Abstract
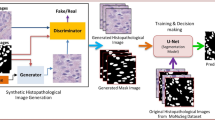
The construction of large tissue images is a challenging task in the field of generative modeling of histopathology images. Such synthetic images can be used for development and evaluation of various types of deep learning methods. However, memory and computational processing requirements limit the sizes of image constructed using neural generative models. To tackle this, we propose a conditional generative adversarial network framework that learns to generate and stitch small patches to construct large tissue image tiles while preserving global morphological characteristics. The key novelty of the proposed scheme is that it can be used to generate tiles larger than those used for training with high fidelity. Our evaluation of the Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Gland (CRAG) dataset shows that the proposed model can generate large tissue tiles that exhibit realistic morphological tissue features including glands appearance, nuclear structure, and stromal architecture. Our experimental results also show that the proposed model can be effectively used for evaluation of image segmentation models as well.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qaiser, T., et al.: Fast and accurate tumor segmentation of histology images using persistent homology and deep convolutional features. Med. Image Anal. 55, 1–14 (2019)
Graham, S., Rajpoot, N.M.: SAMS-NET: stain-aware multi-scale network for instance-based nuclei segmentation in histology images. In: 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), pp. 590–594. IEEE (2018)
Graham, S., et al.: HoVer-Net: simultaneous segmentation and classification of nuclei in multi-tissue histology images. Med. Image Anal. 58, 101563 (2019)
Sirinukunwattana, K., Raza, S.E.A., Tsang, Y.W., Snead, D.R., Cree, I.A., Rajpoot, N.M.: Locality sensitive deep learning for detection and classification of nuclei in routine colon cancer histology images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1196–1206 (2016)
Kovacheva, V.N., Snead, D., Rajpoot, N.M.: A model of the spatial tumour heterogeneity in colorectal adenocarcinoma tissue. BMC Bioinform. 17(1) (2016). Article number: 255. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-016-1126-2
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2672–2680 (2014)
Mirza, M., Osindero, S.: Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.1784 (2014)
Senaras, C., et al.: Optimized generation of high-resolution phantom images using cGAN: application to quantification of Ki67 breast cancer images. PLoS ONE 13(5), e0196846 (2018)
Quiros, A.C., Murray-Smith, R., Yuan, K.: Pathology GAN: learning deep representations of cancer tissue. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.02644 (2019)
Graham, S., et al.: MILD-net: minimal information loss dilated network for gland instance segmentation in colon histology images. Med. Image Anal. 52, 199–211 (2019)
Kingma, D.P., Welling, M.: An introduction to variational autoencoders. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.02691 (2019)
Awan, R., et al.: Glandular morphometrics for objective grading of colorectal adenocarcinoma histology images. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1–12 (2017)
Isola, P., Zhu, J.Y., Zhou, T., Efros, A.A.: Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1125–1134 (2017)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Heusel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., Nessler, B., Hochreiter, S.: GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 6626–6637 (2017)
Wang, Z., Simoncelli, E.P., Bovik, A.C.: Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In: The Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, vol. 2, pp. 1398–1402. IEEE (2003)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Zou, K.H., et al.: Statistical validation of image segmentation quality based on a spatial overlap index1: scientific reports. Acad. Radiol. 11(2), 178–189 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Deshpande, S., Minhas, F., Rajpoot, N. (2020). Train Small, Generate Big: Synthesis of Colorectal Cancer Histology Images. In: Burgos, N., Svoboda, D., Wolterink, J.M., Zhao, C. (eds) Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging. SASHIMI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12417. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59520-3_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59520-3_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59519-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59520-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)