Abstract
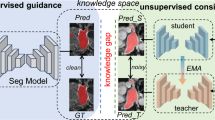
Semi-supervised learning exploits unlabeled data to improve generalization ability with insufficient annotations. In recent years, Mean Teacher method (MT) obtained impressive performance using prediction consistency as regularization. However, severe ambiguity in medical images makes the targets in the teacher model highly unreliable in obscure regions, thereby limits the model capability. To address this problem, we propose a novel multi-task learning semi-supervised framework to gain hierarchical consistency through training process. Specifically, we introduce region and shape predictions as subtasks to obtain the coarse-grained location and fine-grained boundary information. Then we predict pixel-level segmentation by fusing the hierarchical feature. Since calculating consistency loss in more loose regions typically alleviates the degradation caused by learning from unreliable targets, our teacher model generate guidance from each of the subtasks. Moreover, we focus on the geometrical correlations in different tasks and proposed the constraint method to refine the segmentation for accurate guidance. Experiments on the left atrium segmentation dataset show our algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance comparing with other semi-supervised methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, W., et al.: Semi-supervised learning for network-based cardiac MR image segmentation. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017, Part II. LNCS, vol. 10434, pp. 253–260. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66185-8_29
Bortsova, G., Dubost, F., Hogeweg, L., Katramados, I., de Bruijne, M.: Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via learning consistency under transformations. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019, Part VI. LNCS, vol. 11769, pp. 810–818. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_90
Chen, S., Bortsova, G., García-Uceda Juárez, A., van Tulder, G., de Bruijne, M.: Multi-task attention-based semi-supervised learning for medical image segmentation. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019, Part III. LNCS, vol. 11766, pp. 457–465. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32248-9_51
Cui, W., et al.: Semi-supervised brain lesion segmentation with an adapted mean teacher model. In: Chung, A.C.S., Gee, J.C., Yushkevich, P.A., Bao, S. (eds.) IPMI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11492, pp. 554–565. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20351-1_43
Feng, Z., Nie, D., Wang, L., Shen, D.: Semi-supervised learning for pelvic MR image segmentation based on multi-task residual fully convolutional networks. In: 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), pp. 885–888. IEEE (2018)
Laine, S.M., Aila, T.O.: Temporal ensembling for semi-supervised learning. US Patent App. 15/721,433, 12 Apr 2018
Li, X., Yu, L., Chen, H., Fu, C., Heng, P.: Semi-supervised skin lesion segmentation via transformation consistent self-ensembling model. In: British Machine Vision Conference 2018, BMVC 2018, Northumbria University, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 Sept 2018, p. 63. BMVA Press (2018)
Li, X., Yang, F., Cheng, H., Liu, W., Shen, D.: Contour knowledge transfer for salient object detection. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018, Part XV. LNCS, vol. 11219, pp. 370–385. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_22
Liu, S., Shi, J., Liang, J., Yang, M.H.: Face parsing via recurrent propagation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.01936 (2017)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.: V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision, 3DV 2016, Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 Oct 2016, pp. 565–571. IEEE Computer Society (2016)
Nie, D., Gao, Y., Wang, L., Shen, D.: ASDNet: attention based semi-supervised deep networks for medical image segmentation. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018, Part IV. LNCS, vol. 11073, pp. 370–378. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00937-3_43
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1195–1204 (2017)
Yu, L., Wang, S., Li, X., Fu, C.-W., Heng, P.-A.: Uncertainty-aware self-ensembling model for semi-supervised 3D left atrium segmentation. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019, Part II. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 605–613. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_67
Zhang, Y., Yang, L., Chen, J., Fredericksen, M., Hughes, D.P., Chen, D.Z.: Deep adversarial networks for biomedical image segmentation utilizing unannotated images. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017, Part III. LNCS, vol. 10435, pp. 408–416. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66179-7_47
Zhang, Z., Fu, H., Dai, H., Shen, J., Pang, Y., Shao, L.: Et-net: a generic edge-attention guidance network for medical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 442–450 (2019)
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by the Major Scientific and Technological Special Project of Guizhou Province (20183001), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (61976008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Z., Xu, H., Tian, Y., Xie, H. (2021). Hierarchical Consistency and Refinement for Semi-supervised Medical Segmentation. In: Del Bimbo, A., et al. Pattern Recognition. ICPR International Workshops and Challenges. ICPR 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12666. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68780-9_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68780-9_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-68779-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-68780-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)