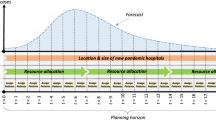
Abstract
Healthcare management, in particular managing a hospital network, is a complex issue which requires taking into account the morbidity process dynamics, simultaneous administration of various therapies, preventive actions, drug supply and responding to emergencies, such as mass casualty traffic incidents, pandemics (e.g. SARS, MERS), etc. The overall objective is to provide appropriate, dedicated aid to patients and affected persons as quickly as possible. One of the aspects of key importance to achieving this objective is the issue of appropriate patient-to-hospital allocation within a specific area. Very often the allocation is determined by constrained resources which the healthcare facilities in the given area have at their disposal, i.e. the number of doctors with specific medical specialties, the number of nurses, the number of beds of specific types in individual hospitals, the number of available medical transportation vehicles, but most importantly, the time limits for initiating successful hospital treatment. Optimal use of constrained resources makes it possible/facilitates optimal allocation in patients, which is essential in emergency situations. The paper proposes a model of optimal patient-to-hospital allocation taking into account the constrained resources of the hospital network and emergency ambulance service which provides medical transportation. The proposed model is formulated using Binary Integer Programming (BIP).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pandemic Influenza Triage Tools. https://www.cdc.gov/cpr/healthcare/pan-flu-app/desktop/pita.html?fbclid=IwAR0mEaCLKvNm8oJn3hfuAhmZp04QmHISVNO3RoJp3ZeYRFzI4UxxUgjAomw. Accessed 8 May 2020
Gurobi. http://www.gurobi.com/. Accessed 8 May 2020
Home-AMPL. https://ampl.com/. Accessed 8 May 2020
Parker, J.: A flexible, large-scale, distributed agent based epidemic model. In: WSC 2007, pp. 1543–1547 (2007)
Larson, R.C.: Simple models of influenza progression within a heterogeneous population. Oper. Res. 55(3), 399–412 (2007)
Lum, M.E., McMillan, A.J., Brook, C.W., Lester, R., Piers, L.S.: Impact of pandemic (HIN1) 2009 influenza on critical care capacity in Victoria. Med. J. Aust. 191(9), 502–506 (2009)
Rico, F., Salari, E., Centeno, G.: Emergency departments nurse allocation to face a pandemic influenza outbreak. In: WSC 2009, pp. 1292–1298 (2007)
Gunes, E.D., Yaman, H.: Health network mergers and hospital re-planning. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 61(2), 275–283 (2010)
Koyuncu, M., Erol, R.: Optimal resource allocation model to mitigate the impact of pandemic influenza: a case study for Turkey. J. Med. Syst. 34(1), 61–70 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9216-y
Yi, W., Ozdamar, L.: A dynamic logistics coordination model for evacuation and support in disaster response activities. EJOR 179(3), 1177–1193 (2007)
Minciardi, R., Sacile, R., Trasforini, E.: Resource allocation in integrated preoperational and operational management of natural hazards. Risk Anal. 29, 62–75 (2009)
Sitek, P., Wikarek, J.: A multi-level approach to ubiquitous modeling and solving constraints in combinatorial optimization problems in production and distribution. Appl. Intell. 48(5), 1344–1367 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1107-9
Goli, A., Aazami, A., Jabbarzadeh, A.: Accelerated cuckoo optimization algorithm for capacitated vehicle routing problem in competitive conditions. Int. J. Artif. Intell. 16(1), 88–112 (2018)
Sitek, P., Wikarek, J.: Capacitated vehicle routing problem with pick-up and alternative delivery (CVRPPAD): model and implementation using hybrid approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 273(1), 257–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-017-2722-x
Sitek, P., Wikarek, J., Nielsen, P.: A constraint-driven approach to food supply chain management. IMDS 117, 2115–2138 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-10-2016-0465
Wikarek, J.: Implementation aspects of hybrid solution framework. In: Szewczyk, R., Zieliński, C., Kaliczyńska, M. (eds.) Recent Advances in Automation, Robotics and Measuring Techniques. AISC, vol. 267, pp. 317–328. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-05353-0_31
Bocewicz, G., Banaszak, Z., Nielsen, I.: Multimodal processes prototyping subject to grid-like network and fuzzy operation time constraints. Ann. Oper. Res. 273(1), 561–585 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-017-2468-5
Kłosowski, G., Gola, A., Świć, A.: Application of fuzzy logic in assigning workers to production tasks. Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, 13th International Conference. AISC, vol. 474, pp. 505–513. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40162-1_54
Relich, M.: Computational intelligence for estimating cost of new product development. Found. Manage. 8(1), 21–34 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sitek, P., Wikarek, J. (2020). Resource-Constrained Model of Optimizing Patient-to-Hospital Allocation During a Pandemic. In: Nguyen, N.T., Hoang, B.H., Huynh, C.P., Hwang, D., Trawiński, B., Vossen, G. (eds) Computational Collective Intelligence. ICCCI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12496. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63007-2_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63007-2_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-63006-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-63007-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)