Abstract
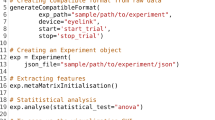
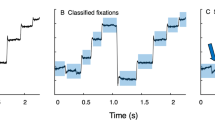
The basic building block of any eye tracking research is the eye fixations. These eye fixations depend on more fine data gathered by the eye tracker device, the raw gaze data. There are many algorithms that can be used to transform the raw gaze data into eye fixation. However, these algorithms require one or more thresholds to be set. A knowledge of the most appropriate values for these thresholds is necessary in order for these algorithms to generate the desired output. This paper examines the effect of a set of different settings of the two thresholds required for the identification-dispersion threshold type of algorithms: the dispersion and duration thresholds on the generated eye fixations. Since this work is at its infancy, the goal of this paper is to generate and visualize the result of each setting and leave the choice for the readers to decide on which setting fits their future eye tracking research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blascheck, T., et al.: Visualization of eye tracking data: a taxonomyand survey. In: Computer Graphics Forum 00, 1–25 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/cgf.13079
Blignaut, P.: Fixation identification: the optimum threshold for a dispersion algorithm. Attention Percept. Psychophys. 71(4), 881–895 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3758/APP.71.4.881
Duchowski, A.T.: Eye Tracking Methodology: Theory and Practice, p. 334. Springer, London (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84628-609-4. ISBN: 9781846286087
Holmqvist, K., et al.: Eye Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide to Methods and Measures, p. 560. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2015). ISBN: 9780198738596
Jacob, R.J.K., Karn, K.S.: Eye tracking in human-computer interaction and usability research: ready to deliver the promises. In: Mind’s Eye: Cognitive and Applied Aspects of Eye Movement Research, Chapter 4, pp. 573–605 (2003)
Nyström, M., Holmqvist, K.: An adaptive algorithm for fixation, saccade, and glissade detection in eyetracking data. Behav. Res. Methods 42(1), 188–204 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.42.1.188. ISSN: 1554–351X
Salvucci, D.D., Goldberg, J.H.: Identifying fixations and saccades in eye-tracking protocols. In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications - ETRA 2000, pp. 71–78. ACM Press, New York (2000). https://doi.org/10.1145/355017.355028. ISBN: 1581132808
Tobii Technology Inc., Tobii TX300 Eye Tracker: Product Description (2010). https://www.tobiipro.com/siteassets/tobii-pro/product-descriptions/tobii-pro-tx300-product-description.pdf. Visited 22 June 2017
Tobii Technology Inc.: Tobii Analytics SDK Developer’s Guide (2013). http://www.acuity-ets.com/downloads/Tobii%20Analytics%20SDK%20Developers%20Guide.pdf. Visited 22 June 2017
Tobii Technology Inc.: Tobii Pro SDK: Develop Eye Tracking Applications for Research (2015). https://www.tobiipro.com/product-listing/tobii-pro-sdk/%7B%5C#%7DDownload. Visited 22 June 2017
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Dr. Ziho Kang for allowing the use of his Human Factors and Simulation Lab equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Alhashim, A.G. (2020). Eye Movement Classification Algorithms: Effect of Settings on Related Metrics. In: Stephanidis, C., Kurosu, M., Degen, H., Reinerman-Jones, L. (eds) HCI International 2020 - Late Breaking Papers: Multimodality and Intelligence. HCII 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12424. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60117-1_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60117-1_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-60116-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-60117-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)