 210–220 (2018)
Smith, A.M.S., Drake, N.A., Wooster, M.J., Hudak, A.T., Holden, Z.A., Gibbons, C.J.: Production of Landsat ETM+ reference imagery of burned areas within Southern African savannahs: comparison of methods and application to MODIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 28, 2753–2775 (2007)
McFeeters, S.: The use of normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 17, 1425–1432 (1996)
Melchiori, E., Setzer, A.W., Morelli, F., Libonati, R., Cândido, P.d.A., Jesús, S.C.d.: A Landsat-TM/OLI Algorithm for Burned Areas in the Brazilian Cerrado: Preliminary Results, pp. 1302–1311. Imprensa da Universidade de Coimbra (2014)
Mithal, V., Nayak, G., Khandelwal, A., Kumar, V., Nemani, R., Oza, N.C.: Mapping burned areas in tropical forests using a novel machine learning framework. Remote Sens. 10, 69 (2018)
Pedregosa, F., et al.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Pereira, A.A., et al.: Burned area mapping in the Brazilian savanna using a one-class support vector machine trained by active fires. Remote Sens. 9(11), 1161 (2017)
Pinty, B., Verstraete, M.: GEMI: a non-linear index to monitor global vegetation from satellites. Vegetation 101, 15–20 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00031911
Rouse Jr., J.W., Haas, R.H., Schell, J.A., Deering, D.W.: Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. NASA Special Publication, vol. 351, p. 309 (1974)
Trigg, S., Flasse, S.: An evaluation of different bi-spectral spaces for discriminating burned shrub-savannah. Int. J. Remote Sens. 22, 2641–2647 (2001)
United States Geological Survey (USGS): Science Data Lifecycle. https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov. Accessed 18 Oct 2018
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq)/Coordination of Associated Laboratories (COCTE/INPE) (no. 300587/2017-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bittencourt, O.O., Morelli, F., Júnior, C.A.S., Santos, R. (2020). An Approach to Classify Burned Areas Using Few Previously Validated Samples. In: Gervasi, O., et al. Computational Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2020. ICCSA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12253. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58814-4_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58814-4_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58813-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58814-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)