Abstract
The human brain is not able to process the vast amount of visual information that originates in the environment around us. Therefore, a complex process of human visual attention based on the principles of selectivity and prioritization helps us to choose only the most important parts of the scene for further analysis. These principles are driven by the visual saliency derived from certain aspects of the scene parts. In this paper, we focus on the objects’ depth salience which undoubtedly plays its role in processing visual information and has still not been thoroughly studied until now.
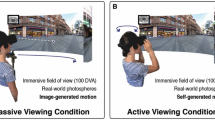
The aim of our work is to investigate depth perception tendencies using an advanced experimental methodology in the environment of virtual reality. Based on the state-of-the-art of the attention modelling in the 3-D environment, we designed and carried out an extensive eye-tracking experimental study in the virtual reality with 37 participants observing artificial scenes designed for exploring trends in the depth perception in the virtual 3-D environment. We analyzed the acquired data and discuss the revealed depth perception tendencies in virtual reality alongside future possible applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The dataset is publicly available on demand.
References
Wang, J., et al.: Study of depth bias of observers in free viewing of still stereoscopic synthetic stimuli. J. Eye Mov. Res. 5(5), 11 (2012)
Borji, A., Itti, L.: State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(1), 185–207 (2013)
Borji, A., Cheng, M., Hou, Q., et al.: Salient object detection: a survey. Comput. Vis. Media 5, 117–150 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-019-0149-9
Bylinskii, Z., et al.: MIT saliency benchmark (2015)
Bylinskii, Z., Judd, T., Oliva, A., Torralba, A., Durand, F.: What do different evaluation metrics tell us about saliency models? IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(3), 740–757 (2018)
Desingh, K., Krishna, K.M., Rajan, D., Jawahar, C.: Depth really matters: improving visual salient region detection with depth. In: BMVC (2013)
Itti, L., Koch, C.: Computational modelling of visual attention. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2(3), 194 (2001)
Laco, M., Benesova, W.: Depth in the visual attention modelling from the egocentric perspective of view. In: Eleventh International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2018). Proceedings of SPIE (2019). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2523059
Laco, M., Polatsek, P., Benesova, W.: Depth perception tendencies on a widescreen display: an experimental study. In: Already Submitted to: Twelfth International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2019). Proceedings of SPIE (2019)
Marmitt, G., Duchowski, A.T.: Modeling visual attention in VR: measuring the accuracy of predicted scanpaths. Ph.D. thesis, Clemson University (2002)
Olesova, V., Benesova, W., Polatsek, P.: Visual attention in egocentric field-of-view using RGB-D data. In: Ninth International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2016), vol. 10341, p. 103410T. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2017). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2268617
Polatsek, P.: Modelling of human visual attention. Dissertation thesis, FIIT STU, Bratislava (2019)
Roberts, K.L., Allen, H.A., Dent, K., Humphreys, G.W.: Visual search in depth: the neural correlates of segmenting a display into relevant and irrelevant three-dimensional regions. NeuroImage 122, 298–305 (2015)
Sitzmann, V., et al.: Saliency in VR: how do people explore virtual environments? IEEE Trans. Visual Comput. Graphics 24(4), 1633–1642 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Polláková, J., Laco, M., Benesova, W. (2020). Depth Perception Tendencies in the 3-D Environment of Virtual Reality. In: Chmielewski, L.J., Kozera, R., Orłowski, A. (eds) Computer Vision and Graphics. ICCVG 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12334. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59006-2_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59006-2_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59005-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59006-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)