Abstract
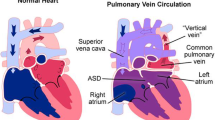
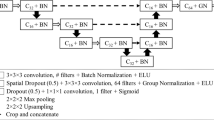
Very often doctors diagnose diseases and prescribe treatments through cross-referencing patients’ clinical data as well as radiology reports. On the other hand, while a few existing machine learning frameworks for diagnosis, treatment planning, and prognosis have used both clinical data and medical images, they all have prior knowledge about what information should be extracted from medical images. However, this is not the case for many diseases. For example, cardiac anatomical structure and tissue shapes are essential for pulmonary venous obstruction (PVO) prediction after correction of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC), but the exact graphical features in the computed tomography (CT) images that should be measured remain unclear. In this paper, we propose to use convolutional neural network to automatically obtain features from CT images and combine them with clinical data in an end-to-end trainable manner. We further collect a dataset consisting of 132 TAPVC patients for evaluation, and find that jointly using clinical data and CT images to predict postoperative PVO outperforms the method based on either clinical data or CT images alone. Our dataset is released to the community to promote further research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
link omitted for blind review
Betancur, J., et al.: Prognostic value of combined clinical and myocardial perfusion imaging data using machine learning. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging 11(7), 1000–1009 (2018)
Burroughs, J.T., Edwards, J.E.: Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Am. Heart J. 59(6), 913–931 (1960)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Herlong, J.R., Jaggers, J.J., Ungerleider, R.M.: Congenital heart surgery nomenclature and database project: pulmonary venous anomalies. Annal. Thorac. Surg. 69(3), 56–69 (2000)
Husain, S.A., et al.: Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: factors associated with mortality and recurrent pulmonary venous obstruction. Annal. Thorac. Surg. 94(3), 825–832 (2012)
Kourou, K., Exarchos, T.P., Exarchos, K.P., Karamouzis, M.V., Fotiadis, D.I.: Machine learning applications in cancer prognosis and prediction. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 13, 8–17 (2015)
Motwani, M., et al.: Machine learning for prediction of all-cause mortality in patients with suspected coronary artery disease: a 5-year multicentre prospective registry analysis. Eur. Heart J. 38(7), 500–507 (2017)
Parisot, S., et al.: Spectral graph convolutions for population-based disease prediction. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10435, pp. 177–185. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66179-7_21
Roth, H.R., et al.: Improving computer-aided detection using convolutional neural networks and random view aggregation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1170–1181 (2015)
Setio, A.A.A., et al.: Pulmonary nodule detection in ct images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1160–1169 (2016)
Shah, S.J., et al.: Phenomapping for novel classification of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 131(3), 269–279 (2015)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Weng, S.F., Reps, J., Kai, J., Garibaldi, J.M., Qureshi, N.: Canmachine-learning improve cardiovascular risk prediction using routineclinical data? PloS one 12(4) (2017)
Yuan, B., Xing, W.: Diagnosing cardiac abnormalities from 12-lead electrocardiograms using enhanced deep convolutional neural networks. In: Liao, H., Balocco, S., Wang, G., Zhang, F., Liu, Y., Ding, Z., Duong, L., Phellan, R., Zahnd, G., Breininger, K., Albarqouni, S., Moriconi, S., Lee, S.-L., Demirci, S. (eds.) MLMECH/CVII-STENT -2019. LNCS, vol. 11794, pp. 36–44. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33327-0_5
Yun, T.J., et al.: Conventional and sutureless techniques for management of the pulmonary veins: evolution of indications from postrepair pulmonary vein stenosis to primary pulmonary vein anomalies. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 129(1), 167–174 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hu, X. et al. (2020). Joint Clinical Data and CT Image Based Prognosis: A Case Study on Postoperative Pulmonary Venous Obstruction Prediction. In: Rekik, I., Adeli, E., Park, S.H., Valdés Hernández, M.d.C. (eds) Predictive Intelligence in Medicine. PRIME 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12329. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59354-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59354-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59353-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59354-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)