Abstract
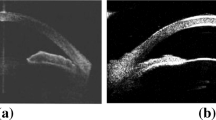
Precise characterization and analysis of iris shape from Anterior Segment OCT (AS-OCT) are of great importance in facilitating diagnosis of angle-closure-related diseases. Existing methods focus solely on analyzing structural properties identified from an individual 2D slice, while accurate characterization of morphological changes of iris shape in 3D AS-OCT may be able to reveal in addition the risk of disease progression. In this paper, we propose a novel framework for reconstruction and quantification of 3D iris surface from AS-OCT volume. We consider it to be the first work to detect angle-closure glaucoma by means of 3D representation. An iris segmentation network with wavelet refinement block (WRB) is first proposed to generate the initial shape of the iris from single AS-OCT slice. The 3D iris surface is then reconstructed using a guided optimization method with Poisson-disk sampling. Finally, a set of surface-based features are extracted, which are used in detecting of angle-closure glaucoma. Experimental results demonstrate that our method is highly effective in iris segmentation and surface reconstruction. Moreover, we show that 3D-based representation achieves better performance in angle-closure glaucoma detection than does 2D-based feature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chansangpetch, S., Rojanapongpun, P., Lin, S.C.: Anterior segment imaging for angle closure. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 188, xvi–xxix (2018)
Ang, M., Baskaran, M., et al.: Anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Progr. Retinal Eye Res. 66, 132–156 (2018)
Xu, B.Y., Chiang, M., et al.: Deep learning classifiers for automated detection of gonioscopic angle closure based on anterior segment OCT images. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 208, 273–280 (2019)
Zhao, Y., et al.: Automated tortuosity analysis of nerve fibers in corneal confocal microscopy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39, 2725–2737 (2020)
Fu, H., Xu, Y., et al.: Segmentation and quantification for angle-closure glaucoma assessment in anterior segment OCT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36(9), 1930–1938 (2017)
Fu, H., Baskaran, M., et al.: A deep learning system for automated angle-closure detection in anterior segment optical coherence tomography images. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 203, 37–45 (2019)
Zhao, Y., et al.: Retinal vascular network topology reconstruction and artery/vein classification via dominant set clustering. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(2), 341–356 (2019)
Wang, B., Sakata, L.M., et al.: Quantitative iris parameters and association with narrow angles. Ophthalmology 117(1), 11–17 (2010)
Huang, J., Wang, Z., Wu, Z., Li, Z., Lai, K., Ge, J.: Comparison of ocular biometry between eyes with chronic primary angle-closure glaucoma and their fellow eyes with primary angle-closure or primary angle-closure suspect. J. Glaucoma 24(4), 323–327 (2015)
Zhao, Y., et al.: Uniqueness-driven saliency analysis for automated lesion detection with applications to retinal diseases. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11071, pp. 109–118. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00934-2_13
Ni Ni, S., Tian, J., Marziliano, P., Wong, H.T.:Anterior chamber angle shape analysis and classification of Glaucomain SS-OCT images. J. Ophthalmol. 2014 (2014)
Shang, Q., Zhao, Y., et al.: Automated iris segmentation from anterior segment OCT images with occludable angles via local phase tensor. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 4745–4749. IEEE (2019)
Cho, H.k., Ahn, D., Kee, C.: Evaluation of circumferential angle closure using iridotrabecular contact index after laser iridotomy by swept-source optical coherence tomography. Acta Ophthalmol. 95(3), e190–e196 (2017)
Zhao, Y., et al.: Automatic 2-D/3-D vessel enhancement in multiple modality images using a weighted symmetry filter. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(2), 438–450 (2017)
Fu, H., et al.: A deep learning system for automated angle-closure detection in anterior segment optical coherence tomography images. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 203, 37–45 (2019)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Gu, Z., Cheng, J., et al.: CE-Net: context encoder network for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(10), 2281–2292 (2019)
Corsini, M., Cignoni, P., Scopigno, R.: Efficient and flexible sampling with blue noise properties of triangular meshes. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 18(6), 914–924 (2012)
Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., et al.: Region-based saliency estimation for 3d shape analysis and understanding. Neurocomputing 197, 1–13 (2016)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017)
Qi, C.R., Su, H., Mo, K., Guibas, L.J.: Pointnet: deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 652–660 (2017)
Xu, Y., Liu, J., et al.: Anterior chamber angle classification using multiscale histograms of oriented gradients for glaucoma subtype identification. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 3167–3170. IEEE (2012)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing System, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LZ19F010001,LQ19H180001), Ningbo “2025 S&T Megaprojects” (2019B10033, 2019B10061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hao, J. et al. (2020). Reconstruction and Quantification of 3D Iris Surface for Angle-Closure Glaucoma Detection in Anterior Segment OCT. In: Martel, A.L., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2020. MICCAI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12265. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59722-1_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59722-1_68
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59721-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59722-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)