Abstract
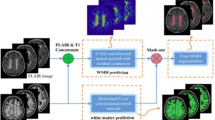
Brain segmentation is key to brain structure evaluation for disease diagnosis and treatment. Much research has been invested to study brain segmentation. However, prior research has not considered separating actual brain pixels from the background of brain images. Not performing such separation may (a) distort brain segmentation models and (b) introduce overhead to the modeling performance. In this paper, we improve the performance of brain segmentation using 3D, fully Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models. We use (i) infant and adult datasets, (ii) a multi-instance loss method to separate actual brain pixels from the background and (iii) Gabor filter banks and K-means clustering to provide additional segmentation features. Our model obtains dice coefficients of \(87.4\%\)–\(94.1\%\) (i.e., an improvement of up to 11% to the results of five state-of-the-art models). Unlike prior studies, we consult experts in medical imaging to evaluate our segmentation results. We observe that our results are fairly close to the manual reference. Moreover, we observe that our model is 1.2x–2.6x faster than prior models. We conclude that our model is more efficient and accurate in practice for both infant and adult brain segmentation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Visser, E., et al.: Automatic segmentation of the striatum and globus pallidus using mist: multimodal image segmentation tool. NeuroImage 125, 479–497 (2016)
Bao, S., Chung, A.C.: Multi-scale structured CNN with label consistency for brain MR image segmentation. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 6(1), 113–117 (2018)
Chen, H., Dou, Q., Yu, L., Qin, J., Heng, P.A.: VoxResNet: deep voxelwise residual networks for brain segmentation from 3D MR images. NeuroImage 170, 446–455 (2018)
Wang, L., et al.: Benchmark on automatic 6-month-old infant brain segmentation algorithms: the ISEG-challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 38(9), 2219–2230 (2019)
Bernal, J., et al.: Deep convolutional neural networks for brain image analysis on magnetic resonance imaging. Artif. Intell. Med. 95, 64–81 (2017)
Dolz, J., Desrosiers, C., Ayed, I.B.: 3D fully convolutional networks for subcortical segmentation in MRI: a large-scale study. NeuroImage 170, 456–470 (2018)
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Segnet, R.: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017)
Fechter, T., Adebahr, S., Baltas, D., Ayed, I.B., Desrosiers, C., Dolz, J.: Esophagus segmentation in CT via 3D fully convolutional neural network and random walk. Med. Phys. 44(12), 6341–6352 (2017)
de Brebisson, A., Montana, G.: Deep neural networks for anatomical brain segmentation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 20–28 (2015)
Moeskops, P., Viergever, M.A., Mendrik, A.M., de Vries, L.S., Benders, M.J., Isgum, I.: Automatic segmentation of MR brain images with a convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1252–1261 (2016)
Glorot, X., Bengio, Y.: Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: The Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 249–256 (2010)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv preprint arXiv. 1502.03167 (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1026–1034 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Foulds, J., Frank, E.: A review of multi-instance learning assumptions. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 25(1), 1–25 (2010)
Deng, X., Feng, S., Guo, P., Yin, Q.: Fast image recognition with Gabor filter and pseudoinverse learning autoencoders. In: Cheng, L., Leung, A.C.S., Ozawa, S. (eds.) ICONIP 2018. LNCS, vol. 11306, pp. 501–511. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04224-0_43
Kamnitsas, K., et al.: Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 36, 61–78 (2017)
Zhang, W., et al.: Deep convolutional neural networks for multi-modality isointense infant brain image segmentation. NeuroImage 108, 214–224 (2015)
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S.S., Brox, T., Ronneberger, O.: 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9901, pp. 424–432. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Nie, D., Wang, L., Gao, Y., Shen, D.: Fully convolutional networks for multi-modality isointense infant brain image segmentation. In: IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 1342–1345 (2016)
Mahbod, A., Chowdhury, M., Smedby, O., Wang, C.: Automatic brain segmentation using artificial neural networks with shape context. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 101, 74–79 (2018)
Stollenga, M.F., Byeon, W., Liwicki, M., Schmidhuber, J.: Parallel multi-dimensional with application to fast biomedical volumetric image segmentation. CoRR abs/1506.07452. arXiv:1506.07452 (2018)
Hitesh, A., Gupta, A., Raju, A.: Non-linear dimension reduction of Gabor features for noise-robust ASR. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1715–1719 (2014)
Jonathan, L., Evan, S., Trevor, D.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Xavier, G., Yoshua, B.: Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: The Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 249–256 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Khaled, A., Own, CM., Tao, W., Ghaleb, T.A. (2020). Improved Brain Segmentation Using Pixel Separation and Additional Segmentation Features. In: Wang, X., Zhang, R., Lee, YK., Sun, L., Moon, YS. (eds) Web and Big Data. APWeb-WAIM 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12318. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60290-1_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60290-1_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-60289-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-60290-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)