Abstract
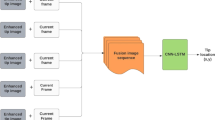
Accurate, real-time segmentation of thin, deformable, and moving objects in noisy medical ultrasound images remains a highly challenging task. This paper addresses the problem of segmenting guidewires and other thin, flexible devices from 4D ultrasound image sequences acquired during minimally-invasive surgical interventions. We propose a deep learning method based on a recurrent fully convolutional network architecture whose design captures temporal information from dense 4D (3D+time) image sequences. The network uses convolutional gated recurrent units interposed between the halves of a VNet-like model such that the skip-connections embedded in the encoder-decoder are preserved. Testing on realistic phantom tissues, ex vivo and human cadaver specimens, and live animal models of peripheral vascular and cardiovascular disease, we show that temporal encoding improves segmentation accuracy compared to standard single-frame model predictions in a way that is not simply associated to an increase in model size. Additionally, we demonstrate that our approach may be combined with traditional techniques such as active splines to further enhance stability over time.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shu, J., Santulli, G.: Update on peripheral artery disease: epidemiology and evidence-based facts. Atherosclerosis 275, 379–381 (2018)
Roth, G.A., Johnson, C., Abajobir, A., et al.: Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 70(1), 1–25 (2017)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.: V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 4th International Conference on 3D Vision (2016)
Mishra, D., Chaudhury, S., Sarkar, M., Soin, A.: Ultrasound image segmentation: a deeply supervised network with attention to boundaries. IEEE TMBE (2018)
Tetteh, G., et al.: DeepVesselNet: vessel segmentation, centerline prediction and bifurcation detection in 3D angiographic volumes. arXiv:1803.09340 [cs.CV] (2018)
Merkow, J., Marsden, A., Kriegman, D., Tu, Z.: Dense volume-to-volume vascular boundary detection. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9902, pp. 371–379. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46726-9_43
Yurdakul, E., Yemez, Y.: Semantic segmentation of RGBD videos with recurrent fully convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the ICCV 2017. IEEE (2017)
Tokmakov, P., Alahari, K., Schmid, C.: Learning video object segmentation with visual memory. In: Proceedings of the IEEE ICCV 2017, pp. 4491–4500. IEEE (2017)
Valipour, S., Siam, M., Jagersand, M., Ray, N.: Recurrent fully convolutional networks for video segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE WACV 2017. IEEE, Santa Rosa (2017)
Oh, S.W., Lee, J.Y., Xu, N., Kim, S.J.: Video object segmentation using space-time memory networks. In: Proceedings of the ICCV 2019. IEEE (2019)
Tong, Q., et al.: RIANet: recurrent interleaved attention network for cardiac MRI segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 109, 290–302 (2019)
Chen, J., Yang, L., Zhang, Y., Alber, M., Chen, D.Z.: Combining fully convolutional and recurrent neural networks for 3D biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the NIPS 2016, pp. 3036–3044. Curran (2016)
Myronenko, A., et al.: 4D CNN for semantic segmentation of cardiac volumetric sequences. In: Pop, M., et al. (eds.) STACOM 2019. LNCS, vol. 12009, pp. 72–80. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39074-7_8
Sun, C., et al.: Segmentation of 4D images via space-time neural networks. In: Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2020. SPIE (2020)
Kang, J., Samarasinghe, G., Senanayak, U., Conjeti, S., Sowmya, A.: Deep learning for volumetric segmentation in spatio-temporal data: application to segmentation of prostate in DCE-MRI. In: Proceedings of the ISBI 2019, pp. 61–65. IEEE (2019)
Cheng, J., Tsai, Y., Wang, S., Yang, M.S.: SegFlow: joint learning for video object segmentation and optical flow. In: Proceedings of the ICCV (2017)
Gao, Y., Phillips, J., Zheng, Y., Min, R., Fletcher, P., Gerig, G.: Fully convolutional structured LSTM networks for joint 4D medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the ISBI 2019, pp. 1104–1108. IEEE (2019)
Milletari, F., Rieke, N., Baust, M., Esposito, M., Navab, N.: CFCM: segmentation via coarse to fine context memory. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11073, pp. 667–674. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00937-3_76
Arbelle, A., Raviv, T.R.: Microscopy cell segmentation via convolutional LSTM networks. In: Proceedings of the ISBI (2019)
Mathai, T., Jin, L., Gorantla, V., Galeotti, J.: Fast vessel segmentation and tracking in ultra high-frequency ultrasound images. arXiv:1807.08784 [cs.CV] (2019)
Fehling, M.K., Grosch, F., Schuster, M.E., Schick, B., Lohscheller, J.: Fully automatic segmentation of glottis and vocal folds in endoscopic laryngeal high-speed videos using a deep Convolutional LSTM Network. PLoS One 15(2), e0227791 (2020)
Ballas, N., Yao, L., Pal, C., Courville, A.: Delving deeper into convolutional networks for learning video representations. arXiv:1511.06432 [cs.CV] (2015)
Odena, A., Dumoulin, V., Olah, C.: Deconvolution and checkerboard artifacts (2016). http://distill.pub/2016/deconv-checkerboard/
Lesage, D., Angelini, E.D., Bloch, I., Funka-Lea, G.: A review of 3D vessel lumen segmentation techniques: models, features and extraction schemes. Med. Image Anal. 13(6), 819–845 (2009)
Zhao, F., Chen, Y., Hou, Y., He, X.: Segmentation of blood vessels using rule-based and machine-learning-based methods: a review. Multimedia Syst. 25(2), 109–118 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-017-0580-7
Slabaugh, G., Kong, K., Unal, G., Fang, T.: Variational guidewire tracking using phase congruency. In: Ayache, N., Ourselin, S., Maeder, A. (eds.) MICCAI 2007. LNCS, vol. 4792, pp. 612–619. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75759-7_74
Chang, P., Rolls, A., Praetere, H., Poorten, E.: Robust catheter and guidewire tracking using B-spline tube model and pixel-wise posteriors. IEEE Autom. Robot. Lett. 1, 303–308 (2016)
Dubuisson, M.P., Jain, A.K.: A modified Hausdorff distance for object matching. In: ICPR 1994, Jerusalem, Israel, pp. A:566–A:568 (1994)
Taha, A.A., Hanbury, A.: Metrics for evaluating 3D medical image segmentation: analysis, selection, and tool. BMC Med. Imaging 15, 29 (2015)
Yang, H., Shan, C., Kolen, A., With, P.H.N.: Improving catheter segmentation and localization in 3D cardiac ultrasound using direction-fused FCN. In: Proceedings of the ISBI (2019)
Gherardini, M., Mazomenos, E., Menciassi, A., Stoyanov, D.: Catheter segmentation in X-ray fluoroscopy using synthetic data and transfer learning with light U-nets. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 192, 105420 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Doug Stanton for the development of the phantom models used in the study. We would like to acknowledge Vipul Pai Raikar, Mingxin Zheng, and Sibo Li for their assistance with the data acquisition setup. We thank Shyam Bharat for reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lee, B.C., Vaidya, K., Jain, A.K., Chen, A. (2020). Guidewire Segmentation in 4D Ultrasound Sequences Using Recurrent Fully Convolutional Networks. In: Hu, Y., et al. Medical Ultrasound, and Preterm, Perinatal and Paediatric Image Analysis. ASMUS PIPPI 2020 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12437. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60334-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60334-2_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-60333-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-60334-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)