Abstract
Nowadays the visual saliency prediction has become a fundamental problem in 3D imaging area. In this paper, we proposed a saliency prediction model from the perspective of addressing three aspects of challenges. First, to adequately extract features of RGB and depth information, we designed an asymmetric encoder structure on the base of U-shape architecture. Second, to prevent the semantic information between salient objects and corresponding contexts from diluting in cross-modal distillation stream, we devised a global guidance module to capture high-level feature maps and deliver them into feature maps in shallower layers. Third, to locate and emphasize salient objects, we introduced a channel-wise attention model. Finally we built the refinement stream with integrated fusion strategy, gradually refining the saliency maps from coarse to fine-grained. Experiments on two widely-used datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed architecture, and the results show that our model outperforms six selective state-of-the-art models.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
When finding the interest objects in an image, human can automatically capture the semantic information between objects and their contexts, paying much attention to the prominent objects, and selectively suppress unimportant factors. This precise visual attention mechanism has already been explained in various of biologically plausible model [1, 2]. Saliency prediction aims to automatically predict the most informative and attractive parts in images. Rather than concentrating on the whole image, noticing salient objects can not only reduce the calculational cost but also improve the performance of saliency models in many imaging applications, including quality assessment [3, 4], segmentation [5,6,7], recognition [8, 9], to name a few. Existing saliency models mainly utilize two strategies to localize salient objects: bottom-up strategy and top-down strategy. Bottom-up strategy is driven by external stimuli. By exploiting low-level features, such as brightness, color and orientation, the bottom-up strategy outputs final saliency maps in an unsupervised manner. However, only using bottom-up strategy cannot recognize sufficient high-level semantic information. Conversely, the top-down strategy is driven by tasks. It can learn high-level features in a supervised manner with labeled ground truth data, which is beneficial to discriminate salient objects and surrounding pixels.
The recent trend is to extract multi-scale and multi-level features in high-level with deep neural networks (DNNs). We have witnessed an unprecedented explosion in the availability of and access to the saliency models focus on RGB images and videos [10, 14, 36]. Although saliency models in 2D images have achieved remarkable performance, most of them are not available in 3D applications. With the recent advent of widely-used RGB-D sensing technologies, RGB-D sensors now have the ability to intelligently capture depth images, which can provide complementary spatial information over RGB information to mimic human visual attention mechanism, as well as improve the performance of saliency models. Therefore, how to make full use of the cross-modal and cross-level information becomes a challenge. Among a variety of DNNs based RGB-D saliency models [40, 41], U-shape based structures [42, 43] attract most attention since their bottom-up pathways can extract low-level feature information while top-down pathways can generate rich and informative high-level features, which can take advantage of cross-modal complementarity and cross-level continuity of RGB-D information. However, in the top-down pathways of U-shape network, while high-level information is transmitting to shallower stages, semantic information is gradually diluting. We remedy this drawback by designing a global guidance module following by a series of global guidance flows. Global guidance flows deliver high-level semantic information to feature maps in shallower layers as complementarity after dilution. And we introduce a channel-wise attention module, which helps to strengthen the feature representation.
What is more, we observed that the current RGB-D visual saliency models are essentially a symmetric dual-stream input encoder structure (both RGB stream and depth stream have the same encoder structure). Although the same encoder structure improves the accuracy of the results, it also imposes a bottleneck on RGB-D saliency prediction. Therefore, the depth stream does not need to use the same deep level encoder structure as the RGB stream. Through the analysis of the asymmetric encoder structure, and inspired by the above studies, we exploit an asymmetric U-shape based network to make full leverage of high-level semantic information with global guidance module. In refinement processing, we build fusion models, which embedding with global guidance flows and channel-wise attention modules, to gradually refine the saliency maps and finally obtain high-quality fine-grained saliency maps. Overall, the main three contributions of our architecture are as follows:
-
1.
Instead of using the symmetric encoder structure, we proposed an asymmetric encoder structure for RGB-D saliency (VGG-16 for RGB stream and ResNet-50 for depth stream), which can extract the RGB-D features effectively.
-
2.
We designed a global guidance module at the top of encoder stream, which links strongly with the top-down stream, to deal with the problem of high-level information diluting in U-shape architecture.
-
3.
We innovatively introduced a channel-wise self-attention model in the cross-modal distillation stream, to emphasize salient objects and suppress unimportant surroundings, thus improves the feature representation.
2 Related Work
Recently, the capability of DNNs attracts more and more attention, which is helpful to extract significant features. Numerous DNN based models have proposed in 2D saliency prediction. For instance, Yang et al. [11] proposed a salient object predicted network for RGB images by using parallel dilated convolutions in different sizes, and providing a set of loss functions to optimize the network. Cordel et al. [12] proposed a DNN-based model, embedding with the improved evaluation metric, to deal with the problem of measure the saliency prediction for 2D images. Cornia et al. [13] proposed an RGB saliency attentive model by combining the dilated convolutions, attention models and learned prior maps. Wang et al. [14] trained an end-to-end architecture with deep supervision manner, to obtain final saliency maps of RGB images. Liu et al. [15] aimed at improving saliency prediction in three aspects, and thus proposed a saliency prediction model to capture multiple contexts. Liu et al. [16] aiming at predicting human eye-fixations in RGB images, hence proposed a computation network. Although these methods achieve great success, they ignore the generalization in 3D scenarios.
To overcome this problem, Zhang et al. [17] proposed a deep learning feature based RGBD visual saliency detection model. Yang et al. [18] proposed a two-stage clustering-based RGBD visual saliency model for human visual fixation prediction in dynamic scenarios. Nguyen et al. [19] investigated a Deep Visual Saliency (DeepVS) model to achieve a more accurate and reliable saliency predictor even in the presence of distortions. Liu et al. [20] first proposed a cluster-contrast saliency prediction model for depth maps, and then obtained the human fixation prediction with the centroid of the largest clusters of each depth super-pixel. Sun et al. [21] proposed a real-time video saliency prediction model in an end-to-end manner, via 3D residual convolutional neural network (3D-ResNet). Despite they emphasize the importance of auxiliary spatial information, there is still a larger room to improve. To fully utilize cross-modal features, we adopt a U-shaped based architecture in light of its cross-modal and cross-level ability.
Considering that different spatial and channel information of features return different salient responses, some works introduce the attention mechanism in saliency models, so as to enhance the discrimination of salient regions and background. Liu et al. [22] on the base of previous studies, but went further, they proposed an attention-guided RGB-D salient object network, the attention model consists of spatial and channel attention mechanism, which provides the better feature representation. Noori et al. [10] employed a multi-scale attention guided model in the RGB-D saliency model, to intelligently pay more attention to salient regions. Li et al. [23] developed an RGB-D object model, embedding with a cross-modal attention model, to enhance the salient objects. Jiang et al. [24] properly exploit the attention model in the RGB-D tracking model to assign larger weights to salient features of two modalities. Therefore, the model obtains the more fined salient features. Different from above attention mechanism, our attention module focuses on channel features, and can model the interdependencies of high-level features. The proposed attention mechanism can be embedded in any network seamlessly and improve the performance of saliency prediction models.
3 The Proposed Method
3.1 Overall Architecture
The proposed RGB-D saliency model comprises five primary parts on the base of the U-shape architectures: the encoder structures, the cross-model distillation streams, the global guidance module, the channel attention module, and the fusion modules for refinement. Figure 1 shows the overall framework of the proposed model. Concretely, we adopt the VGG-16 network [27] as the backbone of encoder structure for depth information, and the ResNet-50 network [28] as the backbone of encoder structure for RGB information. In order to meet the need of saliency prediction, we remain five basic convolution blocks of VGG-16 and ResNet-50 network, and eliminate their last pooling layers and full connection layers. We build the global guidance module inspired by the Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling [29]. More specifically, our global guidance module is placed on the top of RGB and depth bottom-up streams to capture high-level semantic information. The refinement stream mainly consists of fusion modules, gradually refining the coarse saliency maps to high-quality predicted saliency maps.
The overall architecture of proposed saliency prediction model: dotted box here represents the fusion processing in refinement stream, which is explained in Sect. 3.5. (Colour figure online)
3.2 Hierarchical RGB-D Feature Extraction
The main functionality of the RGB and depth streams is to extract the multi-scale and multi-level RGB-D feature information at different levels of abstraction. In proposed U-shape based architecture, we use ImageNet [30] pre-trained VGG-16 network and pre-trained ResNet-50 network as backbone of the bottom-up stream for RGB and depth images, respectively. Since depth information cannot input into backbone network directly, we transform depth image into three-channel HHA image [31]. We resize the input resolution W × H (W represents the width and H represents the height) of RGB image and paired depth image to size 288 × 288, and then feed into backbone networks. Meanwhile, considering that the size of RGB feature maps and depth feature maps in backbone can both denote as \( \left( {\frac{\text{W}}{{2^{{{\text{n}} - 1}} }},\frac{\text{H}}{{2^{{{\text{n}} - 1}} }}} \right) \), (n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5), we utilize RGB feature maps and depth feature maps to learn the multi-scale and multi-level feature maps (FM).
3.3 Global Guidance Module
We utilize U-shape based architecture due to its ability to build affluent feature information with top-down flows. In light of that U-shape network will lead a problem that the high-level features gradually dilutes when transmitting to shallower layers, inspired by introducing dilated convolutions in saliency prediction networks to capture multi-scale high-level semantic information in the top layers [32, 33], we provide an individual module with a set of global guiding flows (GFs) (shown in Fig. 1 as a series of green arrows) to explicitly make high-level feature maps be aware of the locations of the salient targets. To be more specific, the global guidance module (GM) is constructed upon the top of the bottom-up pathways. GM consists of four branches to capture the context information of high-level feature maps (GFM). We design the first branch by using a traditional convolution with kernel size as 1 × 1. And we use 2, 6, 12 dilation convolutions for other branches with kernel size as 2 × 2, 6 × 6, 12 × 12, respectively. All the strides are set to 1. To deal with the diluting issues, we introduce a set of GFs, which deliver GFM to and merge with feature maps in shallower layers. Following this way, we effectively supplement the high-level feature information to lower layers when transmitting, and prevent the salient information from diluting when refining the saliency maps.
3.4 Channel Attention Module
In top-down streams we introduce attention mechanism to enhance the feature representation, which is beneficial for discriminating salient details and background. The proposed channel-wise attention module (CWAM) is illustrated in Fig. 2.
Specifically, from the origin hierarchical feature maps FM ∈ ℝC × H × W, we calculate the channel attention map AM ∈ ℝC × N through reshaping the H × W dimension into N dimensions. Then use a matrix multiplication between AM and transpose of AM, which denotes as RA. Next, for the purpose of distinguishing salient targets and background, we import Max() function to determine the maximum between the value and −1, and then utilize multiplication results subtract the maximum. Then we adopt Mean() function to obtain an average result, which is denoted as AB, to suppress useless targets and emphasize significant pixels. The operation is shown in Eq. (1).
where \( \otimes \) denotes the matrix multiplication operation. Then input AB into the Softmax layer to obtain channel-wise attention maps. In addition, we adopt another matrix multiplication and reshape into origin dimension. The formula of final output is shown as Eq. (2).
where \( \oplus \) denotes the addition operation, θ represents a scale parameter learnt gradually from zero.
3.5 Refinement
We improve the quality of feature maps in refinement stream. Although attention mechanism can reinforce feature representation, this leads to unsatisfactory salient constructions. Aiming to obtain subtle and accurate saliency prediction, we employ integrated fusion modules (IFM) in the refinement stream. Specifically, four IFMs linking with four CWAMs make up of one top-down stream, and two top-down streams combines with global features GFM transmitting with GFs comprise the refinement stream. Figure 3 illustrates the details in refinement stream.
Illustration of the details in refinement stream: as shown in the dotted box in Fig. 1, at end of our network, the global guidance flow (the green thick arrow) compromises IFM of RGB information (right dotted boxes) and IFM of depth information (left dotted boxes); Two IFMs concatenate with high-level global features, then expand their size with an up-sampling layer to obtain the final saliency maps. (Colour figure online)
For each IFMm (m = 1, 2, 3, …, 8), its input contains three parts:
-
i)
FM of the RGB encoder stream (shown as a red cuboid in Fig. 3), or the depth encoder stream (shown as a pale blue cuboid in Fig. 3).
-
ii)
AF output by CWAM in corresponding top-down stream, following by traditional convolution layers, nonlinear activation function ReLU and Batchnormal layers, and up-sampling layers.
-
iii)
GFM following by traditional convolution layers, nonlinear activation function ReLU, Batchnormal layers, and up-sampling layers.
We set all the size of convolution kernels to 3 × 3, and the stride set to 1. We formulate the output of IFM as Eq. (4).
Where γ() denotes the ReLU function, and λ() denotes the Batchnormal layer. ci, ui (i = 1, 2) represents traditional convolution layers and upsampling layers of AF and GFM, respectively. Symbol \( \odot \) denotes the concatenate operation.
At last, we combine two types metric, including MSE and modified Pearsons Linear Correlation Coefficient (CC) metric as the loss function, to compare the final saliency prediction map and the ground truth. We use the standard deviation σ() here, and the loss function is shown as Eq. (3).
Where T denotes the real value, and \( \hat{T} \) denotes the predicted value. σ() denotes the function of correlation coefficient.
4 Experiments
4.1 Implementation Details
The entire experiments were implemented on the PyTorch 1.1.0 [34] framework. The training and testing processes were equipped with a TITAN Xp GPU with 8 GB memory workspace. Our backbone, including VGG-16 network and ResNet-50 network, their parameters are initialized on the ImageNet dataset. We use 288 × 288 resolution images to train the network in an end-to-end manner. The batch size was set to one image in every iteration, and we initiate the learning rate to 10−5. We trained the proposed network for 70 epochs altogether.
4.2 Datasets
We conduct experiments on two popular public saliency prediction datasets, including NUS dataset [25] and NCTU dataset [26], to evaluate the performance of our proposed network. The NUS dataset is comprised of 600 images, including 3D images and corresponding color stimuli, fixation maps, smooth depth maps, as well as paired depth images. The NCTU dataset is comprised of 475 images with 1920 × 1080 resolution, including 3D images, corresponding left and right view maps, fixation maps, disparity maps, and paired depth images.
4.3 Evaluation Criteria
To evaluate our approach performance, we use four widely-agreed and evaluation metrics: Pearsons Linear Correlation Coefficient (CC), Area Under Curve (AUC), Normalized Scanpath Saliency (NSS), and Kullback-Leibler Divergence (KL-Div).
CC is a statistical index, which reflects the linear correlation between our model (T) and predicted human fixation (G). The bigger the CC value is, the more relevant two variables are. Equation (5) represents the calculation of CC.
where cov means the covariance between the final output T and the round truth G.
AUC is defined as the area under the ROC curve. We use AUC as the evaluation criteria since a single ROC curve cannot assess the performance of the model adequately. The larger the AUC value is, the better the model performance is. Equation (6) shows the formulation of AUC.
where the ∑posk in the nominator is a fixed value, and only relevant with the amount of positive instances. ∑pos represents the sum of positive instances, and k is the ranking. NUMpos and NUMneg denote the number of positive and negative instances, respectively.
NSS mainly evaluates the average of M human fixations in a normalized map. The bigger the NSS value is, the better the performance of model is. We utilize the standard deviation σ() to calculate NSS with Eq. (7).
KLDiv measure is used for saliency prediction model evaluation. The smaller the KLDiv value is, the better the saliency model performance is. Given two probability distribution for x, which are denoted as c(x) and d(x), the KLDiv can be calculated with Eq. (8).
4.4 Ablation Studies and Analysis
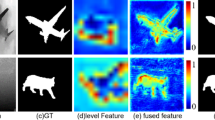
In order to thoroughly investigate the effectiveness of different components in proposed network, we conduct a series of ablation studies on NCTU and NUS datasets. The comparison results are demonstrated in Table 1. We remove GM and CWAMs of proposed network, what is more, we denote the backbone as B in the Table 1. Figure 4 shows a visual comparison of different model components on NCTU dataset. To explore the effectiveness of GM, we remove them from the network, which is denoted as B + A in Table 1. We can find that GM contributes to the proposed network. To prove the positive effects of CWAMs, we take away them from the proposed network, which is denoted as B + G in Table 1.
In Fig. 4, we can see clearly that B trained with GM (see column 3), learns more elaborate salient region. And B trained with CWAMs (see column 4) can enhance prominent regions, learn more certain and less blurry salient objects. Thus, taking the advantages of adopting above modules in our network, our model (see column 5) can generate more accurate saliency maps, which are much closer to the ground truth (see column 6) compared to other six methods.
4.5 Comparison with Other Saliency Prediction Models
We compared our proposed model on the two benchmark datasets against with six other state-of-the-art models, namely, Qi’s [39], Fang’s [35], DeepFix [36], ML-net [37], DVA [14], and iSEEL [38]. Note that all the saliency maps of above models are obtained by running source codes with recommended parameters. For fair comparison, we trained all models on NCTU and NUS datasets. Table 2 presents the quantitative results of different models, and we show a visual comparison between selective six models and our proposed model in Fig. 5.
Visual comparison between selective six models and our proposed model: we comparing with six saliency prediction models; column 1 shows origin left images, column 2 represents the ground truth, column 3 is our proposed method, and column 4 to 9 represents the saliency prediction models from [14, 35,36,37,38,39].
For stimuli-driven scenes, no matter the discrimination between targets and background is explicit (see row 1, 3), or implicit (see row 4, 7), our model can handle effectively. For task-driven scenes, our model can predict faces (see row 2, 5, 8) and people in complex background (see row 6). As for the scenes are influenced by light (see row 9, 10), our attention mechanism locates the salient objects appropriately. It can be seen that our method is capable of ignoring disturbed background and highlighting salient objects in various scenes.
5 Conclusion
In this paper, we proposed an asymmetric attention-based network. Concretely, in bottom-up streams, we capture multi-scale and multi-level features of RGB and paired depth images. In top-down streams for cross-modal features, incorporating with global guidance information and features from parallel layers, we introduce a channel-wise attention model to enhance salient feature representation. Experimental results show that our model out-performs six state-of-the-art models. For the future work, we expect the proposed model can be applied in other 3D scenarios including video object detection and object tracking.
References
Itti, L., Koch, C.: Computational modelling of visual attention. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2(3), 194–203 (2001)
Moon, J., Choe, S., Lee, S., Kwon, O.S.: Temporal dynamics of visual attention allocation. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–11 (2019)
Bosse, S., Maniry, D., Müller, K.R., Wiegand, T., Samek, W.: Deep neural networks for no-reference and full-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(1), 206–219 (2017)
Po, L.M., et al.: A novel patch variance biased convolutional neural network for no-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 29(4), 1223–1229 (2019)
Liu, C., et al.: Auto-DeepLab: hierarchical neural architecture search for semantic image segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 82–92. IEEE (2019)
Lei, X., Ouyang, H.: Image segmentation algorithm based on improved fuzzy clustering. Cluster Comput. 22(6), 13911–13921 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2128-9
Huang, H., Meng, F., Zhou, S., Jiang, F., Manogaran, G.: Brain image segmentation based on FCM clustering algorithm and rough set. IEEE Access 7, 12386–12396 (2019)
Chen, Z., Wei, X., Wang, P., Guo, Y.: Multi-label image recognition with graph convolutional networks. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 5172–5181. IEEE (2019)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778, Las Vegas, NV. IEEE (2016)
Noori, M., Mohammadi, S., Majelan, S.G., Bahri, A., Havaei, M.: DFNet: discriminative feature extraction and integration network for salient object detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 89, 103419 (2020)
Yang, S., Lin, G., Jiang, Q., Lin, W.: A dilated inception network for visual saliency prediction. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 22, 2163–2176 (2019)
Cordel, M.O., Fan, S., Shen, Z., Kankanhalli, M.S.: Emotion-aware human attention prediction. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 4021–4030. IEEE (2019)
Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Serra, G., Cucchiara, R.: SAM: pushing the limits of saliency prediction models. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, pp. 1971–19712. IEEE (2018)
Wang, W., Shen, J.: Deep visual attention prediction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(5), 2368–2378 (2017)
Liu, W., Sui, Y., Meng, L., Cheng, Z., Zhao, S.: Multiscope contextual information for saliency prediction. In: 2019 IEEE 3rd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chengdu, China, pp. 495–499, IEEE (2019)
Liu, N., Han, J., Liu, T., Li, X.: Learning to predict eye fixations via multiresolution convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Systems 29(2), 392–404 (2016)
Tao, X., Xu, C., Gong, Y., Wang, J.: A deep CNN with focused attention objective for integrated object recognition and localization. In: Chen, E., Gong, Y., Tie, Y. (eds.) PCM 2016. LNCS, vol. 9917, pp. 43–53. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48896-7_5
Yang, Y., Li, B., Li, P., Liu, Q.: A two-stage clustering based 3D visual saliency model for dynamic scenarios. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 21(4), 809–820 (2019)
Nguyen, A., Kim, J., Oh, H., Kim, H., Lin, W., Lee, S.: Deep visual saliency on stereoscopic images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(4), 1939–1953 (2019)
Piao, Y., Ji, W., Li, J., Zhang, M., Lu, H.: Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), pp. 7253–7262. IEEE (2019)
Sun, Z., Wang, X., Zhang, Q., Jiang, J.: Real-time video saliency prediction via 3D residual convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 7, 147743–147754 (2019)
Liu, Z., Duan, Q., Shi, S., Zhao, P.: Multi-level progressive parallel attention guided salient object detection for RGB-D images. Vis. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01821-9
Li, G., Gan, Y., Wu, H., Xiao, N., Lin, L.: Cross-modal attentional context learning for RGB-D object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(4), 1591–1601 (2018)
Jiang, M.X., Deng, C., Shan, J.S., Wang, Y.Y., Jia, Y.J., Sun, X.: Hierarchical multi-modal fusion FCN with attention model for RGB-D tracking. Inf. Fusion 50, 1–8 (2019)
Lang, C., Nguyen, T.V., Katti, H., Yadati, K., Kankanhalli, M., Yan, S.: Depth matters: influence of depth cues on visual saliency. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012. LNCS, vol. 7573, pp. 101–115. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33709-3_8
Ma, C.Y., Hang, H.M.: Learning-based saliency model with depth information. J. Vis. 15(6), 19 (2015)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, pp. 770–778. IEEE (2016)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05587 (2017)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: 2012 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, US, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Gupta, S., Girshick, R., Arbeláez, P., Malik, J.: Learning rich features from RGB-D images for object detection and segmentation. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8695, pp. 345–360. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_23
Song, H., Wang, W., Zhao, S., Shen, J., Lam, K.-M.: Pyramid dilated deeper ConvLSTM for video salient object detection. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11215, pp. 744–760. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01252-6_44
Huang, M., Liu, Z., Ye, L., Zhou, X., Wang, Y.: Saliency detection via multi-level integration and multi-scale fusion neural networks. Neurocomputing 364, 310–321 (2019)
Paszke, A., et al.: Automatic differentiation in PyTorch. In: NIPS 2017 Workshop Autodiff Decision Program Chairs. NIPS, Long Beach, US (2017)
Fang, Y., Wang, J., Narwaria, M., Le Callet, P., Lin, W.: Saliency detection for stereoscopic images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(6), 2625–2636 (2014)
Kruthiventi, S.S., Ayush, K., Babu, R.V.: DeepFix: a fully convolutional neural network for predicting human eye fixations. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(9), 4446–4456 (2017)
Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Serra, G., Cucchiara, R.: A deep multi-level network for saliency prediction. In: 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cancun, Mexico, pp. 3488–3493. IEEE (2017)
Tavakoli, H.R., Borji, A., Laaksonen, J., Rahtu, E.: Exploiting inter-image similarity and ensemble of extreme learners for fixation prediction using deep features. Neurocomputing 244, 10–18 (2017)
Qi, F., Zhao, D., Liu, S., Fan, X.: 3D visual saliency detection model with generated disparity map. Multimedia Tools Appl. 76(2), 3087–3103 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3229-6
Hou, Q., Cheng, M.M., Hu, X., Borji, A., Tu, Z., Torr, P.H.: Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(4), 815–828 (2017)
Wang, T., Borji, A., Zhang, L., Zhang, P., Lu, H.: A stagewise refinement model for detecting salient objects in images. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, pp. 4039–4048. IEEE (2017)
Liang, Y., et al.: TFPN: twin feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: 2019 IEEE 31st International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Portland, OR, USA, pp. 1702–1707. IEEE (2019)
Zhao, B., Zhao, B., Tang, L., Wang, W., Chen, W.: Multi-scale object detection by top-down and bottom-up feature pyramid network. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 30(1), 1–12 (2019)
Acknowledgement
This paper is supported by Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (618QN217) and National Nature Science Foundation of China (61862021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, X., Jin, T. (2020). Attention-Based Asymmetric Fusion Network for Saliency Prediction in 3D Images. In: Xu, R., De, W., Zhong, W., Tian, L., Bai, Y., Zhang, LJ. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Services – AIMS 2020. AIMS 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12401. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59605-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59605-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59604-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59605-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)