Abstract
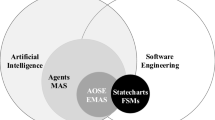
This work aims to bring forward the intersection between the world of statecharts and that of agent technology. We begin by disambiguating the different terms related to statecharts, i.e. state machines and finite state automata/machines. Subsequently we review their impact to agent technology, mainly in the area of Agent-Oriented Software Engineering. Our findings are that multi-agent systems modeling has used and, some times, extended the language of statecharts, mainly for modeling agent interaction protocols and for coordinating the different modules of an agent. We conclude with some future directions related to the use of statecharts by the Multi-agent Systems community in the coming years.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, J.L.: How To Do Things With Words. Harvard University Press, Cambridge (1975)
Bellifemine, F.L., Caire, G., Greenwood, D.: Developing Multi-Agent Systems with JADE. Wiley Series in Agent Technology. Wiley, Hoboken (2007)
Bordini, R.H., et al.: A survey of programming languages and platforms for multi-agent systems. Informatica 30(1) (2006)
Brand, D., Zafiropulo, P.: On communicating finite-state machines. J. ACM (JACM) 30(2), 323–342 (1983)
Braubach, L., Pokahr, A., Lamersdorf, W.: Extending the capability concept for flexible BDI agent modularization. In: Bordini, R.H., Dastani, M.M., Dix, J., El Fallah Seghrouchni, A. (eds.) ProMAS 2005. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3862, pp. 139–155. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11678823_9
Broad, A., Argall, B.: Path planning under interface-based constraints for assistive robotics. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, ICAPS 2016, pp. 450–458. AAAI Press (2016)
Dastani, M.: Programming multi-agent systems. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 30(4), 394–418 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0269888915000077
Dastani, M., van Birna Riemsdijk, M., Meyer, J.-J.C.: Programming multi-agent systems in 3APL. In: Bordini, R.H., Dastani, M., Dix, J., El Fallah Seghrouchni, A. (eds.) Multi-Agent Programming. MSASSO, vol. 15, pp. 39–67. Springer, Boston, MA (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-26350-0_2
DeLoach, S.A., Garcia-Ojeda, J.C.: O-MaSE: a customisable approach to designing and building complex, adaptive multi-agent systems. Int. J. Agent-Oriented Softw. Eng. 4(3), 244–280 (2010)
DeLoach, S.A., Wood, M.F., Sparkman, C.H.: Multiagent systems engineering. Int. J. Softw. Eng. Knowl. Eng. 11(03), 231–258 (2001)
Dunn-Davies, H., Cunningham, R., Paurobally, S.: Propositional statecharts for agent interaction protocols. Electron. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci. 134, 55–75 (2005)
Eilenberg, S.: Automata, Languages, and Machines. Academic Press (1974)
Fortino, G., Garro, A., Mascillaro, S., Russo, W.: Using event-driven lightweight DSC-based agents for MAS modelling. Int. J. Agent-Oriented Softw. Eng. 4(2), 113–140 (2010)
Fortino, G., Rango, F., Russo, W.: Statecharts-based JADE agents and tools for engineering multi-agent systems. In: Setchi, R., Jordanov, I., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C. (eds.) KES 2010. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6276, pp. 240–250. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15387-7_28
Fortino, G., Rango, F., Russo, W., Santoro, C.: Translation of statechart agents into a BDI framework for MAS engineering. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 41, 287–297 (2015)
Fortino, G., Russo, W., Zimeo, E.: A statecharts-based software development process for mobile agents. Inf. Softw. Technol. 46(13), 907–921 (2004)
Girault, A., Lee, B., Lee, E.A.: Hierarchical finite state machines with multiple concurrency models. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 18(6), 742–760 (1999)
Goldsby, H.J., Cheng, B.H., McKinley, P.K., Knoester, D.B., Ofria, C.A.: Digital evolution of behavioral models for autonomic systems. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Autonomic Computing (ICAC 2008), pp. 87–96. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos (2008)
Harel, D.: Statecharts: a visual formalism for complex systems. Sci. Comput. Program. 8(3), 231–274 (1987)
Harel, D., Naamad, A.: The statemate semantics of statecharts. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. (TOSEM) 5(4), 293–333 (1996)
Huynh, T.D., Jennings, N.R., Shadbolt, N.R.: An integrated trust and reputation model for open multi-agent systems. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 13(2), 119–154 (2006)
Kienzle, J., Denault, A., Vangheluwe, H.: Model-based design of computer-controlled game character behavior. In: Engels, G., Opdyke, B., Schmidt, D.C., Weil, F. (eds.) MODELS 2007. LNCS, vol. 4735, pp. 650–665. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75209-7_44
König, R.: State-based modeling method for multiagent conversation protocols and decision activities. In: Carbonell, J.G., Siekmann, J., Kowalczyk, R., Müller, J.P., Tianfield, H., Unland, R. (eds.) NODe 2002. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2592, pp. 151–166. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36559-1_13
Marron, A., Limonad, L., Pollack, S., Harel, D.: Expecting the unexpected: developing autonomous-system design principles for reacting to unpredicted events and conditions (2020)
McBurney, P., Parsons, S.: Dialogue games for agent argumentation. In: Simari, G., Rahwan, I. (eds.) Argumentation in Artificial Intelligence, pp. 261–280. Springer, US, Boston (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-98197-0_13
Mens, T., Decan, A., Spanoudakis, N.I.: A method for testing and validating executable statechart models. Softw. Syst. Model. 18(2), 837–863 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-018-0676-3
Moore, S.A.: On conversation policies and the need for exceptions. In: Dignum, F., Greaves, M. (eds.) Issues in Agent Communication. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1916, pp. 144–159. Springer, Heidelberg (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/10722777_10
Moraïtis, P., Petraki, E., Spanoudakis, N.I.: Engineering JADE agents with the Gaia methodology. In: Carbonell, J.G., Siekmann, J., Kowalczyk, R., Müller, J.P., Tianfield, H., Unland, R. (eds.) NODe 2002. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2592, pp. 77–91. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36559-1_8
Moraitis, P., Spanoudakis, N.: The GAIA2JADE process for multi-agent systems development. Appl. Artif. Intell. 20(2–4), 251–273 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1080/08839510500484249
Moulin, B., Chaib-Draa, B.: An overview of distributed artificial intelligence. In: O’Hare, G.M., Jennings, N.R. (eds.) Foundations of Distributed Artificial Intelligence. Wiley (1996)
Murray, J.: Specifying agent behaviors with UML statecharts and StatEdit. In: Polani, D., Browning, B., Bonarini, A., Yoshida, K. (eds.) RoboCup 2003. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3020, pp. 145–156. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-25940-4_13
Nwana, H.S., Ndumu, D.T., Lee, L.C., Collis, J.C.: Zeus: a toolkit for building distributed multiagent systems. Appl. Artif. Intell. 13(1–2), 129–185 (1999)
Obst, O.: Specifying rational agents with statecharts and utility functions. In: Birk, A., Coradeschi, S., Tadokoro, S. (eds.) RoboCup 2001. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2377, pp. 173–182. Springer, Heidelberg (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45603-1_18
Paraschos, A., Spanoudakis, N.I., Lagoudakis, M.G.: Model-driven behavior specification for robotic teams. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, vol. 1, pp. 171–178. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (2012)
Paurobally, S., Cunningham, J., Jennings, N.R.: Developing agent interaction protocols using graphical and logical methodologies. In: Dastani, M.M., Dix, J., El Fallah-Seghrouchni, A. (eds.) ProMAS 2003. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3067, pp. 149–168. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-25936-7_8
Rao, A.S., Georgeff, M.P.: Modeling rational agents within a BDI-architecture. In: KR, pp. 473–484 (1991)
Riemenschneider, C.K., Hardgrave, B.C., Davis, F.D.: Explaining software developer acceptance of methodologies: a comparison of five theoretical models. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 28(12), 1135–1145 (2002)
Selic, B.: The pragmatics of model-driven development. IEEE Softw. 20(5), 19–25 (2003)
Seo, H.-S., Araragi, T., Kwon, Y.R.: Modeling and testing agent systems based on statecharts. In: Núñez, M., Maamar, Z., Pelayo, F.L., Pousttchi, K., Rubio, F. (eds.) FORTE 2004. LNCS, vol. 3236, pp. 308–321. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30233-9_23
Spanoudakis, N., Moraitis, P.: An agent modeling language implementing protocols through capabilities. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology, vol. 02, pp. 578–582. IEEE Computer Society (2008)
Spanoudakis, N.: The agent systems engineering methodology (ASEME). Ph.D. thesis, Paris Descartes University (2009)
Spanoudakis, N., Moraitis, P.: Gaia agents implementation through models transformation. In: Yang, J.-J., Yokoo, M., Ito, T., Jin, Z., Scerri, P. (eds.) PRIMA 2009. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5925, pp. 127–142. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11161-7_9
Spanoudakis, N.I., Moraitis, P.: The ASEME methodology. Int. J. Agent-Oriented Softw. Eng. (in press)
Topalidou-Kyniazopoulou, A., Spanoudakis, N.I., Lagoudakis, M.G.: A CASE tool for robot behavior development. In: Chen, X., Stone, P., Sucar, L.E., van der Zant, T. (eds.) RoboCup 2012. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 7500, pp. 225–236. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39250-4_21
Wächter, M., Ottenhaus, S., Kröhnert, M., Vahrenkamp, N., Asfour, T.: The ArmarX statechart concept: graphical programing of robot behavior. Front. Robot. AI 3, 33 (2016)
Wooldridge, M., Jennings, N.R., Kinny, D.: The Gaia methodology for agent-oriented analysis and design. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 3(3), 285–312 (2000)
Zambonelli, F., Jennings, N.R., Wooldridge, M.: Developing multiagent systems: the Gaia methodology. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 12(3), 317–370 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1145/958961.958963
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Spanoudakis, N.I. (2020). Statecharts and Agent Technology: The Past and Future. In: Bassiliades, N., Chalkiadakis, G., de Jonge, D. (eds) Multi-Agent Systems and Agreement Technologies. EUMAS AT 2020 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12520. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66412-1_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66412-1_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-66411-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-66412-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)