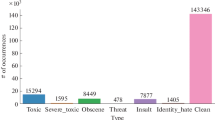
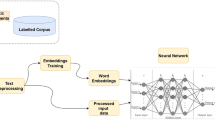
Abstract
The ever-increasing online communication landscape provides circumstances for people with significant differences in their views to cross paths unlike it was ever possible before. This leads to the raise of toxicity in online comments and discussions and makes the development of means to detect instances of such phenomenon critically important. The toxic language detection problem is fairly researched and some solutions produce highly accurate predictions when significantly large datasets are available for training. However, such datasets are not always available for various languages. In this paper, we review different ways to approach the problem targeting transferring knowledge from one language to another: machine translation, multi-lingual models, and domain adaptation. We also focus on the analysis of methods for word embedding such as Word2Vec, FastText, GloVe, BERT, and methods for classification of toxic comment: Naïve Bayes, Random Forest, Logistic regression, Support Vector Machine, Majority vote, and Recurrent Neural Networks. We demonstrate that for small datasets in the Russian language, traditional machine-learning techniques produce highly competitive results on par with deep learning methods, and also that machine translation of the dataset to the English language produces more accurate results than multi-lingual models.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Risch, J., Krestel, R.: Toxic comment detection in online discussions. In: Deep Learning-Based Approaches for Sentiment Analysis, pp. 85–109 (2020)
Badjatiya, P., Gupta, S., Gupta, M., Varma, V.: Deep learning for hate speech detection in tweets. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW), pp. 759–760. International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee (2017)
Matveev, A., et al.: A virtual dialogue assistant for conducting remote exams. In: Proceedings of the 26th Conference of Open Innovations Association FRUCT, pp. 284–290 (2020)
Elnaggar, A., Waltl, B., Glaser, I., Landthaler, J., Scepankova, E., Matthes, F.: Stop illegal comments: a multitask deep learning approach. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, pp. 41–47 (2018)
Pitsilis, G.K., Ramampiaro, H., Langseth, H.: Effective hate-speech detection in Twitter data using recurrent neural networks. Appl. Intell. 48(12), 4730–4742 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1242-y
Wang, C.: Interpreting neural network hate speech classifiers. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Abusive Language Online, Brussels, Belgium, pp. 86–92. Association for Computational Linguistics (2018)
Risch, J., Krebs, E., Loser, A., Riese, A., Krestel, R.: Fine-grained classification of offensive language. In: Proceedings of GermEval (co-located with KONVENS), pp. 38–44 (2018)
Banik, N., Rahman, M.H.H.: Toxicity detection on Bengali social media comments using supervised models. In: International Conference on Innovation in Engineering and Technology (ICIET) (2019)
Kharlamov, A.A., Orekhov, A.V., Bodrunova, S.S., Lyudkevich, N.S.: Social network sentiment analysis and message clustering. In: El Yacoubi, S., Bagnoli, F., Pacini, G. (eds.) INSCI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11938, pp. 18–31. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34770-3_2
Zucco, C., Calabrese B., Agapito, G., Hiram Guzzi, P., Cannataro M.: Sentiment analysis for mining texts and social networks data: methods and tools. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 10(1), 1–32 (2020)
Gupta, S., Singh, A., Ranjan, J.: Sentiment analysis: usage of text and emoji for expressing sentiments. In: Advances in Data and Information Sciences, pp. 477–486 (2020)
Sarkar, D.: Sentiment analysis. In: Text Analytics with Python, pp. 567–629 (2019)
Risch, J., Krestel, R.: Aggression identification using deep learning and data augmentation. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (2018)
Morzhov, S.V.: Modern approaches to detect and classify comment toxicity using neural networks. Model. Anal. Inf. Syst. 27(1), 48–61 (2020)
Qian, J., ElSherief, M., Belding, E.M., Yang Wang, W.: Leveraging intra-user and inter-user representation learning for automated hate speech detection. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, vol. 2, pp. 118–123 (2018)
D’Sa, A., Illina, I., Fohr, D.: Towards non-toxic landscapes: automatic toxic comment detection using DNN (2019)
Saia, R., Corriga, A., Mulas, R., Recupero, D.R., Carta, S.: A supervised multi-class multi-label word embeddings approach for toxic comment classification. In: 11th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (KDIR-2019), Vienna, Austria (2019)
Shtovba, S., Petrychko, M., Shtovba, O.: Detection of social network toxic comments with usage of syntactic dependencies in the sentences. In: The Second International Workshop on Computer Modeling and Intelligent Systems, CEUR Workshop 2353 (2019)
Shtovba, S., Shtovba, O., Yahymovych, O., Petrychko, M.: Impact of the syntactic dependencies in the sentences on the quality of the identification of the toxic comments in the social networks. In: SWVNTU, no. 4 (2019)
Obadimu, A., Mead, E.L., Hussain, H., Agarwal, N.: Identifying toxicity within YouTube video comment text data (2019)
Saif, M.A., Medvedev, A.N., Medvedev, M.A., Atanasova, T.: Classification of online toxic comments using the logistic regression and neural networks models. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2048, no. 1, p. 060011 (2018)
Hosam, O.: Toxic comments identification in Arabic social media. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. Ind. Manage. Appl. 219–226 (2019)
Haralabopoulos, G., Anagnostopoulos, I., McAuley, D.: Ensemble deep learning for multilabel binary classification of user-generated content. Algorithms 13(4), 83 (2020)
Banitz, B.: Machine translation: a critical look at the performance of rule-based and statistical machine translation. In: Cad. Tradução, val. 40, pp. 54–71 (2020)
López-Pereira, A.: Neural machine translation and statistical machine translation: perception and productivity. In: Tradumàtica Tecnol. la traducció (2019)
Wang, X., Lu, Z., Tu, Z., Li, H., Xiong, D., Zhang, M.: Neural machine translation advised by statistical machine translation (2016)
Liu C.L., Hsu T.Y., Chuang, Y.S., Lee, H.: A study of cross-lingual ability and language-specific information in multilingual BERT (2020)
Virtanen, A., et al.: Multilingual is not enough: BERT for Finnish (2019)
Vries, W., Cranenburgh, A., Bisazza, A., Caselli, T., Noord, G., Nissim, M.: BERTje: a Dutch BERT model (2019)
Ghosh, S., Singh, R., Vatsa, M., Ratha, N., Patel, V.M.: Domain adaptation for visual understanding. In: Domain Adaptation for Visual Understanding, pp. 1–15 (2020)
Kouw, W.M.: On domain-adaptive machine learning (2018)
Li, Z., Tang, X., Li, W., Wang, C., Liu, C., He, J.: A two-stage deep domain adaptation method for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens. 12(7), 1054 (2020)
Xu, S., Mu, X., Zhang, X., Chai, D.: Unsupervised remote sensing domain adaptation method with adversarial network and auxiliary task. In: Cehui Xuebao/Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin., pp. 1969–1977 (2017)
Mikolov, T., Corrado, G.S, Chen, K., Dean, J.: Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2013), pp 1–12 (2013)
Bojanowski, P., Grave, E., Joulin, A., Mikolov, T.: Enriching word vectors with subword information (2016)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pretraining of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding (2018)
Pires, T., Schlinger, E., Garrette, D.: How multilingual is multilingual BERT? (2019)
Wu, S., Dredze, M.: Beto, Bentz, Becas. The Surprising Cross-Lingual Effectiveness of BERT (2019)
Vaidya, A., Mai, F., Ning, Y.: Empirical analysis of multi-task learning for reducing model bias in toxic comment detection (2020)
Reichert, E., Qiu, H., Bayrooti, J.: Reading between the demographic lines: resolving sources of bias in toxicity classifiers (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially financially supported by the Government of the Russian Federation (Grant 08-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Makhnytkina, O., Matveev, A., Bogoradnikova, D., Lizunova, I., Maltseva, A., Shilkina, N. (2020). Detection of Toxic Language in Short Text Messages. In: Karpov, A., Potapova, R. (eds) Speech and Computer. SPECOM 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12335. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60276-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60276-5_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-60275-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-60276-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)