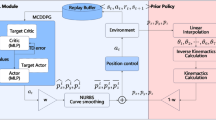
Abstract
For traditional constant impedance control, the robot suffers from constant stiffness, poor flexibility, large wear and high energy consumption in the process of movement. To address these problems, a variable impedance control method based on reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm Deep Q Network (DQN) is proposed in this paper. Our method can optimize the reference trajectory and gain schedule simultaneously according to the completion of task and the complexity of surroundings. Simulation experiments show that, compared with the constant impedance control, the proposed algorithm can adjust impedance in real time while manipulator is executing the task, which implies a better compliance, less wear and less control energy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchli, J., Stulp, F., Theodorou, E., Schaal, S.: Learning variable impedance control. Int. J. Rob. Res. 30(7), 820–833 (2011)
Mitrovic, D., Klanke, S., Vijayakumar, S.: Learning impedance control of antagonistic systems based on stochastic optimization principles. Int. J. Robot. Res. 30(5), 556–573 (2011)
Luo, J., Solowjow, E., Wen, C., Ojea, J. A., Agogino, A. M., Tamar, A., Abbeel, P.: Reinforcement learning on variable impedance controller for high-precision robotic assembly. In: International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3080–3087. IEEE (2019)
Ya-hui, G., Jin-jun, D., Xian-zhong, D.: Adaptive variable impedance control for robot force tracking in unstructured environment. Control and Decision, p. 10 (2019)
Lynch, K.M., Park, F.C.: Modern Robotics: Mechanics, Planning, and Control. Cambridge University Press (2017)
Theodorou, E.A., Buchli, J., Schaal, S.: A generalized path integral control approach to reinforcement learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11(2010), 3137–3181 (2010)
O’Regan, Gerard: Robotics. The Innovation in Computing Companion, pp. 221–226. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02619-6_47
Kober, J., Bagnell, J.A., Peters, J.: Reinforcement learning in robotics: a survey. Int. J. Robot. Res. 32(11), 1238–1274 (2013)
Sergey, L., Wagener, N., Abbeel, P.: Learning contactrich manipulation skills with guided policy search. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, pp. 26–30 (2015)
Chebotar, Y., Kalakrishnan, M., Yahya, A., Li, A., Schaal, S., Levine, S.: Path integral guided policy search. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3381–3388. IEEE (2017)
Peters, J., Mulling, K., Altun, Y.: Relative entropy policy search. In: AAAI, Atlanta, pp. 1607–1612 (2010)
Fu, J., Levine, S., Abbeel, P.: One-shot learning of manipulation skills with online dynamics adaptation and neural network priors. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) pp. 4019–4026. IEEE (2016)
Abbeel, P., Coates, A., Quigley, M., Ng, A.: An application of reinforcement learning to aerobatic helicopter flight. In: International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1–8 (2006)
Luo, J., Edmunds, R., Rice, F., Agogino, M.: Tensegrity robot locomotion under limited sensory inputs via deep reinforcement learning. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 6260–6267. IEEE. (2018)
Schulman, J., Levine, S., Abbeel, P., Jordan, M., Moritz, P.: Trust region policy optimization. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1889–1897 (2015)
Levine, S., Abbeel, P.: Learning neural network policies with guided policy search under unknown dynamics. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. 1071-1079 (2014)
Zhang, T., Kahn, G., Levine, S., Abbeel, P.: Learning deep control policies for autonomous aerial vehicles with mpc-guided policy search. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA), pp. 528–535 (2016)
Mnih, V., et al.: Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.5602 (2013)
Mnih, V., et al.: Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1928–1937 (2016)
Lillicrap, T.P., et al.: Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1509.02971 (2015)
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. Vol. 1. 1. MIT press Cambridge (1998)
Deisenroth, M.P., et al.: A Survey on Policy Search for Robotics. Foundations and Trends in Robotics, pp. 1–142 (2013)
Levine, S., Finn, C., Darrell, T., Abbeel, P.: End-to-end training of deep visuomotor policies. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 1334–1373 (2016)
Hogan, N.: Impedance control: an approach to manipulation. In: American Control Conference, pp. 1–24. IEEE (1985)
Jung, S., Hsia, T.C., Bonitz, R.G.: Force tracking impedance control of robot manipulators under unknown environment. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 12(3), 474–483 (2004)
Yi, S.: Stable walking of qauadruped robot by impedance control for body motion. Int. J. Control Autom. 6(2), 99–110 (2013)
Sano, Y., Hori, R., Yabuta, T.: Comparison between admittance and impedance control method of a finger-arm robot during grasping object with internal and external impedance control. Nihon Kikai Gakkai Ronbunshu C Hen/Trans. Japan Soc. Mech. Eng. C, 79(807), 4330–4334 (2013)
He, W., Dong, Y.: Adaptive fuzzy neural network control for a constrained robot using impedance learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(4), 1174–1186 (2017)
Huang, L., Ge, S.S., Lee, T.H.: Fuzzy unidirectional force control of constrained robotic manipulators. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 134(1), 135–146 (2003)
Funding
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation (NNSF) of China under Grant U1713203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hou, Y., Xu, H., Luo, J., Lei, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, HT. (2020). Variable Impedance Control of Manipulator Based on DQN. In: Chan, C.S., et al. Intelligent Robotics and Applications. ICIRA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12595. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66645-3_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66645-3_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-66644-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-66645-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)