Abstract
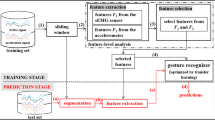
Gesture is a typical human-machine interaction manner, accurate and robust gesture recognition can assist to achieve more natural interaction and understanding. Multi-modal gesture recognition can improve the recognition performance with the help of complex multi-modal relationship. However, it still faces the challenge of how to effectively balance the correlation and redundancy among different modalities, so as to guarantee the accuracy and robustness of the recognition. Hence, in this paper, a collaborative multi-modal learning method based on Random Variational Information Bottleneck (RVIB) is proposed. With random local information selection strategy, some information is compressed by information bottleneck, and the rest is retained directly, so as to make full use of effective redundant information while eliminating invalid redundant information. Experiments on open dataset show that the proposed method can achieve 95.77% recognition accuracy for 21 dynamic gestures, and can guarantee the recognition accuracy when some modality is missing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltrušaitis, T., Ahuja, C., Morency, L.-P.: Multimodal machine learning: a survey and taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(2), 423–443 (2018)
Abavisani, M., Joze, H.R.V., Patel, V.M.: Improving the performance of unimodal dynamic hand-gesture recognition with multimodal training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1165–1174 (2019)
Caglayan, O., Sanabria, R., Palaskar, S., Barraul, L., Metze, F.: Multimodal grounding for sequence-to-sequence speech recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), ICASSP 2019, pp. 8648–8652. IEEE (2019)
Hu, P., Zhen, L., Peng, D., Liu, P.: Scalable deep multimodal learning for cross-modal retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 635–644 (2019)
Zhang, J., Wang, B., Zhang, C., Xiao, Y., Wang, M.Y.: An EEG/EMG/EOG-based multimodal human-machine interface to real-time control of a soft robot hand. Front. Neurorobot. 13, 7 (2019)
Tishby, N., Pereira, F.C., Bialek, W.: The information bottleneck method. arXiv preprint physics/0004057 (2000)
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Sukthankar, R., Fei-Fei, L.: Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1725–1732 (2014)
Tur, A.O., Keles, H.Y.: Evaluation of hidden Markov models using deep CNN features in isolated sign recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.11183 (2020)
Escalera, S., et al.: ChaLearn looking at people challenge 2014: dataset and results. In: Agapito, L., Bronstein, M.M., Rother, C. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8925, pp. 459–473. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16178-5_32
Xiao, Q., Qin, M., Guo, P., Zhao, Y.: Multimodal fusion based on LSTM and a couple conditional hidden Markov model for Chinese sign language recognition. IEEE Access 7, 112258–112268 (2019)
Neverova, N., Wolf, C., Taylor, G., Nebout, F.: ModDrop: adaptive multi-modal gesture recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(8), 1692–1706 (2015)
Joze, H.R.V., Shaban, A., Iuzzolino, M.L., Koishida, K.: MMTM: multimodal transfer module for CNN fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2020
Li, F., Neverova, N., Wolf, C., Taylor, G.: Modout: learning multi-modal architectures by stochastic regularization. In: 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), pp. 422–429. IEEE (2017)
Ben-Younes, H., Cadene, R., Thome, N., Cord, M.: Block: bilinear superdiagonal fusion for visual question answering and visual relationship detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence vol. 33, pp. 8102–8109 (2019)
Ma, S., McDuff, D., Song, Y.: Unpaired image-to-speech synthesis with multimodal information bottleneck. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 7598–7607 (2019)
Alemi, A.A., Fischer, I., Dillon, J.V., Murphy, K.: Deep variational information bottleneck. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.00410 (2016)
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Salakhutdinov, R.: Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15(1), 1929–1958 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Plan of China (No. 2017YFB1002802), Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61902377), and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 4194091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gu, Y., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, J., Shen, J. (2021). A Collaborative Multi-modal Fusion Method Based on Random Variational Information Bottleneck for Gesture Recognition. In: Lokoč, J., et al. MultiMedia Modeling. MMM 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12572. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67832-6_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67832-6_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-67831-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-67832-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)