Abstract
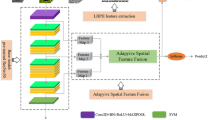
Predicting malignant potential of breast lesions based on breast ultrasound (BUS) images is crucial for computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system for breast cancer. However, since breast lesions in BUS images have various shapes with relatively low contrast and the textures of breast lesions are often complex, it still remains challenging to predict the malignant potential of breast lesions. In this paper, a novel multi-scale gradational-order fusion (MsGoF) framework is proposed to make full advantages of features from different scale images for predicting malignant potential of breast lesions. Specifically, the multi-scale patches are first extracted from the annotated lesions in BUS images as the multi-channel inputs. Multi-scale features are then automatically learned and fused in several fusion blocks that armed with different fusion strategies to comprehensively capture morphological characteristics of breast lesions. To better characterize complex textures and enhance non-linear modeling capability, we further propose isotropous gradational-order feature module in each block to learn and combine different-order features. Finally, these multi-scale gradational-order features are utilized to perform prediction for malignant potential of breast lesions. The major advantage of our framework is embedding the gradational-order feature module into a fusion block, which is used to deeply integrate multi-scale features. The proposed model was evaluated on an open dataset by using 5-fold cross-validation. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MsGoF framework obtains the promising performance when compared with other deep learning-based methods.
Z. Ning and C. Tu—Equally contribute to this paper.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeSantis, C., Ma, J., Bryan, L., Jemal, A.: Breast cancer statistics 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 64(1), 52–62 (2014)
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Jemal, A.: Cancer statistics 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 69(1), 7–34 (2019)
Wang, Y., et al.: Deeply-supervised networks with threshold loss for cancer detection in automated breast ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(4), 833–879 (2019)
Qi, X., et al.: Automated diagnosis of breast ultrasonography images using deep neural networks. Med. Image Anal. 52, 185–198 (2019)
Huang, Q., Zhang, F., Li, X.: Machine learning in ultrasound computer-aided diagnostic systems: a survey. BioMed Res. Int. 2018(7), 1–10 (2018)
Litjens, G., et al.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017)
Cheng, J.Z., et al.: Computer-aided diagnosis with deep learning architecture: applications to breast lesions in us images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 1–13 (2016)
Yap, M.H., et al.: Automated breast ultrasound lesions detection using convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 22(4), 1218–1226 (2017)
Byra, M., et al.: Breast mass classification in sonography with transfer learning using a deep convolutional neural network and color conversion. Med. Phys. 46(2), 746–755 (2019)
Lee, H., Park, J., Hwang, J.Y.: Channel attention module with multi-scale grid average pooling for breast cancer segmentation in an ultrasound image. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 67(7), 1344–1353 (2020)
Zoumpourlis, G., Doumanoglou, A., Vretos, N., Daras, P.: Non-linear convolution filters for CNN-based learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4761–4769 (2017)
Gao, Z., Xie, J., Wang, Q., Li, P.: Global second-order pooling convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3024–3033 (2019)
Ning, Z., et al.: Pattern classification for gastrointestinal stromal tumors by integration of radiomics and deep convolutional features. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 23(3), 1181–1191 (2018)
Härdle, W.K., Simar, L.: Canonical correlation analysis. In: Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis, pp. 443–454. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45171-7_16
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [61971213, 61671230], and in part by the Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province [2019A1515010417].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ning, Z., Tu, C., Xiao, Q., Luo, J., Zhang, Y. (2020). Multi-scale Gradational-Order Fusion Framework for Breast Lesions Classification Using Ultrasound Images. In: Martel, A.L., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2020. MICCAI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12266. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59724-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59725-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)