Abstract
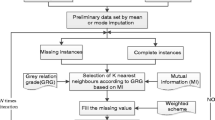
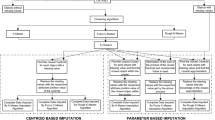
In healthcare domains, dealing with missing data is crucial since absent observations compromise the reliability of decision support models. K-nearest neighbours imputation has proven beneficial since it takes advantage of the similarity between patients to replace missing values. Nevertheless, its performance largely depends on the distance function used to evaluate such similarity. In the literature, k-nearest neighbours imputation frequently neglects the nature of data or performs feature transformation, whereas in this work, we study the impact of different heterogeneous distance functions on k-nearest neighbour imputation for biomedical datasets. Our results show that distance functions considerably impact the performance of classifiers learned from the imputed data, especially when data is complex.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbdAllah, L., Shimshoni, I.: K-means over incomplete datasets using mean Euclidean distance. MLDM 2016. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 9729, pp. 113–127. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41920-6_9
Abreu, P.H., Santos, M.S., Abreu, M.H., Andrade, B., Silva, D.C.: Predicting breast cancer recurrence using machine learning techniques: a systematic review. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 49(3), 1–40 (2016)
Amorim, J.P., Domingues, I., Abreu, P.H., Santos, J.: Interpreting deep learning models for ordinal problems. In: ESANN (2018)
Belanche Muñoz, L.A., Hernández González, J.: Similarity networks for heterogeneous data. In: ESANN 2012, pp. 215–220 (2012)
Das, S., Datta, S., Chaudhuri, B.B.: Handling data irregularities in classification: foundations, trends, and future challenges. Pattern Recogn. 81, 674–693 (2018)
García-Laencina, P., Abreu, P.H., Abreu, M.H., Afonoso, N.: Missing data imputation on the 5-year survival prediction of breast cancer patients with unknown discrete values. Comput. Biol. Med. 59, 125–133 (2015)
Hu, L.-Y., Huang, M.-W., Ke, S.-W., Tsai, C.-F.: The distance function effect on k-nearest neighbor classification for medical datasets. SpringerPlus 5(1), 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2941-7
Juhola, M., Laurikkala, J.: On metricity of two heterogeneous measures in the presence of missing values. Artif. Intell. Rev. 28(2), 163–178 (2007)
Pereira, R.C., Santos, M.S., Rodrigues, P.P., Abreu, P.H.: MNAR imputation with distributed healthcare data. In: Moura Oliveira, P., Novais, P., Reis, L.P. (eds.) EPIA 2019. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 11805, pp. 184–195. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30244-3_16
Sáez, J.A., Krawczyk, B., Woźniak, M.: Handling class label noise in medical pattern classification systems. J. Med. Inform. Technol. 24 (2015)
Santos, M.S., Abreu, P.H., García-Laencina, P., Simão, A., Carvalho, A.: A new cluster-based oversampling method for improving survival prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J. Biomed. Inform. 58, 49–59 (2015)
Santos, M.S., Abreu, P.H., Wilk, S., Santos, J.: How distance metrics influence missing data imputation with k-nearest neighbours. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 136, 111–119 (2020)
Santos, M.S., Pereira, R.C., Costa, A., Soares, J., Santos, J., Abreu, P.H.: Generating synthetic missing data: a review by missing mechanism. IEEE Access 1(1), 1–18 (2019)
Santos, M.S., Soares, J.P., Abreu, P.H., Araújo, H., Santos, J.: Cross-validation for imbalanced datasets: avoiding overoptimistic and overfitting approaches [research frontier]. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 13(4), 59–76 (2018)
Santos, M.S., Soares, J.P., Henriques Abreu, P., Araújo, H., Santos, J.: Influence of data distribution in missing data imputation. In: ten Teije, A., Popow, C., Holmes, J.H., Sacchi, L. (eds.) AIME 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10259, pp. 285–294. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59758-4_33
Tutz, G., Ramzan, S.: Improved methods for the imputation of missing data by nearest neighbor methods. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 90, 84–99 (2015)
Twala, B., Cartwright, M.: Ensemble missing data techniques for software effort prediction. Intell. Data Anal. 14(3), 299–331 (2010)
Wilson, R., Martinez, T.: Improved heterogeneous distance functions. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 6, 1–34 (1997)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the project NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000027 (Norte Portugal Regional Operational Programme – Norte 2020) and in part by the FCT Research Grant SFRH/BD/138749/2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Santos, M.S., Abreu, P.H., Wilk, S., Santos, J. (2020). Assessing the Impact of Distance Functions on K-Nearest Neighbours Imputation of Biomedical Datasets. In: Michalowski, M., Moskovitch, R. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. AIME 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12299. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59137-3_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59137-3_43
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59136-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59137-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)