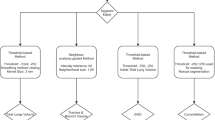
Abstract
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a critical impairment of the lung function, which occurs – among others – in severe cases of patients with Covid-19. Its therapeutic management is based on mechanical ventilation, but this may aggravate the patient’s condition if the settings are not adapted to the actual lung state. Computed tomography images allow for assessing the lung ventilation with fine spatial resolution, but their quantitative analysis is hampered by the contrast loss due to the disease. This article describes software developed to assist the clinicians in this analysis by implementing semi-automatic algorithms as well as interactive tools. The focus is the assessment of the cyclic hyperinflation, which may lead to ventilator-induced lung injury. For this purpose aerated parts of the lungs were segmented in twenty ARDS patients, half with Covid-19. The results were in very good agreement with manual segmentation performed by experts: \(5.3\%\) (5.1 ml) mean difference in measured cyclic hyperinflation.
This work was performed within the framework of the LABEX PRIMES (ANR-11-LABX-0063) of Université de Lyon, within the program “Investissements d’Avenir” (ANR-11-IDEX-0007) operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dávila Serrano, E.E., et al.: CreaTools: a framework to develop medical image processing software: application to simulate pipeline stent deployment in intracranial vessels with aneurysms. In: Bolc, L., Tadeusiewicz, R., Chmielewski, L.J., Wojciechowski, K. (eds.) ICCVG 2012. LNCS, vol. 7594, pp. 55–62. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33564-8_7
Gattinoni, L., Caironi, P., Pelosi, P., Goodman, L.R.: What has computed tomography taught us about the acute respiratory distress syndrome? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164(9), 1701–11 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.164.9.2103121
Gattinoni, L., et al.: Lung recruitment in patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. New Engl. J. Med. 354(17), 1775–1786 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa052052
Gerard, S.E., Herrmann, J., Kaczka, D.W., Musch, G., Fernandez-Bustamante, A., Reinhardt, J.M.: Multi-resolution convolutional neural networks for fully automated segmentation of acutely injured lungs in multiple species. Med. Image Anal. 60, 101592 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.101592
Klapsing, P., Herrmann, P., Quintel, M., Moerer, O.: Automatic quantitative computed tomography segmentation and analysis of aerated lung volumes in acute respiratory distress syndrome - a comparative diagnostic study. J. Crit. Care 42, 184–191 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.11.001
Lidayová, K., Gómez Betancur, D.A., Frimmel, H., Hernández Hoyos, M., Orkisz, M., Smedby, Ö.: Airway-tree segmentation in subjects with acute respiratory distress syndrome. In: Sharma, P., Bianchi, F.M. (eds.) SCIA 2017. LNCS, vol. 10270, pp. 76–87. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59129-2_7
Mansoor, A., et al.: Segmentation and image analysis of abnormal lungs at CT: current approaches, challenges, and future trends. RadioGraphics 35(4), 1056–1076 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2015140232
Morales Pinzón, A., Orkisz, M., Richard, J.C., Hernández Hoyos, M.: Lung segmentation by cascade registration. IRBM 38(5), 266–280 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2017.07.003
Nieman, G.F., Satalin, J., Andrews, P., Aiash, H., Habashi, N.M., Gatto, L.A.: Personalizing mechanical ventilation according to physiologic parameters to stabilize alveoli and minimize ventilator induced lung injury (VILI). Intensive Care Med. Exp. 5(1), 1–21 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40635-017-0121-x
Yin, Y., Hoffman, E.A., Lin, C.L.: Mass preserving nonrigid registration of CT lung images using cubic B-spline. Med. Phys. 36(9), 4213–4222 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3193526
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dávila Serrano, E.E., Dhelft, F., Bitker, L., Richard, JC., Orkisz, M. (2020). Software for CT-image Analysis to Assist the Choice of Mechanical-Ventilation Settings in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. In: Chmielewski, L.J., Kozera, R., Orłowski, A. (eds) Computer Vision and Graphics. ICCVG 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12334. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59006-2_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59006-2_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59005-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59006-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)