Abstract
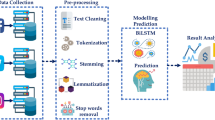
With the number of users of social media and web platforms increasing day-by-day in recent years, cyberbullying has become a ubiquitous problem on the internet. Controlling and moderating these social media platforms manually for online abuse and cyberbullying has become a very challenging task. This paper proposes a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) based approach for the identification and classification of cyberbullying posts. In highly imbalanced input data, a Tomek Links approach does under-sampling to reduce the data imbalance and remove ambiguities in class labelling. Further, the proposed classification model uses Max-Pooling in combination with Bi-directional Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network and attention layers. The proposed model is evaluated using Wikipedia datasets to establish the effectiveness of identifying and classifying cyberbullying posts. The extensive experimental results show that our approach performs well in comparison to competing approaches in terms of precision, recall, with F1 score as 0.89, 0.86 and 0.88, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu, T., Jue, K., Wang, M.: Comment abuse classification with deep learning. Von https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs224n/reports/2762092.pdf. abgerufen (2016)
Wulczyn, E., Thain, N., Dixon, L.: Ex machina: personal attacks seen at scale. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 1391–1399 (2017)
Yin, D., Xue, Z., Hong, L., Davison, B.D., Kontostathis, A., Edwards, L.: Detection of harassment on web 2.0. In: Proceedings of the Content Analysis in the WEB, vol. 2, pp. 1–7 (2009)
Tokunaga, R.S.: Following you home from school: a critical review and synthesis of research on cyberbullying victimization. Comput. Hum. Behav. 26(3), 277–287 (2010)
Schrock, A., Boyd, D.: Problematic youth interaction online: Solicitation, harassment, and cyberbullying. In: Computer-Mediated Communication in Personal Relationships, pp. 368–398 (2011)
Warner, W., Hirschberg, J.: Detecting hate speech on the world wide web. In: Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Language in Social Media, pp. 19–26. Association for Computational Linguistics (2012)
Kwok, I., Wang, Y.: Locate the hate: detecting tweets against blacks. In: Twenty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2013)
Cheng, J., Danescu-Niculescu-Mizil, C., Leskovec, J.: Antisocial behavior in online discussion communities. In: Ninth International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media (2015)
Waseem, Z., Hovy, D.: Hateful symbols or hateful people? Predictive features for hate speech detection on Twitter. In: Proceedings of the NAACL Student Research Workshop, pp. 88–93 (2016)
Waseem, Z.: Are you a racist or am i seeing things? Annotator influence on hate speech detection on Twitter. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on NLP and Computational Social Science, pp. 138–142 (2016)
Ross, B., Rist, M., Carbonell, G., Cabrera, B., Kurowsky, N., Wojatzki, M.: Measuring the reliability of hate speech annotations: the case of the european refugee crisis, arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.08118 (2017)
Nobata, C., Tetreault, J., Thomas, A., Mehdad, Y., Chang, Y.: Abusive language detection in online user content. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 145–153 (2016)
Saleem, H.M., Dillon, K.P., Benesch, S., Ruths, D.: A web of hate: tackling hateful speech in online social spaces, arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.10159 (2017)
Sahlgren, M., Isbister, T., Olsson, F.: Learning representations for detecting abusive language. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Abusive Language Online (ALW2), pp. 115–123 (2018)
Aroyehun, S.T., Gelbukh, A.: Aggression detection in social media: using deep neural networks, data augmentation, and pseudo labeling. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (TRAC-2018), pp. 90–97 (2018)
Mishra, P., Yannakoudakis, H., Shutova, E.: Neural character-based composition models for abuse detection, arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.00378 (2018)
Kumar, R., Ojha, A.K., Malmasi, S., Zampieri, M.: Benchmarking aggression identification in social media. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (TRAC-2018), pp. 1–11 (2018)
Chen, H., McKeever, S., Delany, S.J.: The use of deep learning distributed representations in the identification of abusive text. In: Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, vol. 13, no. 01, pp. 125–133 (2019)
Schuster, M., Paliwal, K.K.: Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(11), 2673–2681 (1997)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Tomek, I.: Two modifications of CNN (1976)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization, arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Machackova, H., Cerna, A., Sevcikova, A., Dedkova, L., Daneback, K.: Effectiveness of coping strategies for victims of cyberbullying. Cyberpsychol.: J. Psychosoc. Res. Cyberspace 7(3) (2013)
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: Glove: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 1532–1543 (2014)
Wieting, J., Bansal, M., Gimpel, K., Livescu, K.: Towards universal paraphrastic sentence embeddings, arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.08198 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Agarwal, A., Chivukula, A.S., Bhuyan, M.H., Jan, T., Narayan, B., Prasad, M. (2020). Identification and Classification of Cyberbullying Posts: A Recurrent Neural Network Approach Using Under-Sampling and Class Weighting. In: Yang, H., Pasupa, K., Leung, A.CS., Kwok, J.T., Chan, J.H., King, I. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1333. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63823-8_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63823-8_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-63822-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-63823-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)