Abstract
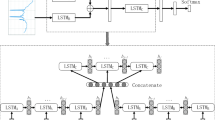
In this work, we propose a method to predict the progress of the hyperthyroidism disease based on the sequence of the patient’s blood test data in the early stage. Long-Short-Term-Memory (LSTM) network is employed to process the sequence information in the tests. We design an adaptive loss function for the LSTM learning. We set bigger weights to the blood test data samples which are nearby the range boundaries when judging the hyperthyroidism. We have carried out a set of experiments against a real world dataset from a hospital in Shanghai, China. The experimental results show that our method outperforms the traditional LSTM significantly.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strieder, T.G.A., et al.: Prediction of progression to overt hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism in female relatives of patients with autoimmune thyroid disease using the thyroid events amsterdam (THEA) score. Arch. Intern. Med. 168(15), 1657 (2008)
Wu, C.C., Yeh, W.C., et al.: Prediction of fatty liver disease using machine learning algorithms. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 170, 23–29 (2018)
Wang, Y., Zhao, F., et al.: Role of selenium intake for risk and development of hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 104, 568–580 (2019)
Sarraf, S.: French word recognition through a quick survey on recurrent neural networks using long-short term memory RNN-LSTM. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 39(1), 250–267 (2018)
Iyidir, O.T., et al.: Evaluation of ambulatory arterial stiffness index in hyperthyroidism. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 47, 1751–1756 (2017)
Chen, Y.K., Lin, C.L., et al.: Cancer risk in patients with Graves’ disease: a nationwide cohort study. Thyroid 23(7), 879–884 (2013)
Mckinney, S.M., et al.: International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature 577, 89–94 (2020)
World Health Organization, Global Health and Aging. https://www.who.int/ageing/publications/global_health.pdf
Vos, X.G., Endert, E., et al.: Predicting the risk of recurrence before the start of antithyroid drug therapy in patients with Graves’ hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 101, 1381–1389 (2016)
Wiersinga, W., et al.: Predictive score for the development or progression of Graves’ orbitopathy in patients with newly diagnosed Graves’ hyperthyroidism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 178, 635–643 (2018)
Salvi, M., et al.: Prediction of the progression of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy at first ophthalmologic examination: use of a neural network. Thyroid 12(3), 233–6 (2002)
Stephanie, L.L., et al.: What is the typical disease progression of hyperthyroidism? Medscape Monday, 24 February 2020
Choi, E., Bahadori, M.T., et al.: GRAM: graph-based attention model for healthcare representation learning. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD 2017, pp. 787–795 (2017)
Ma, F.L., You, Q.Z., et al.: KAME: knowledge-based attention model for diagnosis prediction in healthcare. In: CIKM 2018, pp. 743–752 (2018)
Ma, F.L., Chitta, R., et al.: Dipole: diagnosis prediction in healthcare via attention-based bidirectional recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD 2017, pp. 1903–1911 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lu, H., Wang, M., Zhao, W., Su, T., Yang, J. (2020). Hyperthyroidism Progress Prediction with Enhanced LSTM. In: Wang, X., Zhang, R., Lee, YK., Sun, L., Moon, YS. (eds) Web and Big Data. APWeb-WAIM 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12318. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60290-1_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60290-1_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-60289-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-60290-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)