Abstract
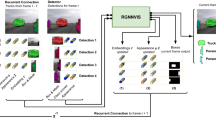
Tracking and segmentation of moving objects in videos continues to be the central problem in the separation and prediction of concurrent episodes and situation understanding. Along with critical issues such as collision avoidance, tracking and segmentation have numerous applications in other disciplines, including medicine research. To infer the potential side effects of a given treatment, behaviour analysis of la-boratory animals should be performed, which can be achieved via tracking. This presents a difficult task due to the special circumstances, such as the highly similar shape and the unpredictable movement of the subject creatures, but a precise solution would accelerate research by eliminating the need of manual supervision. To this end, we propose Cluster R-CNN, a deep architecture that uses clustering to segment object instances in a given image and track them across subsequent frames. We show that pairwise clustering coupled with a recurrent unit successfully extends Mask R-CNN to a model capable of tracking and segmenting highly similar moving and occluded objects, providing proper results even in certain cases where related networks fail. In addition to theoretical background and reasoning, our work also features experiments on a unique rat tracking data set, with quantitative results to compare the aforementioned model with other architectures. The proposed Cluster R-CNN serves as a baseline for future work towards achieving an automatic monitoring tool for biomedical research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmann, P., Meinhardt, T., Leal-Taixe, L.: Tracking without bells and whistles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 941–951 (2019)
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Henriques, J.F., Vedaldi, A., Torr, P.H.S.: Fully-convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking. In: Hua, G., Jégou, H. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9914, pp. 850–865. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48881-3_56
de Chaumont, F., et al.: Real-time analysis of the behaviour of groups of mice via a depth-sensing camera and machine learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 3(11), 930–942 (2019)
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., Girshick, R.: Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2961–2969 (2017)
Hsu, Y.C., Lv, Z., Schlosser, J., Odom, P., Kira, Z.: A probabilistic constrained clustering for transfer learning and image category discovery. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.11078 (2018)
Hsu, Y.C., Xu, Z., Kira, Z., Huang, J.: Learning to cluster for proposal-free instance segmentation. In: 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2018)
Huang, Z., Huang, L., Gong, Y., Huang, C., Wang, X.: Mask scoring R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6409–6418 (2019)
Jung, M., Tani, J.: Adaptive detrending for accelerating the training of convolutional recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference of the Japanese Neural Network Society, pp. 48–49 (2018)
Porzi, L., Hofinger, M., Ruiz, I., Serrat, J., Bulò, S.R., Kontschieder, P.: Learning multi-object tracking and segmentation from automatic annotations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.02096 (2019)
Voigtlaender, P., et al.: Mots: multi-object tracking and segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7942–7951 (2019)
Wang, Q., Zhang, L., Bertinetto, L., Hu, W., Torr, P.H.: Fast online object tracking and segmentation: a unifying approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1328–1338 (2019)
Xingjian, S., Chen, Z., Wang, H., Yeung, D.Y., Wong, W.K., Woo, W.c.: Convolutional LSTM network: a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 802–810 (2015)
Yang, L., Fan, Y., Xu, N.: Video instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5188–5197 (2019)
Acknowledgements
We thank Bence D. Szalay for his careful help in composing this paper; his work was supported by the Hungarian Government and co-financed by the European Social Fund (EFOP-3.6.3-VEKOP-16-2017-00002: EFOP-3.6.3-VEKOP-16-2017-00002, Integrated Program for Training New Generation of Scientists in the Fields of Computer Science). We also thank Árpád Dobolyi and Dávid Keller for providing the database. ÁF and AL were supported by the ELTE Institutional Excellence Program of the National Research, Development and Innovation Office (NKFIH-1157-8/2019-DT) and by the Thematic Excellence Programme (Project no. ED_18-1-2019-0030 titled Application-specific highly reliable IT solutions) of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fóthi, Á., Faragó, K.B., Kopácsi, L., Milacski, Z.Á., Varga, V., Lőrincz, A. (2020). Multi Object Tracking for Similar Instances: A Hybrid Architecture. In: Yang, H., Pasupa, K., Leung, A.CS., Kwok, J.T., Chan, J.H., King, I. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12532. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63830-6_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63830-6_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-63829-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-63830-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)