Abstract
We compare classic scalar temporal difference learning with three new distributional algorithms for playing the game of 5-in-a-row using deep neural networks: distributional temporal difference learning with constant learning rate, and two distributional temporal difference algorithms with adaptive learning rate. All these algorithms are applicable to any two-player deterministic zero sum game and can probably be successfully generalized to other settings.
All algorithms in our study performed well and developed strong strategies. The algorithms implementing the adaptive methods learned more quickly in the beginning, but in the long run, they were outperformed by the algorithms using constant learning rate which, without any prior knowledge, learned to play the game at a very high level after 200 000 games of self play.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
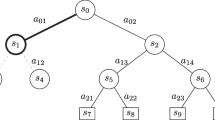
The arrow (\(\leftarrow \)) is a pseudo code notation for assigning a new value to the function. In our implementation, the new value is used immediately to create new values for preceding states and the input/output pair is used as training data for the neural network at the end of the training iteration.
References
Bellemare, M.G., Dabney, W., Munos, R.: A distributional perspective on reinforcement learning. CoRR abs/1707.06887 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06887
Bellman, R.: The theory of dynamic programming. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 60(6), 503–516 (1954)
Berglind, F.: Deep distributional temporal difference learning for game playing. Master’s thesis, Lund University (2020)
Goyal, P., Dollár, P., Girshick, R.B., Noordhuis, P., Wesolowski, L., Kyrola, A., Tulloch, A., Jia, Y., He, K.: Accurate, large minibatch SGD: training imagenet in 1 h. CoRR abs/1706.02677 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Identity mappings in deep residual networks. CoRR abs/1603.05027 (2016). http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.05027
Irpan, A.: Deep reinforcement learning doesn’t work yet (2018). https://www.alexirpan.com/2018/02/14/rl-hard.html
Ailis, L.V., van den Herik, H.J., Huntjens, M.H.: GoMoku solved by new search techniques. AAAI Technical Report FS-93-02 (1993). https://www.aaai.org/Papers/Symposia/Fall/1993/FS-93-02/FS93-02-001.pdf
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Graves, A., Antonoglou, I., Wierstra, D., Riedmiller, M.: Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning, NIPS Deep Learning Workshop (2013). arxiv:1312.5602
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Rusu, A.A., Veness, J., Bellemare, M.G., Graves, A., Riedmiller, M., Fidjeland, A.K., Ostrovski, G., Petersen, S., Beattie, C., Sadik, A., Antonoglou, I., King, H., Kumaran, D., Wierstra, D., Legg, S., Hassabis, D.: Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518(7540), 529–533 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14236
Russell, S., Norvig, P.: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall Press, Upper Saddle River (2009)
Samuel, A.L.: Some studies in machine learning using the game of checkers. IBM J. Res. Dev. 3(3), 210–229 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1147/rd.33.0210
Silver, D., Huang, A., Maddison, C.J., Guez, A., Sifre, L., van den Driessche, G., Schrittwieser, J., Antonoglou, I., Panneershelvam, V., Lanctot, M., Dieleman, S., Grewe, D., Nham, J., Kalchbrenner, N., Sutskever, I., Lillicrap, T.P., Leach, M., Kavukcuoglu, K., Graepel, T., Hassabis, D.: Mastering the game of go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 529, 484–489 (2016)
Silver, D., Hubert, T., Schrittwieser, J., Antonoglou, I., Lai, M., Guez, A., Lanctot, M., Sifre, L., Kumaran, D., Graepel, T., Lillicrap, T., Simonyan, K., Hassabis, D.: Mastering chess and shogi by self-play with a general reinforcement learning algorithm (2017)
Silver, D., Schrittwieser, J., Simonyan, K., Antonoglou, I., Huang, A., Guez, A., Hubert, T., Baker, L.R., Lai, M., Bolton, A., Chen, Y., Lillicrap, T.P., Hui, F., Sifre, L., van den Driessche, G., Graepel, T., Hassabis, D.: Mastering the game of go without human knowledge. Nature 550, 354–359 (2017)
Silver, D., Sutton, R.S., Müller, M.: Temporal-difference search in computer go. Mach. Learn. 87(2), 183–219 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-012-5280-0
Sutton, R.S.: Learning to predict by the methods of temporal differences. Mach. Learn. 3, 9–44 (1988)
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, 2nd edn. The MIT Press, Cambridge (2018). http://incompleteideas.net/book/the-book-2nd.html
Tesauro, G.: Temporal difference learning and TD-Gammon. Commun. ACM 38, 58–68 (1995)
Watkins, C.: Learning from delayed rewards. Ph.D. thesis, Cambridge University (1989)
Yannakakis, G.N., Togelius, J.: Artificial Intelligence and Games. Springer, Cham (2018). http://gameaibook.org
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Berglind, F., Chen, J., Sopasakis, A. (2021). Deep Distributional Temporal Difference Learning for Game Playing. In: Stettinger, M., Leitner, G., Felfernig, A., Ras, Z.W. (eds) Intelligent Systems in Industrial Applications. ISMIS 2020. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 949. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67148-8_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67148-8_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-67147-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-67148-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)