Abstract
This paper proposes a family of hyperelliptic curves of genus two for public-key cryptographic primitives. Being subfield curves, the members of this family are easy to generate. Although slightly slower than elliptic curves at the same security level, hyperelliptic curves of our family exhibit performance comparable to widely used hyperelliptic curves over prime fields.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
References
Adleman, L.M., Huang, M.-D.A.: Counting rational points on curves and abelian varieties over finite fields. In: Cohen, H. (ed.) ANTS 1996. LNCS, vol. 1122, pp. 1–16. Springer, Heidelberg (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-61581-4_36
Avanzi, R.M.: Aspects of hyperelliptic curves over large prime fields in software implementations. In: Joye, M., Quisquater, J.-J. (eds.) CHES 2004. LNCS, vol. 3156, pp. 148–162. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28632-5_11
Bos, J.W., Costello, C., Hisil, H., Lauter, K.: Fast cryptography in genus 2. In: Johansson, T., Nguyen, P.Q. (eds.) EUROCRYPT 2013. LNCS, vol. 7881, pp. 194–210. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38348-9_12
Buhler, J., Koblitz, N.: Lattice basis reduction, jacobi sums and hyperelliptic cryptosystems. Bull. Aust. Math. Soc. 58(1), 147–154 (1998)
Cantor, D.G.: Computing in the Jacobian of a hyperelliptic curve. Math. Comput. 48(177), 99–101 (1987)
Cohen, H., et al.: Handbook of Elliptic and Hyperelliptic Curve Cryptography. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London (2005)
Costello, C., Lauter, K.: Group law computations on Jacobians of hyperelliptic curves. In: Miri, A., Vaudenay, S. (eds.) SAC 2011. LNCS, vol. 7118, pp. 92–117. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28496-0_6
Diem, C.: The GHS attack in odd characteristic. J. Ramanujan Math. Soc. 18(1), 1–32 (2003)
Elkies, N.D., et al.: Elliptic and modular curves over finite fields and related computational issues. AMS IP Stud. Adv. Math. 7, 21–76 (1998)
Furukawa, E., Kawazoe, M., Takahashi, T.: Counting points for hyperelliptic curves of type \(y^2=x^5+ax\) over finite prime fields. In: Matsui, M., Zuccherato, R.J. (eds.) SAC 2003. LNCS, vol. 3006, pp. 26–41. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24654-1_3
Galbraith, S.D.: Weil descent of Jacobians. Electron. Notes Discrete Math. 6, 459–468 (2001)
Galbraith, S.D.: Mathematics of Public Key Cryptography. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Gaudry, P., Hess, F., Smart, N.: Constructive and destructive facets of Weil descent. J. Cryptol. 15(1), 19–46 (2002)
Gaudry, P., Schost, E.: Genus 2 point counting over prime fields. J. Symb. Comput. 47, 368–400 (2012)
Gaudry, P.: Index calculus for abelian varieties of small dimension and the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem. J. Symb. Comput. 44(12), 1690–1702 (2009)
Gaudry, P., Gürel, N.: An extension of Kedlaya’s point-counting algorithm to superelliptic curves. In: Boyd, C. (ed.) ASIACRYPT 2001. LNCS, vol. 2248, pp. 480–494. Springer, Heidelberg (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45682-1_28
Gaudry, P., Harley, R.: Counting points on hyperelliptic curves over finite fields. In: Bosma, W. (ed.) ANTS 2000. LNCS, vol. 1838, pp. 313–332. Springer, Heidelberg (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/10722028_18
Gaudry, P., Thomé, E.: The mpFq library and implementing curve-based key exchanges. In: SPEED: Software Performance Enhancement for Encryption and Decryption, pp. 49–64. ECRYPT Network of Excellence in Cryptology, Amsterdam, Netherlands, June 2007
Granlund, T.: The GNU multiple precision arithmetic library (1996). https://gmplib.org/
Harley, R.: Fast arithmetic on genus 2 curves (2000). http://cristal.inria.fr/ harley/hyper
Hess, F.: The GHS attack revisited. In: Biham, E. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 2003. LNCS, vol. 2656, pp. 374–387. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-39200-9_23
Hisil, H., Costello, C.: Jacobian coordinates on genus 2 curves. J. Cryptol. 30(2), 572–600 (2017)
Huang, M.D., Ierardi, D.: Counting rational points on curves over finite fields. In: Proceedings of 1993 IEEE 34th Annual Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 616–625. IEEE (1993)
Huang, Y., Su, Z., Zhang, F., Ding, Y., Cheng, R.: Quantum algorithm for solving hyperelliptic curve discrete logarithm problem. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(2), 1–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2562-5
Joux, A., Vitse, V.: Cover and decomposition index calculus on elliptic curves made practical. In: Pointcheval, D., Johansson, T. (eds.) EUROCRYPT 2012. LNCS, vol. 7237, pp. 9–26. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29011-4_3
Kedlaya, K.S., Sutherland, A.V.: Computing L-series of hyperelliptic curves. In: van der Poorten, A.J., Stein, A. (eds.) ANTS 2008. LNCS, vol. 5011, pp. 312–326. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79456-1_21
Koblitz, N.: Elliptic curve cryptosystems. Math. Comput. 48(177), 203–209 (1987)
Lange, T.: Formulae for arithmetic on genus 2 hyperelliptic curves. Appl. Algebra Eng. Commun. Comput. 15, 295–328 (2004)
Lange, T.: Efficient arithmetic on hyperelliptic curves. IEM (2002)
Lidl, R., Niederreiter, H.: Finite Fields. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997)
Locke, G., Gallagher, P.: Digital signature standard (DSS). Federal Inf. Process. Stand. Publ. 186–3 (2009)
Matsuo, K., Chao, J., Tsujii, S.: Fast genus two hyperelliptic curve cryptosystems. Technical report ISEC2001-23, IEICE (2001)
Menezes, A., Wu, Y., Zuccherato, R.: An elementary introduction to hyperelliptic curves. Research report, Faculty of Mathematics, University of Waterloo (1996). http://books.google.co.in/books?id=yxZYNAEACAAJ
Mumford, D.: Tata Lectures on Theta II. Progress in Mathematics, vol. 43, pp. 243–265. Springer, Heidelberg (1984)
Nagao, K.: Decomposition attack for the Jacobian of a hyperelliptic curve over an extension field. In: Hanrot, G., Morain, F., Thomé, E. (eds.) ANTS 2010. LNCS, vol. 6197, pp. 285–300. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14518-6_23
Pelzl, J., Wollinger, T., Guajardo, J., Paar, C.: Hyperelliptic curve cryptosystems: closing the performance gap to elliptic curves. In: Walter, C.D., Koç, Ç.K., Paar, C. (eds.) CHES 2003. LNCS, vol. 2779, pp. 351–365. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-45238-6_28
Pila, J.: Frobenius maps of abelian varieties and finding roots of unity in finite fields. Math. Comput. 55(192), 745–763 (1990)
Proos, J., Zalka, C.: Shor’s discrete logarithm quantum algorithm for elliptic curves. arXiv preprint quant-ph/0301141 (2003)
Sadanandan, S.: Counting in the Jacobian of hyperelliptic curves. Ph.D. thesis, Technische Universität München (2010)
Satoh, T.: Generating genus two hyperelliptic curves over large characteristic finite fields. In: Joux, A. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 2009. LNCS, vol. 5479, pp. 536–553. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01001-9_31
Schoof, R.: Elliptic curves over finite fields and computation of square roots mod p. Math. Comput. 44(170), 483–494 (1985)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134. IEEE (1994)
Shoup, V.: NTL: a library for doing number theory (2001). http://www.shoup.net/ntl/
Miller, V.S.: Use of elliptic curves in cryptography. In: Williams, H.C. (ed.) CRYPTO 1985. LNCS, vol. 218, pp. 417–426. Springer, Heidelberg (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-39799-X_31
Wollinger, T.: Software and hardware implementation of hyperelliptic curve cryptosystems. Citeseer (2004)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the anonymous referees for providing useful suggestions. This work is funded by Space Application Center, Ahmedabad, ISRO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendix
Appendix
This section lists a set of subfield curves at various security levels. These curves are of the special form \(y^2=x^5+x+a\), \(a\in \mathbb {F}_p\), where p is a single-precision prime. The curves are naturally defined over the quintic extension \(\mathbb {F}_q=\mathbb {F}_{p^5}\). We represent \(\mathbb {F}_q\) as \(\mathbb {F}_p[t]/\langle F(t)\rangle \), where \(F(t)\in \mathbb {F}_p[t]\) is a monic irreducible polynomial of degree 5. The Jacobian of a curve over \(\mathbb {F}_p\) and \(\mathbb {F}_q\) are denoted by \(\mathbb {J}_p\) and \(\mathbb {J}_q\), and their sizes by \(n_p=|\mathbb {J}_p|\) and \(n_q=|\mathbb {J}_q|\). We have \(\mathbb {J}_q=\mathbb {J}_p\oplus G\). For all the curves listed here, G is a group of prime order \(n=|G|=n_q/n_p\). At all security levels, it is recommended to use the curves with \(n=2^{\cdots }-\cdots \). The curves with \(n=2^{\cdots }+\cdots \) should work well, but would be slightly (and unnecessarily) inefficient.
-
Security Level l = 80:
\(p=2^{20}-5=1048571\), \(n\approx 2^{160}\)
\(F(t)=t^5+2\) or \(t^5-2\)
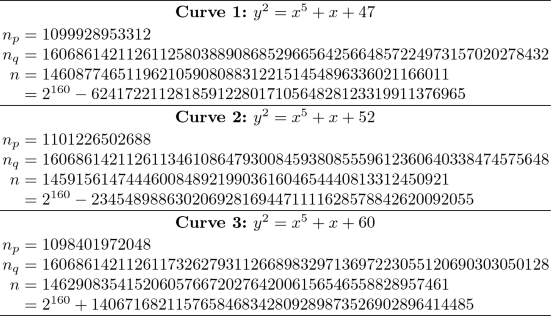
-
Security Level \({\textit{\textbf{l}}} = \mathbf{96:}\)
\(p=2^{24}-17=16777199\), \(n\approx 2^{192}\)
\(F(t)=t^5+t-3\) or \(t^5-4t-1\)

-
Security Level l = 112:
\(p=2^{28}-57=268435399\), \(n\approx 2^{224}\)
\(F(t)=t^5-t-2\)

-
Security Level l = 128:
\(p=2^{32}-2^{17}-61=4294836163\), \(n\approx 2^{256}\),
\(F(t)=t^5+2t-1\)

Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ganguly, A., Das, A., Chowdhury, D.R., Mehta, D. (2020). A Family of Subfield Hyperelliptic Curves for Use in Cryptography. In: Meng, W., Gollmann, D., Jensen, C.D., Zhou, J. (eds) Information and Communications Security. ICICS 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12282. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61078-4_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61078-4_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-61077-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-61078-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)





