Abstract
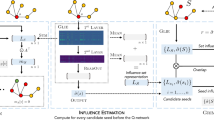
Influence maximization is the task of finding the smallest set of nodes whose activation in a social network can trigger an activation cascade that reaches the targeted network coverage, where threshold rules determine the outcome of influence. This problem is NP-hard and it has generated a significant amount of recent research on finding efficient heuristics. We focus on a Balance Index algorithm that relies on three parameters to tune its performance to the given network structure. We propose using a supervised machine-learning approach for such tuning. We select the most influential graph features for the parameter tuning. Then, using random-walk-based graph-sampling, we create small snapshots from the given synthetic and large-scale real-world networks. Using exhaustive search, we find for these snapshots the high accuracy values of BI parameters to use as a ground truth. Then, we train our machine-learning model on the snapshots and apply this model to the real-word network to find the best BI parameters. We apply these parameters to the sampled real-world network to measure the quality of the sets of initiators found this way. We use various real-world networks to validate our approach against other heuristic.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kempe, D., Kleinberg, J., Tardos, É.: Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network. In: Proceedings of the Ninth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 137–146 (2003)
Chen, W., Yuan, Y., Zhang, L.: Scalable influence maximization in social networks under the linear threshold model. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 88–97. IEEE (2010)
Kempe, D., Kleinberg, J., Tardos. , É.: Influential nodes in a diffusion model for social networks. In: International Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming, pp. 1127–1138. Springer (2005)
Kitsak, M., et al.: Identification of influential spreaders in complex networks. Nat. Phys. 6(11), 888–893 (2010)
Morone, F., Makse, H.A.: Influence maximization in complex networks through optimal percolation. Nature 524(7563), 65–68 (2015)
Pei, S., Teng, X., Shaman, J., Morone, F., Makse, H.A.: Efficient collective influence maximization in cascading processes with first-order transitions. Sci. Rep. 7, 45240 (2017)
Karsai, M., Iñiguez, G., Kikas, R., Kaski, K., Kertész, J.: Local cascades induced global contagion: How heterogeneous thresholds, exogenous effects, and unconcerned behaviour govern online adoption spreading. Sci. Rep. 6(1), (2010)
Unicomb, S., Iñiguez, G., Karsai, M.: Threshold driven contagion on weighted networks. Sci. Rep. 8(1), (2018)
Yuchen Li, J., Fan, Y.W., Tan, K.-L.: Influence maximization on social graphs: a survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 30(10), 1852–1872 (2018)
Karampourniotis, P.D., Szymanski, B.K., Korniss, G.: Influence maximization for fixed heterogeneous thresholds. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–12 (2019)
Backstrom, L., Leskovec, J.: Supervised random walks: predicting and recommending links in social networks. In: Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 635–645 (2011)
Abu-Mostafa, Y.Y., Magdon-Ismail, M., Lin, H.-T.: Learning From Data (2012). amlbook.com
Newman, M.E.J.: Mixing patterns in networks. Phys. Rev. E 67(2), 026126 (2003)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by the Army Research Laboratory (ARL) through the Cooperative Agreement (NS CTA) Number W911NF-09-2-0053, the Office of Naval Research (ONR) under Grant N00014-15-1-2640, and by the Army Research Office (ARO) under Grant W911NF-16-1-0524. The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies either expressed or implied of the Army Research Laboratory or the U.S. Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ma, M., Korniss, G., Szymanski, B.K. (2021). Learning Parameters for Balanced Index Influence Maximization. In: Benito, R.M., Cherifi, C., Cherifi, H., Moro, E., Rocha, L.M., Sales-Pardo, M. (eds) Complex Networks & Their Applications IX. COMPLEX NETWORKS 2020 2020. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 944. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65351-4_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65351-4_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-65350-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-65351-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)